- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Golden ratio
Содержание
- 2. What is Golden Ratio? The Golden Ratio is
- 3. AC is to CB as AB is to AC
- 4. What is the Fibonacci Sequence of Numbers?
- 5. Relationship between the Fibonacci Sequence and the
- 6. As we can see, the ratio approaches
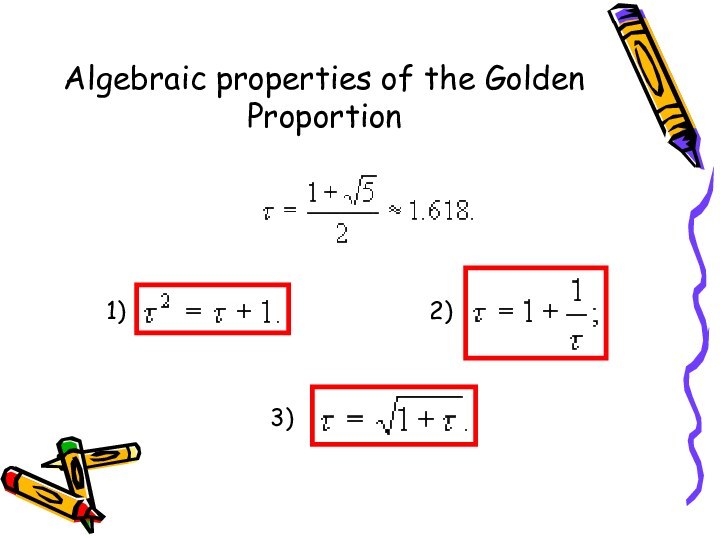
- 7. Algebraic properties of the Golden Proportion1)2)3)
- 8. Constructing a Golden Rectangle Given:
- 9. Golden triangle The golden triangle is an isosceles
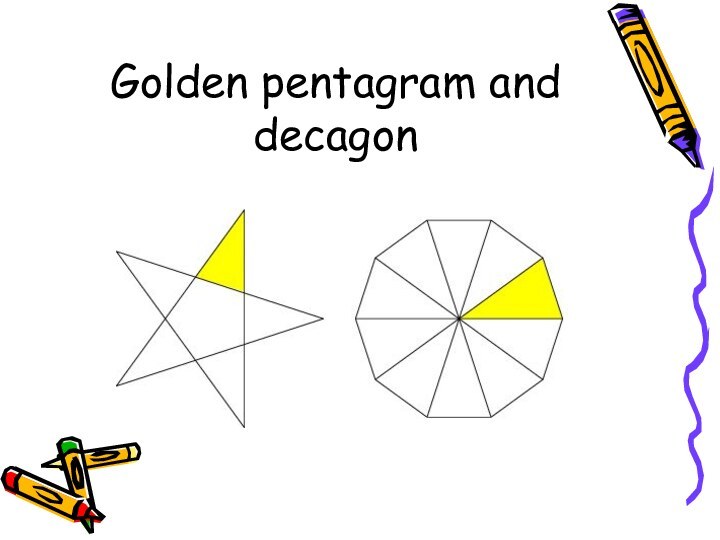
- 10. Golden pentagram and decagon
- 11. Plants growth The branching rates in plants occur
- 12. Flowers On the back of the passiflora incarnate,
- 13. Petal counts The petals of the different flowers
- 14. The Golden Ratio in Humans Dr. Stephen Marquardt
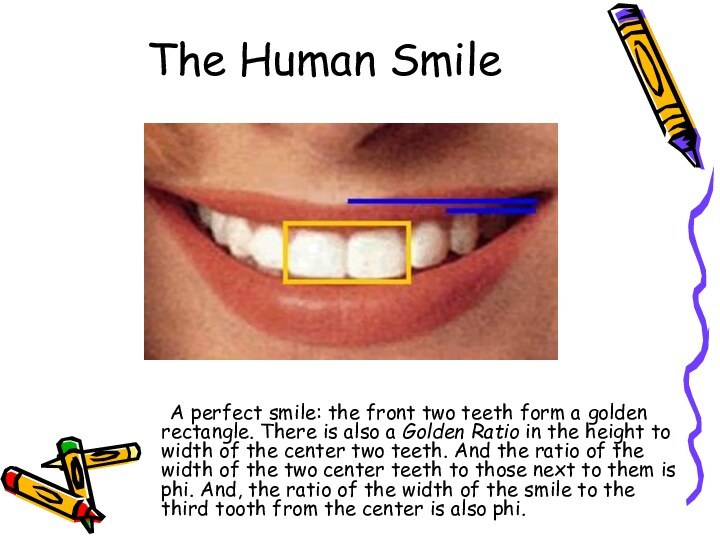
- 15. The Human Smile A perfect smile: the front
- 16. The Golden Ratio in Arts The Golden Ratio
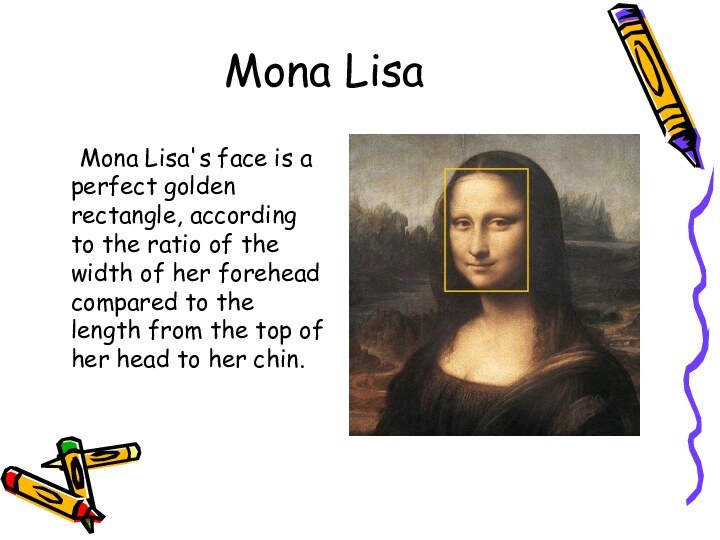
- 17. Mona Lisa Mona Lisa's face is a perfect
- 18. The last supper The masterpiece "Last Supper," contains
- 19. Statue of Athena In the Statue of Athena,
- 20. The Golden Ratio in Architecture The Golden Ratio
- 21. The Great Pyramid at Giza Half of
- 22. The Parthenon The exterior dimensions of the
- 23. The UN Building In the United Nations
- 24. Скачать презентацию
- 25. Похожие презентации
What is Golden Ratio? The Golden Ratio is a unique number, approximately 1.618033989. It is also known as the Divine Ratio, the Golden Mean, the Golden Number, and the Golden Section.

















Слайд 4
What is the Fibonacci Sequence of Numbers?
The Fibonacci
numbers are a unique sequence of integers, starting with
1, where each element is the sum of the two previous numbers. For example: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, etc.Слайд 5 Relationship between the Fibonacci Sequence and the Golden
Ratio
The Fibonacci Sequence is an infinite sequence, which means
it goes on for ever, and as it develops, the ratio of the consecutive terms converges (becomes closer) to the Golden Ratio, ~1.618. For example, to find the ratio of any two successive numbers, take the latter number and divide by the former. So, we will have: 1/1=1, 2/1=2, 3/2=1.5, 5/3=1.66, 8/5=1.6, 13/8=1.625, 21/13=1.615.Слайд 6 As we can see, the ratio approaches the
Golden Ratio. Even though we know it approaches this
one particular constant, we can see from the graph that it will never reach this exact value.
Слайд 8
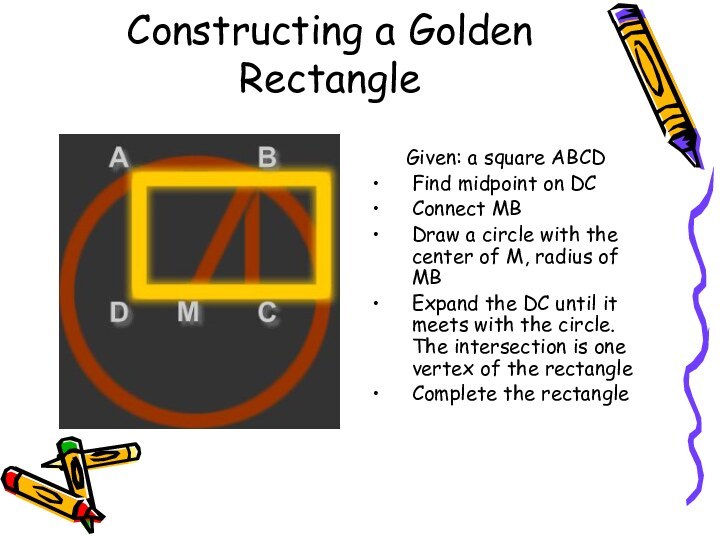
Constructing a Golden Rectangle
Given: a square ABCD
Find midpoint
on DC
Connect MB
Draw a circle with the center of
M, radius of MB Expand the DC until it meets with the circle. The intersection is one vertex of the rectangle
Complete the rectangle
Слайд 9
Golden triangle
The golden triangle is an isosceles triangleThe
golden triangle is an isosceles triangle such that the
ratio of the hypotenuse a to base b is equal to the golden ratio. From the above figure, this means that the triangle has vertex angle equal to
Слайд 11
Plants growth
The branching rates in plants occur in
the Fibonacci pattern, where the first level has one
"branching" (the trunk), the second has two branches, than 3, 5, 8, 13 and so on. Also, the spacing of leaves around each branch or stalk spirals with respect to the Golden Ratio.
Слайд 12
Flowers
On the back of the passiflora incarnate, the
3 sepals (the part of the flower that is
not the petal) that protected the bud are outermost, followed by the 5 outer green petals and an inner layer of 5 more paler green petals.





























