Слайд 2
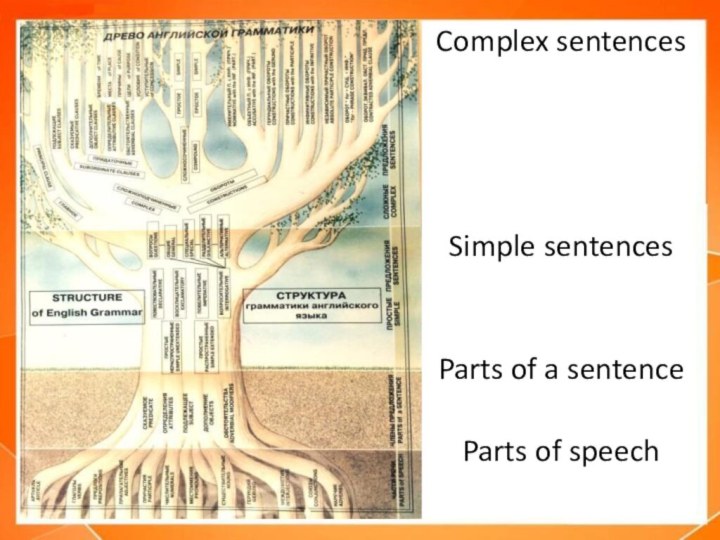
Complex sentences
Simple sentences
Parts of a sentence
Parts of speech
Слайд 3
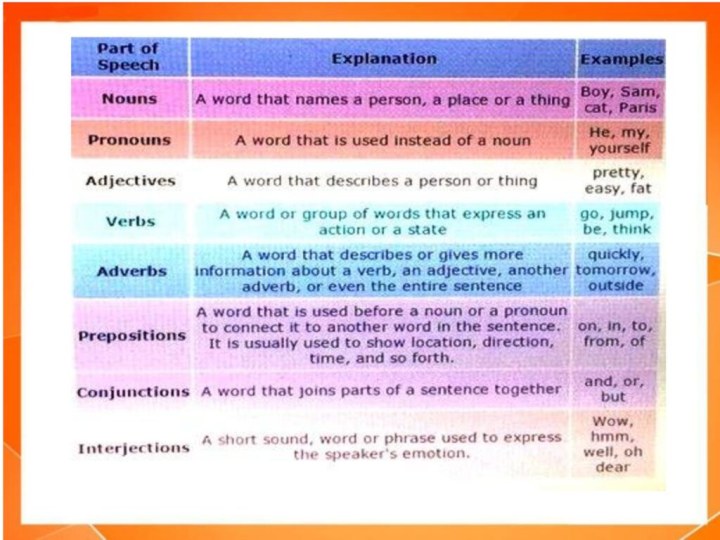
Parts of speech:
Article
Verbs
Prepositions
Adjectives
Participle
Numerals
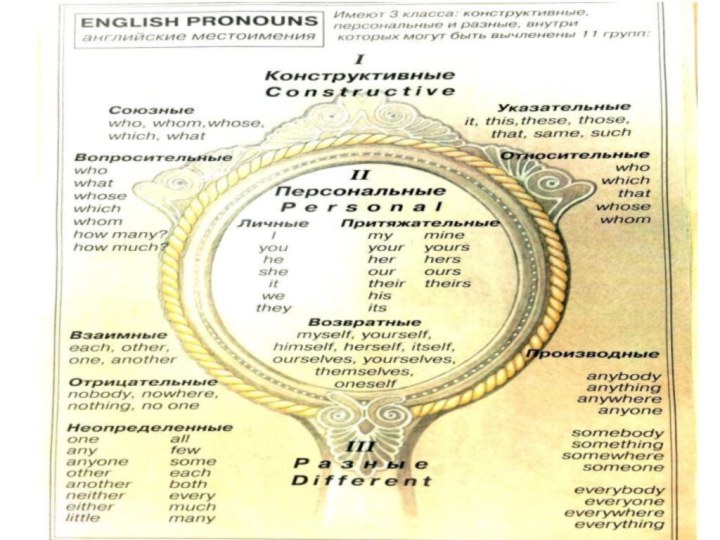
Pronouns
Nouns
Gerund
Interjections
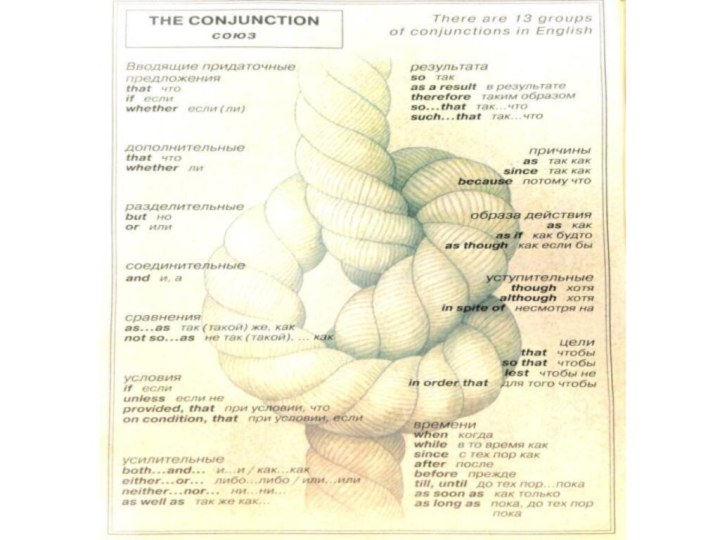
Conjunctions
Adverbs
Слайд 5
Verbs
A verb is a word or group of words that
express an action or a state.
Examples: Go, jump, sleep, eat, think, be, change, become, drive, complete.
Example sentences:
We had a nice lunch.
I think that he is right.
He drove for hours.
The word "verb" comes for the Latin word verbum, which means "word."
Слайд 6
English modal verbs are special verbs that are used to show
possibility, ability, permission, and so forth.
Examples:
"It might rain" – shows possibility.
"I can juggle"
– shows ability.
"You may sit down" – shows permission.
Слайд 8
Examples:
1. Ты не должен парковаться здесь.
You mustn’t park
here.
2. Ты можешь взять еще один кусок, если хочешь.
You can have one more piece if you want.
3. Тебе следует гулять больше.
You should walk more.
4. Ты должен выбрасывать свой мусор в корзину.
You must throw your rubbish in the bin.
Слайд 9
Nouns
A noun is a word that names a person, a
place or a thing.
Examples:
Sarah, lady, cat, New York, Canada,
room, school, football, reading.
Example sentences:
People like to go to the beach.
My parents are traveling to Japan next month.
The word "noun" comes from the Latin word nomen, which means "name," and nouns are indeed how we name people, places and things.
Слайд 10
Nouns:
Abstract Nouns
An abstract noun is a noun that
names an idea, not a physical thing.
(Hope, interest, love,
peace, ability, success, knowledge, trouble.)
Concrete Nouns
A concrete noun is a noun that names a physical thing.
(Boy, table, floor, coffee, beach, king, rain, children, professor.)
Common Nouns
A common noun is a noun that names a general thing, not a specific thing.
(Boy, girl, city, country, company, planet, location, war.)
Proper Nouns
A proper noun is a noun that indicates the specific name of a thing. It begins with a capital letter. (Robin, Alice, London, Sweden, Google, Earth, Civil War.)
Countable Nouns
A countable noun is a noun that indicates something you could actually count.
(teacher, tree, lion, eye, cloud, pencil, heart, movie.)
Uncountable Nouns
An uncountable noun is a noun that indicates something you cannot count.
Examples:
Furniture, advice, mail, news, equipment, luggage, work, coffee, information.
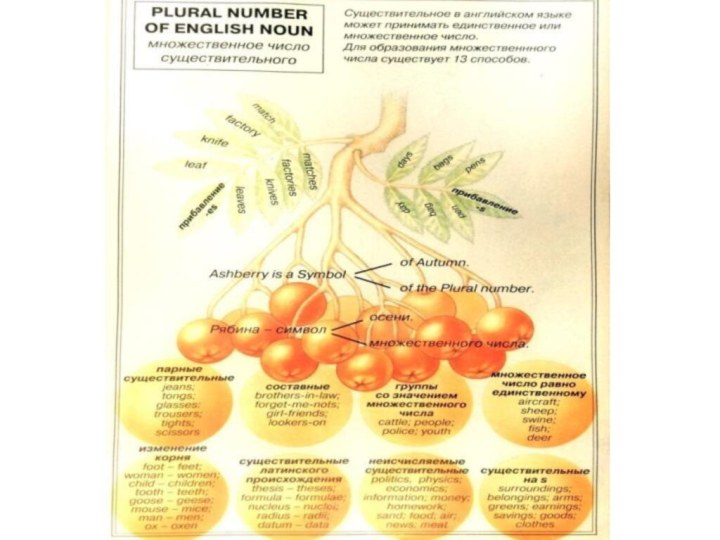
Слайд 13
lives
families
boys
houses
cities
men
children
sandwiches
nurses
shelves
Слайд 14
Gender is that property of the noun or pronounthat
distinguishes sex.
gender of nouns is shown in three ways:
By
using different words for the masculine and feminine.
boy., girl, brother, sister, father, mother ,husband ,wife, son, daughter, uncle, aunt, nephew, niece, lord, lady, king, queen, wizard, witch.
2. By using different suffixes.
Baron- baroness, host – hostess, lion – lioness, duke – duchess, master – mistress.
3. By using different prefixes or words.
he-bear, she-bear, he-goat, she-goat, man-servant ,maid-servant, cock-sparrow ,hen-sparrow, Mr. Smith , Mrs. Smith, Mr. Jones, Miss Jones.
Слайд 16
Pronouns
A pronoun is a word that is used instead of
a noun.
Examples:
I, he, it, we, them, us, mine,
itself.
Example sentences:
He doesn't want go with them.
Would they help us?
His house is bigger than ours.
Who is she?
The word "pronoun" comes from "pro" (in the meaning of "substitute") + "noun."
Слайд 17
Pronouns
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns represent people or things. The
personal pronouns are: I, you, he, she, it, we,
they, me, him, her, us, them.
Demonstrative Pronouns
"Demonstrative" means "showing, making something clear.“ Demonstrative pronouns point to things. The demonstrative pronouns are: this, that, these, those.
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. The interrogative pronouns are: who, whom, which, what, whoever, whatever, etc.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns indicate that something belongs to somebody/something. The possessive pronouns are: my, your, his, her, its, our, their, mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs.
Слайд 18
Relative Pronouns
"Relative" means "connected with something.“ Relative pronouns
are pronouns that link different parts of a sentence.
The
relative pronouns are: who, whom, which, that, whoever.
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns show that the action affects the person who performs the action. Reflexive pronouns end in "-self" (singular) or "-selves" (plural). The reflexive pronouns are: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves.
Indefinite Pronouns
"Indefinite" means "not exact, not limited.
Examples: Anything, everybody, another, each, few, many, none, some.
Слайд 20
Examples
1. Я знаю девушку, которая сейчас поет.
2. Говорят,
что скоро здесь построят новый театр.
3. Никогда не знаешь
что он может принести в следующий раз.
4. Оказалось, что никто не взял ключ от квартиры.
I know the girl which is singing now.
They say that a new theatre will soon be built here.
You never know what he may bring next time.
It happened that nobody had taken the key to the flat.
Слайд 21
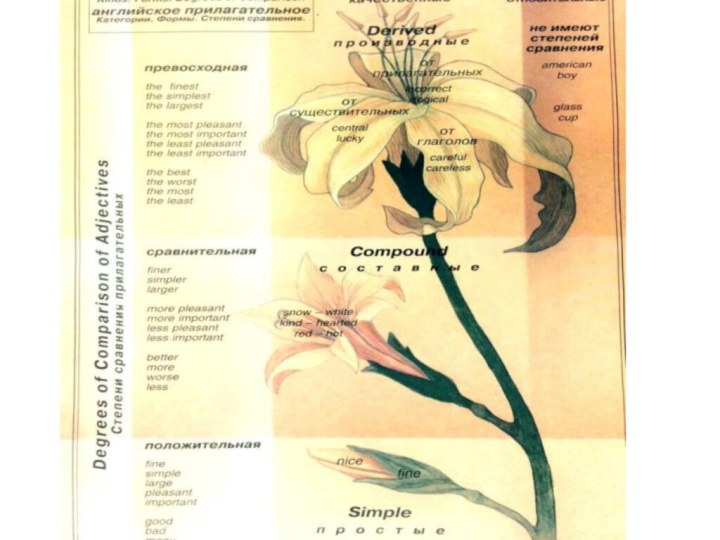
Adjectives
An adjective is a word that describes a
person or thing.
Examples:
Big, pretty, expensive, green, round, French, loud,
quick, fat.
Example sentences:
He has big blue eyes.
The new car broke down.
The old lady was talking in a quiet voice.
Слайд 22
Different Types of adjectives
Adjectives can be divided into
several types:
Opinion: Nice, pretty, stupid, original, expensive, etc.
Size: Big,
small, large, tiny, enormous, little, etc.
Age: Young, old, new, ancient, antique, etc.
Shape: Round, square, flat, straight, etc.
Color: Blue, red, white, black, dark, bright, yellow, etc.
Origin: Italian, British, Mexican, western, southern, etc.
Material: Metal, wooden, plastic, golden, etc.
Слайд 25
Examples
1. Её платье в два раз дороже моего.
2. Этот фильм интереснее, чем предыдущий.
3. Мой
сосед – весьма своеобразный человек.
Her dress is twice as
expensive as mine.
This film is more interesting than the previous one.
My neighbour is a most extraordinary man.
4. Чем дольше я нахожусь здесь, тем больше мне нравится.
The longer I stay here the more I like it.
5. Я расскажу тебе что-то потрясающее.
I'll tell you something wonderful.
Слайд 26
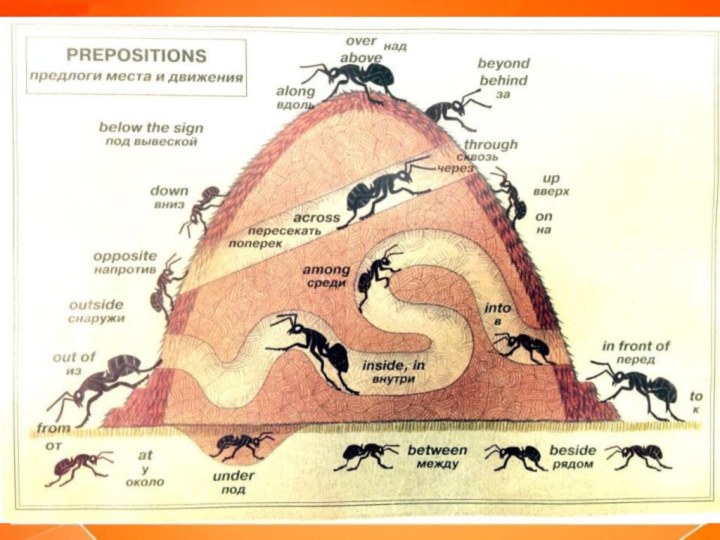
Preposition
A preposition is a word that is used
before a noun or a pronoun to connect it to
another word in the sentence. It is usually used to show location, direction, time, and so forth.
Examples:
On, in, at, by, under, above, beside, to, out, from, for.
Example sentences:
I sat on the floor.
Let's go into the house.
We will meet at four o'clock.
Have a look under the couch.
He went to school.
This letter is for you.
Слайд 28
Examples
1. Между тобой и мной нет секретов.
2.
Мы обсудим этот вопрос в следующий раз.
3. Он в
отпуске до пятницы.
4. Пройди 5 шагов в направлении дома.
5. Она стояла перед зеркалом
Between you and me there are no secrets.
We will discuss the matter next time.
He is on holiday till / until Friday.
Go 5 steps towards the house.
She stood in front of the mirror.
Слайд 29
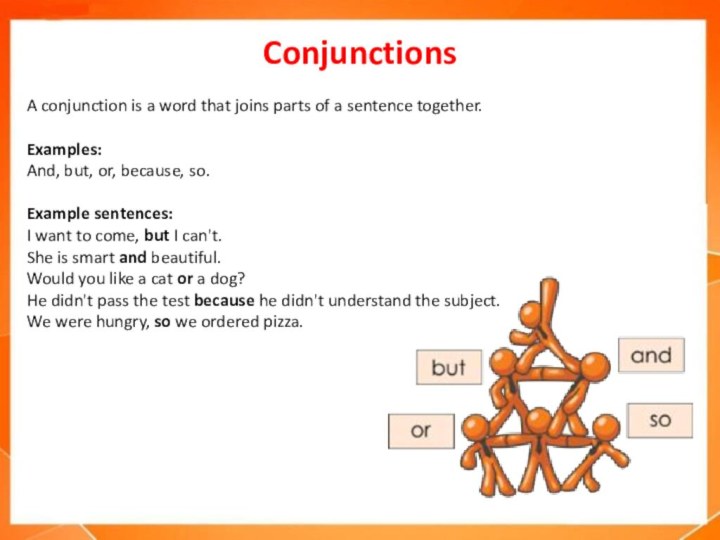
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that joins parts
of a sentence together.
Examples:
And, but, or, because, so.
Example sentences:
I
want to come, but I can't.
She is smart and beautiful.
Would you like a cat or a dog?
He didn't pass the test because he didn't understand the subject.
We were hungry, so we ordered pizza.
Слайд 31
Examples
Both the brother and the sister were punished.
1. Как брат, так и сестра
были наказаны.
2. Как только взошло солнце, мы отправились на
экскурсию.
As soon as the sun rose, we started on an excursion.
3. Закрой все окна перед уходом.
Shut all the windows before you go.
4. Мы не могли найти его ни в магазине, ни в офисе .
We could find him neither in the shop nor in the office.
5. Шел дождь и все были дома.
It was raining and everyone was at home.
Слайд 32
Sentence stress – pronouncing certain words within a sentence more strongly
than others – can completely change the meaning of a sentence
Слайд 33
Complex Object is a syntactic construction typical of modern English. It’s used
as one member of the sentence – an object.
Слайд 34
Examples
1. Я хочу, чтобы моя бабушка сводила меня в цирк
I
want my granny to take me to the circus.
2. Мисс Брайт
считала, что Браун украл деньги.
Miss Bright believed Brown to have stolen the money.
3. Они думали (ожидали), что его поймает полиция.
They expected him to be caught by the police.
4. Она видела как дверь за ними закрылась.
She saw the door close behind them.
5. Он слышал, что она была очень груба с Питером вчера.
He heard her be really rude to Peter yesterday.
Слайд 35
mood = a way to express the attitude of
the speaker to what is being said.
English moods include
the indicative mood, the imperative mood and the subjunctive mood.
Слайд 36
Indicative Mood
Imperative Mood
Subjunctive Mood
"We finished the project on
time."
"Get plenty of rest!"
"I wish I had some cheese..."
Слайд 37
Examples
I wish I were now at the seaside.
1.
Не переходите улицу здесь!
Don’t cross the street here!
2.
Теперь соберите словари и отнесите их в библиотеку.
Now collect the dictionaries and take them to the library.
3. Тебе следовало бы это сделать и без чьей-либо помощи.
You should have done it without anyone’s help.
4. Как бы мне хотелось быть сейчас на морском побережье.
5. Не сердись на меня
Don’t be angry with me.
Слайд 38
There are four kinds of questions in English: general, alternative, special, disjunctive.
Types
of questions
Слайд 39
Examples
1. Ему часто приходится рано вставать?
Does he often have to get up early?
2. Сколько (денег) он собирается заплатить?
How much (money) is he going to pay?
3. Кому учитель читал рассказ?
To whom did the teacher read a story?
4. Вы или ваш брат помогает им?
Do you or does your brother help them?
5. Вы не знаете, как ответить на этот вопрос, не так ли?
You do not know how to answer the question, do you?