of Commons.
The party system.
The House of Lords.
The monarchy.
Local government.
Parliament's
history at a glance. The official head of state.
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
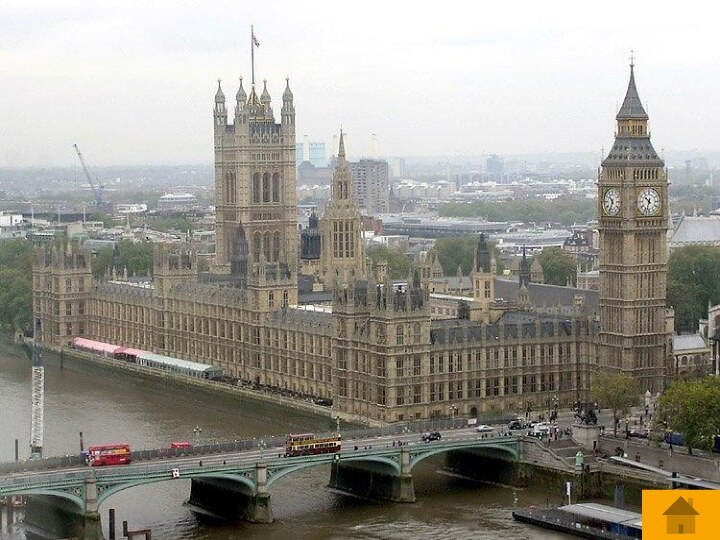


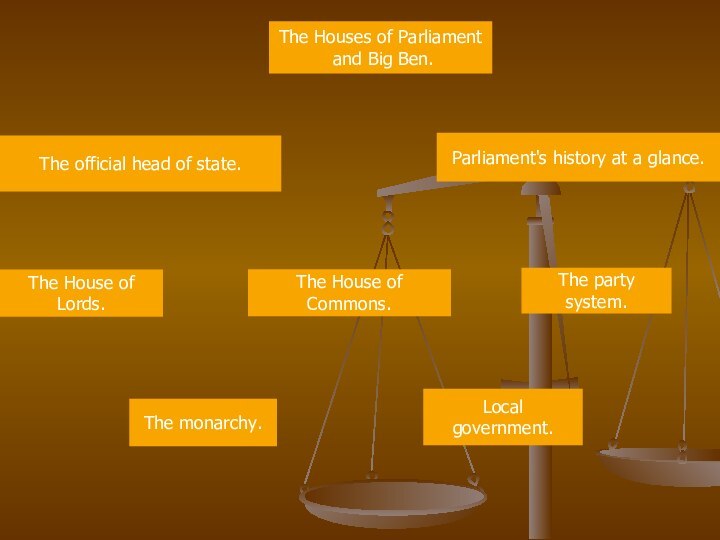

















The official head of state.