- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Environmental administration and legislation
Содержание
- 2. REVISIONWhat did you learn last week?18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
- 3. EU waste legislationEnvironmental Administration and Legislation, 2016Framework
- 4. Directive on waste: Waste hierarchy* “In order to
- 5. Directive on waste: Permits and Registrations
- 6. Treatment OperationsPreventionPreparing for reuse Recycling Tax incentives, bans,
- 7. Incineration of wasteThe WI Directive sets emission
- 8. Landfill of wasteThe Landfill Directive applies to
- 9. Hazardous Waste Waste from Consumer GoodsPackaging WasteWaste
- 10. Directive 2006/66/EC on batteries and accumulators and waste batteries
- 11. Directive 2012/19/EU on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE)Designed
- 12. Legislation on Packaging and Packaging WasteDirective 94/62/EC
- 13. Legislation Controlling Hazardous Waste Management18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
- 14. Hazardous WasteHazardous wastes pose a greater risk
- 15. Hazardous WasteDirective 2008/98/EC provides additional labelling, record
- 16. Hazardous WasteConvention on the control of transboundary
- 17. Hazardous WasteThe classification into hazardous and non
- 18. Hazardous WasteWastes classified as hazardous are considered
- 19. Hazardous WasteList includes 20 categories of waste,
- 20. Hazardous Waste ManagementCollection – requirements for registers,
- 21. 18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
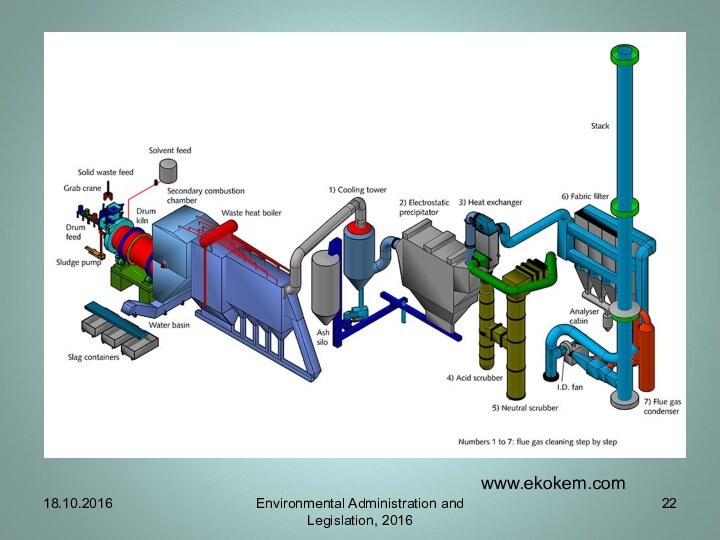
- 22. 18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016www.ekokem.com
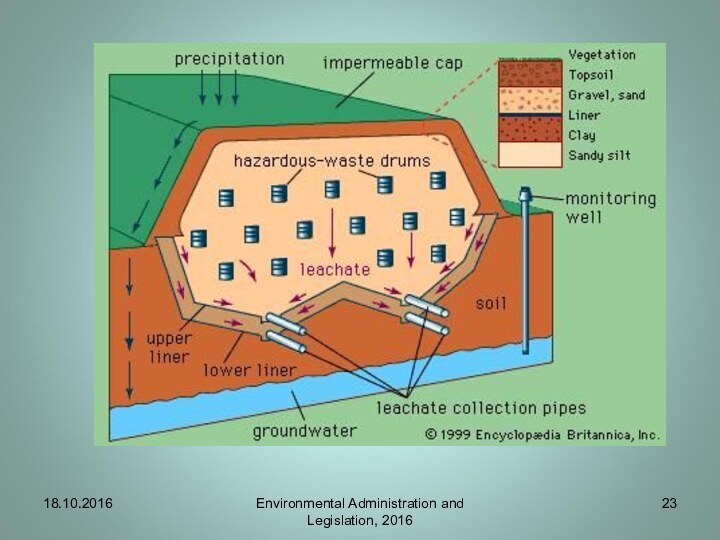
- 23. 18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
- 24. Legislation Controlling the Use of Hazardous Substances18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
- 25. REACH“The EU has modernized European chemicals legislation
- 26. REACHThe idea is that “testing on humans”
- 27. Risk Management18.10.2016Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016Management of
- 28. REACH: ScopeThe scope of the Regulation covers
- 29. REACH: ScopeThe rules on registration, downstream users,
- 30. Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of CHemicals.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 201618.10.2016
- 31. REACH: RegistrationRegistration is the key component of
- 32. REACH: RegistrationSome groups of substances (listed in
- 33. REACH: RegistrationRegistration requires the industry to provide
- 34. REACH: RegistrationAn application to register a substance
- 35. REACH: RegistrationThere are special arrangements for the
- 36. REACH: RegistrationThe European Chemicals Agency is responsible
- 37. REACH: RegistrationDownstream users must consider the safety
- 38. Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of CHemicals.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 201618.10.2016
- 39. REACH: EvaluationEvaluation makes it possible for the
- 40. REACH: EvaluationDossier evaluation is compulsory for any
- 41. REACH: EvaluationSubstances suspected of posing a risk
- 42. REACH: EvaluationIf a substance is suspected of
- 43. REACH: EvaluationEvaluation can lead to the following
- 44. REACH: Evaluation…information must be supplied to the
- 45. Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of CHemicals.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 201618.10.2016
- 46. REACH: AuthorisationSubstances of extremely high concern may
- 47. REACH: AuthorisationThe Agency publishes and regularly updates
- 48. REACH: AuthorisationAfter inclusion of this substance any
- 49. REACH: AuthorisationThe burden of proof is placed
- 50. Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of CHemicals.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 201618.10.2016
- 51. REACH: RestrictionsThe restriction procedure provides a safety
- 52. REACH: Restrictionsmay relate to the conditions of
- 53. REACH: RestrictionsRestrictions are suggested by Member States
- 54. ECHAThe Regulation establishes a European Chemicals Agency,
- 55. Competent AuthoritiesThe Regulation requires there to be
- 56. Competent Authorities: FinlandThe following authorities are responsible
- 57. The CLP RegulationEnvironmental Administration and Legislation, 201618.10.2016
- 58. The CLP RegulationThe classification, labelling and packaging
- 59. The CLP RegulationThe regulation seeks to ensure
- 60. CLP PictogramsA hazard pictogram is an image
- 61. Скачать презентацию
- 62. Похожие презентации



























































Слайд 2
REVISION
What did you learn last week?
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and
Legislation, 2016
Слайд 3
EU waste legislation
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Framework legislation
on waste
Legislation on waste management operations
Legislation on specific waste
streams
Reporting legislation
18.10.2016
Слайд 4
Directive on waste:
Waste hierarchy*
“In order to better protect
the environment, the Member States should take measures for
the treatment of their waste in line with the following hierarchy which is listed in order of priority:prevention;
preparing for reuse;
recycling;
other recovery, notably energy recovery;
disposal.”
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 5
Directive on waste:
Permits and Registrations
Any establishment or
undertaking intending to carry out waste treatment must obtain
a permit (IPPC licence) from the competent authorities who determine notably the quantity and type of treated waste, the method used as well as monitoring and control operations.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 6
Treatment Operations
Prevention
Preparing for reuse
Recycling
Tax incentives, bans, …
other
recovery, notably energy recovery
Incineration
Disposal
Landfill
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 7
Incineration of waste
The WI Directive sets emission limit
values and monitoring requirements for pollutants to air such
as dust, nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulphur dioxide (SO2), hydrogen chloride (HCl), hydrogen fluoride (HF), heavy metals and dioxins and furans.The Directive also sets controls on releases to water resulting from the treatment of the waste gases.
Most types of waste incineration plants fall within the scope of the WI.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 8
Landfill of waste
The Landfill Directive applies to all
landfills, defined as waste disposal sites for the deposit
of waste onto or into land.Defines the different categories of waste:
municipal waste,
hazardous waste,
non-hazardous waste and
inert waste (waste which is neither chemically or biologically reactive and will not decompose)
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 9
Hazardous Waste
Waste from Consumer Goods
Packaging Waste
Waste from
Specific Activities
Radioactive Waste and Substances
Environmental Administration and
Legislation, 201618.10.2016
Слайд 10 Directive 2006/66/EC on batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and
accumulators (and amending acts).
“The producers have to bear the
cost of collecting, treating and recycling industrial, automotive and portable batteries and accumulators, as well as the costs of campaigns to inform the public of these arrangements. Small producers may be exempted from this obligation if this does not impede the proper functioning of the collection and recycling schemes. All producers of batteries and accumulators have to be registered.”18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 11
Directive 2012/19/EU on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE)
Designed to
prevent electrical and electronic waste by requiring EU countries
to ensure the equipment is recovered, reused or recycled.Producers have to make a financial contribution to cover the costs of collecting, treating and sustainably disposing of both non-household equipment and private electrical waste deposited at dedicated collection points.
Variable collection target from 2016 onwards, taking account of individual national economies: 45 % of the average weight of products placed on the market in a given country in the 3 preceding years.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 12
Legislation on Packaging and Packaging Waste
Directive 94/62/EC on
packaging and packaging waste
covers all packaging placed on
the European market and all packaging waste, whether it is used or released at industrial, commercial, office, shop, service, household or any other level, regardless of the material used.Member States should take measures to prevent the formation of packaging waste, and to develop packaging reuse systems reducing their impact on the environment.
Specific targets for packaging waste recovery or incineration and reduction of materials contained in packaging waste must be attained.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 13
Legislation Controlling
Hazardous Waste Management
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation,
2016
Слайд 14
Hazardous Waste
Hazardous wastes pose a greater risk to
the environment and human health than non hazardous wastes
and thus require a stricter control regime.18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 15
Hazardous Waste
Directive 2008/98/EC provides additional labelling, record keeping,
monitoring and control obligations from the "cradle to the
grave”Mixing of hazardous substances is banned in order to prevent risks for the environment and human health.
The permit exemptions that may be granted to installations dealing with hazardous wastes are more restrictive than for installations dealing with other wastes.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 16
Hazardous Waste
Convention on the control of transboundary movements
of hazardous wastes and their disposal (Basel Convention) 1997
Council
Directive (91/689/EEC) on hazardous waste -> repealed by Directive 2008/98/EC (Directive on waste)Decision 2000/532/EC List of Hazardous Wastes:
Definition of hazardous waste
Harmonised list of wastes
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 17
Hazardous Waste
The classification into hazardous and non hazardous
waste is based on the system for the classification
and labelling of dangerous substances and preparations, which ensures the application of similar principles over their whole life cycle.The properties which render waste hazardous are laid down in Annex III of Directive 2008/98/EC and are further specified by the Decision 2000/532/EC establishing a List of Wastes as last amended by Decision 2001/573/EC.
(The List of Wastes is currently being reviewed)
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 18
Hazardous Waste
Wastes classified as hazardous are considered to
display one or more of the properties listed in
Annex III to Directive 91/689/EEC and, as regards H3 to H8, H10 (1 ) and H11 of the said Annex, one or more of the following characteristics:— flash point ≤ 55 ºC,
— one or more substances classified (2 ) as very toxic at a total concentration ≥ 0,1 %,
— one or more substances classified as toxic at a total concentration ≥ 3 %,
….
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 19
Hazardous Waste
List includes 20 categories of waste, each
containing several subcategories.
01 Wastes resulting from exploration, mining, quarrying,
physical and chemical treatment of minerals02 Wastes from agriculture, horticulture, aquaculture, forestry, hunting and fishing, food preparation and processing
….
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 20
Hazardous Waste Management
Collection – requirements for registers, containers
and transportation.
Treatment – requirements on treatment facilities.
Disposal –
requirements for HW landfillsHazardous wastes can take the form of solids, liquids, sludges, or contained gases. This needs to be considered when deciding on the management options.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 24
Legislation Controlling the Use of Hazardous Substances
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration
and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 25
REACH
“The EU has modernized European chemicals legislation and
established an integrated system for the registration, evaluation, authorisation
and restriction of chemicals.”objective is to improve the protection of human health and the environment
European Chemicals Agency
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 26
REACH
The idea is that “testing on humans” is
no longer accepted – the burden of proving that
chemicals produced and placed on the market are safe is now on the chemicals industry. (Precautionary Principle)“REACH requires firms which manufacture and import chemicals to evaluate the risks resulting from the use of those chemicals and to take the necessary steps to manage any identified risk.”
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 27
Risk Management
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Management of a
risk requires steps of
Hazard identification
Assessment of the risk(s) caused
by this hazard (including likelihood and severity of effects)Deciding on risk control option (avoiding, mitigating, transfering or accepting the risk)
Monitoring
Слайд 28
REACH: Scope
The scope of the Regulation covers all
substances , whether manufactured, imported, placed on the market,
or used on their own or in mixtures with the exceptions of:radioactive substances (covered by Directive 96/29/Euratom);
substances under customs supervision which are in temporary storage, in free zones or free warehouses with a view to re-exportation or still in transit;
non-isolated intermediates ;
the transport of dangerous substances; and
waste.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 29
REACH: Scope
The rules on registration, downstream users, evaluation
and authorisation do not apply to substances used in
medicinal products for human or veterinary use or in food or feedingstuffs (including additives) provided they fall within the scope of Community legislation on medicinal products or food.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 30
Registration,
Evaluation,
Authorisation and
restriction of CHemicals.
Environmental Administration
and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 31
REACH: Registration
Registration is the key component of the
REACH system.
It is compulsory to register in a
central database chemicals which are manufactured or imported in quantities of one tonne or more per annum. The database is managed by the European Chemicals Agency.
If a substance is not registered it cannot be produced or placed on the European market.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 32
REACH: Registration
Some groups of substances (listed in the
Regulation) are exempt from the obligation to register, for
example:polymers (however monomers which make up polymers must still be registered);
some substances for which the estimated risk is negligible (water, glucose, etc.);
naturally occurring and chemically unaltered substances;
substances used in research and development, under certain conditions.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 33
REACH: Registration
Registration requires the industry to provide information
on the properties and uses of chemicals and the
precautionary measures to be taken when using them.The data required are proportional to the production volume of and the risks presented by the substance concerned (for example, extensive toxicity tests for substances manufactured or imported in quantities of more than 1000 tonnes).
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 34
REACH: Registration
An application to register a substance which
is imported or manufactured in a quantity of 10
tonnes or more per year must include a detailed description of the risks associated with that substance and the different possible exposure scenarios and risk management measures (chemical safety report).Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 35
REACH: Registration
There are special arrangements for the registration
of substances present in articles: given the millions of
articles that are placed on the market in the EU and the potential risk some of them represent to human health and the environment, certain substances incorporated into articles must be registered.Registration is compulsory when the substance in question is normally released when the article is used and is present in those articles in quantities totalling over one tonne per producer or importer per year.
For substances that are not normally released but which are particularly hazardous and are contained in a minimum concentration of 0.1% and placed on the market in quantities of over one tonne per producer or importer per year, simple notification is required, on the basis of which the European Chemicals Agency may request a registration.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 36
REACH: Registration
The European Chemicals Agency is responsible for
managing the database, receiving registration dossiers and developing technical
guides aimed at helping manufacturers, importers and the competent authorities in implementing these provisions.During the first eleven years of application of the REACH system, around 30 000 substances already on the market should be registered.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 37
REACH: Registration
Downstream users must consider the safety of
substances, based primarily on information from their suppliers, and
to take appropriate risk management measures. These provisions also allow authorities to have an overview of the uses of a substance as it moves through the supply chain and, if necessary, to request further information and take appropriate measures.18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 38
Registration,
Evaluation,
Authorisation and
restriction of CHemicals.
Environmental Administration
and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 39
REACH: Evaluation
Evaluation makes it possible for the Agency
to check that industry is fulfilling its obligations and
avoiding tests on vertebrate animals when unnecessary.Two types of evaluation are provided for:
dossier evaluation
substance evaluation
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 40
REACH: Evaluation
Dossier evaluation is compulsory for any applications
to carry out tests specified in Annexes IX and
X to the Regulation (these are the most stringent tests, mostly involving the use of vertebrate animals). The aim is essentially to minimise the need for experiments of this kind.Dossier evaluation may also be carried out in order to check the conformity of a registration. The Agency is expected to carry out a thorough review of at least 5% of the dossiers filed.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 41
REACH: Evaluation
Substances suspected of posing a risk to
human health or the environment may also be evaluated
by the competent authorities in the Member States in order to determine whether further information is required. The evaluation programme is developed by the Agency, in cooperation with the competent authorities.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 42
REACH: Evaluation
If a substance is suspected of posing
a risk to human health or the environment, the
Agency will include this substance in a specific list and a designated Member State will carry out an evaluation in order to determine whether further information is required from the registrant.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 43
REACH: Evaluation
Evaluation can lead to the following conclusions:
the
substance must be subject to restriction or authorisation procedures;
the
classification and labelling of the substance must be harmonised;….
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 44
REACH: Evaluation
…
information must be supplied to the other
authorities so that they can adopt appropriate measures.
For
example, if, while the substance is being evaluated, information on risk management measures become available and could have an impact on the conditions of use of that substance, the information should be transmitted to the authorities responsible for this legislation.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 45
Registration,
Evaluation,
Authorisation and
restriction of CHemicals.
Environmental Administration
and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 46
REACH: Authorisation
Substances of extremely high concern may be
subject to authorisation by the Commission with regard to
particular uses.The objective is to ensure that the risks linked with these substances are validly controlled and that these substances are gradually replaced by other appropriate substances or technologies where this is economically and technically viable.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 47
REACH: Authorisation
The Agency publishes and regularly updates a
list of substances (list of candidate substances) identified as
having characteristics of extremely high concern. These may include the following:CMRs (carcinogens, mutagens and reproductive toxins);
PBTs (persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic substances);
vPvBs (very persistent and very bioaccumulative substances);
some substances of concern which have irreversible serious effects on humans and the environment, such as endocrine disruptors.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 48
REACH: Authorisation
After inclusion of this substance any placing
on the market and use of such chemical substances
is subject to authorisation. This is granted if the risks arising from the substance in question can be validly controlled. If they cannot and if no alternative exists, the Commission is to assess the level of risk and the socio-economic advantages of using the substance and decide whether to authorise it or not.Some substances, such as PBTs and vPvBs can be authorised only if the socio-economic advantages override the risks and there are no alternatives.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 49
REACH: Authorisation
The burden of proof is placed on
the applicant. All authorisations must be reviewed after a
certain period of time, determined on a case-by-case basis.Downstream users may use a substance for an authorised use provided they obtain the substance from a company to which an authorisation has been granted and keep within the conditions of that authorisation.
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 50
Registration,
Evaluation,
Authorisation and
Restriction of CHemicals.
Environmental Administration
and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 51
REACH: Restrictions
The restriction procedure provides a safety net,
making it possible to manage the risks which are
not adequately covered by other provisions of the REACH system.Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 52
REACH: Restrictions
may relate to
the conditions of manufacture,
use(s)
placing on the market of a substance, or the
possible prohibition of such activities, if necessary. Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 53
REACH: Restrictions
Restrictions are suggested by Member States or
by the Agency and decided on by the Commission.
Please
visit: echa.europa.eu (link in Moodle) for further informationEnvironmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
18.10.2016
Слайд 54
ECHA
The Regulation establishes a European Chemicals Agency, responsible
for managing the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of
REACH and ensuring consistency of decision-making at Community level.The Agency is also to manage the registration process and play a key role in the evaluation process. It receives applications for authorisation and delivers opinions and issues recommendations in relation to the authorisation and restriction procedures.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 55
Competent Authorities
The Regulation requires there to be authorities
in each of the Member States with the competence
and resources necessary to carry out the tasks assigned to them. These authorities must cooperate with each other and with the Agency in the performance of their duties.18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 56
Competent Authorities: Finland
The following authorities are responsible for
the enforcement of REACH Regulation in Finland:
The Ministry of Social
Affairs and Health and the Ministry of the Environment are responsible for the overall management and supervision of the REACH Regulation in Finland.The Finnish Safety and Chemicals Agency (Tukes) has been appointed as the REACH Competent Authority and is also responsible for REACH enforcement in regard to all provisions relating to placing on the market of chemicals. Tukes is responsible for the national REACH Helpdesk.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 58
The CLP Regulation
The classification, labelling and packaging of
dangerous substances have been harmonised since 1967 to ensure
the protection of health and the environment, and to ensure the free movement of such products.Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures (amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006.)
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 59
The CLP Regulation
The regulation seeks to ensure that
European Union workers and consumers are clearly informed of
the hazards associated with chemicals by means of a system of classification and labelling. The aim is to ensure that the same hazards are described and labelled in the same way in all EU countries.It lays down uniform requirements for the classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures according to the United Nations’ Globally Harmonized System (GHS). It requires companies to classify, label and package appropriately their hazardous chemicals before placing them on the market.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016
Слайд 60
CLP Pictograms
A hazard pictogram is an image on
a label that includes a warning symbol and specific
colours intended to provide information about the damage a particular substance or mixture can cause to our health or the environment.The new pictograms are in the shape of a red diamond with a white background, and will replace the old orange square symbols which applied under the previous legislation.
18.10.2016
Environmental Administration and Legislation, 2016