and its peculiarities
2 Reasons and ways of borrowings
3 Types
of borrowings4 Assimilation of borrowings
5 Types of assimilated words
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть





![Etymological Characteristics of the Modern English Lexicon 2 its etymology Ex. hand (n.) [www.etymonline.com] O.E. hond, hand](/img/tmb/15/1404893/56b9f54b598d21b3742c2e3f205a4898-720x.jpg)


























![Etymological Characteristics of the Modern English Lexicon 3) the consonant combinations [pn], [ps], [pt] in the words pneumatics, psychology,](/img/tmb/15/1404893/417949b12225050ebbeea31f956c5f71-720x.jpg)






Plan
Plan
Extralinguistic (historic) reasons include wars and conquest and peaceful contacts as well.
through written speech
(by indirect contact through books, etc.)
Plan
3
Wunderkind
first dancer
словосочетание
word-combination
prima-ballerina
Plan
Plan
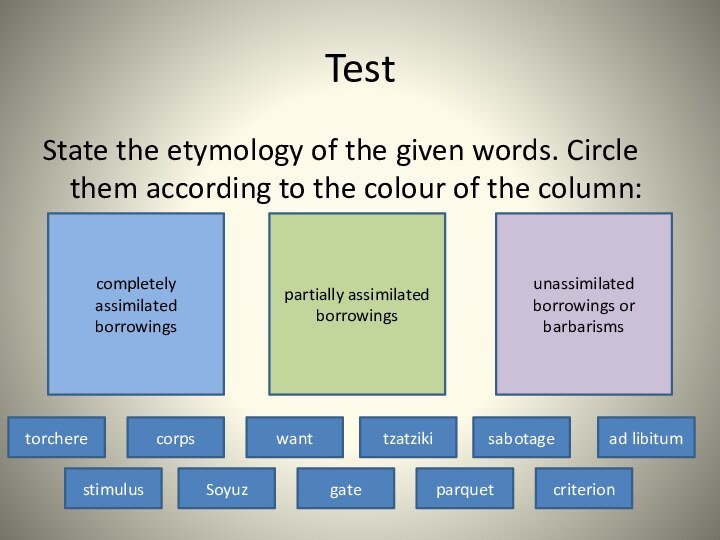
completely assimilated borrowings
partially assimilated borrowings
Soyuz
gate
want
tzatziki
sabotage
ad libitum
torchere
corps
stimulus
criterion
parquet
Plan