……………………………
……………………………
……………………………
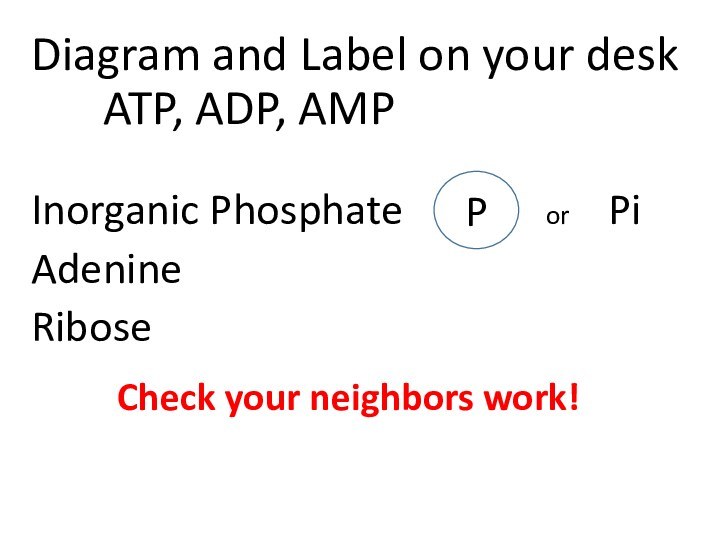
…………………………..Adenine High Energy Bonds Phosphate Ribose Nucleoside
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть


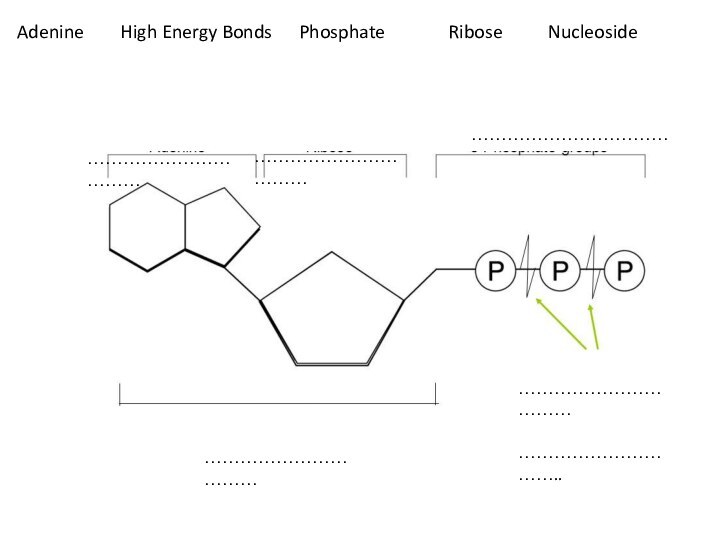
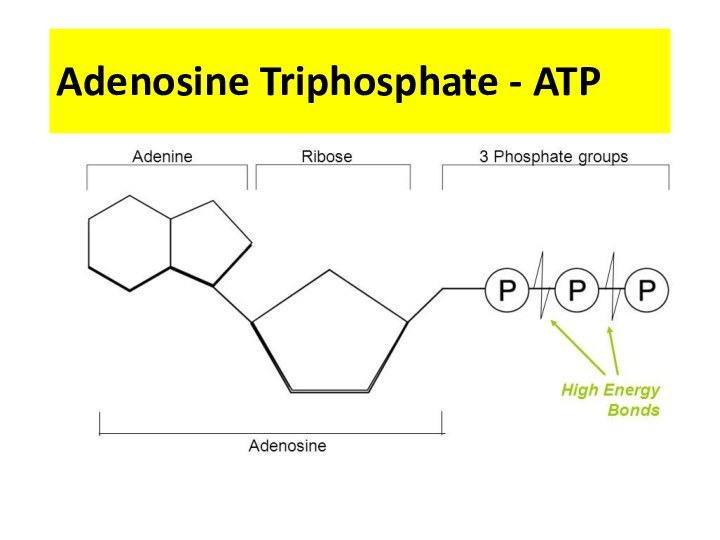




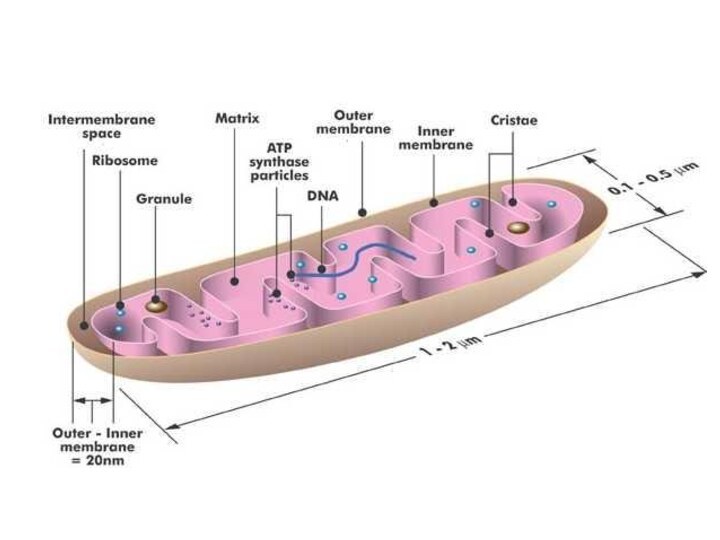
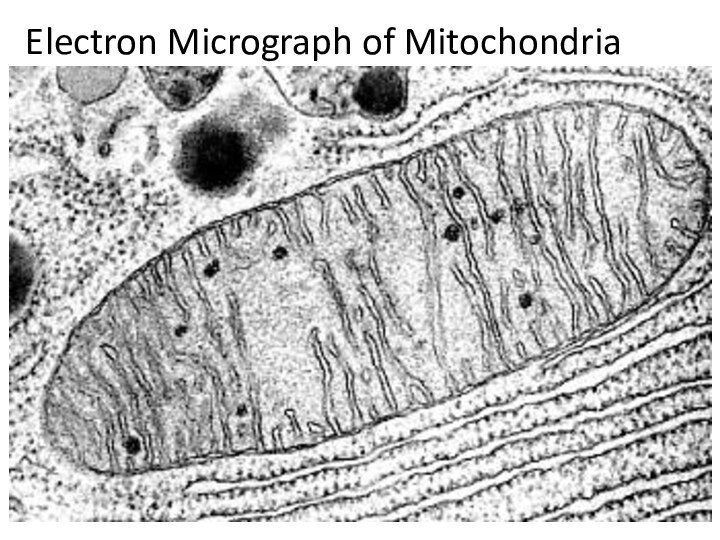
Adenine High Energy Bonds Phosphate Ribose Nucleoside
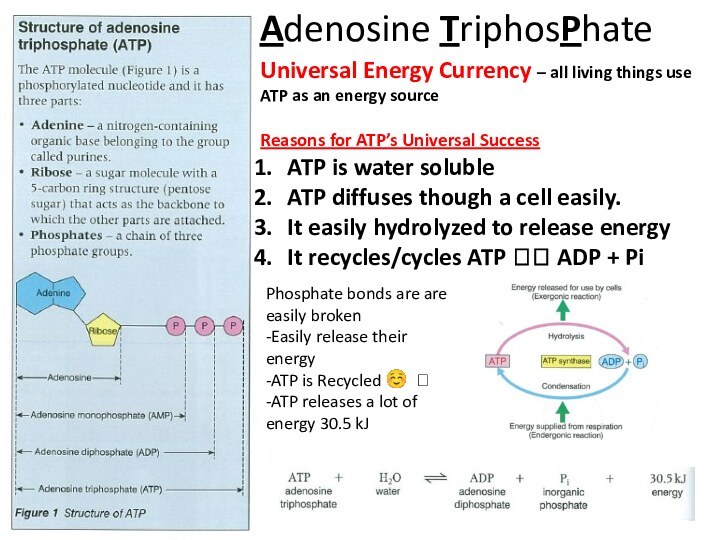
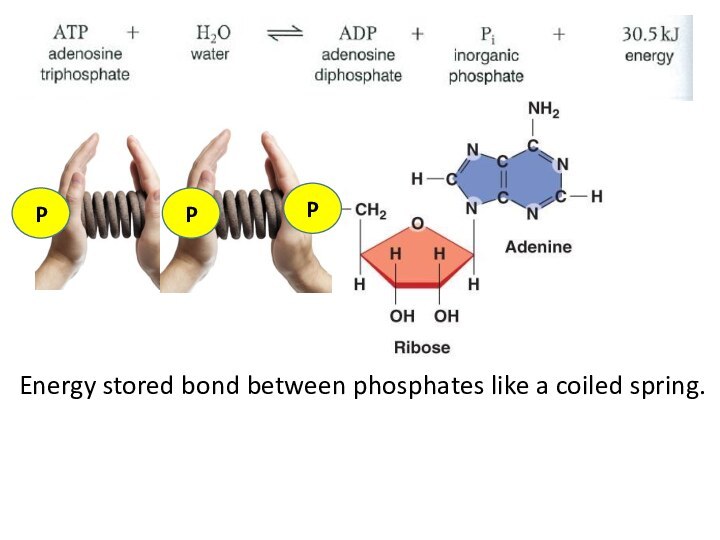
Phosphate bonds are are easily broken
-Easily release their energy
-ATP is Recycled ☺ ?
-ATP releases a lot of energy 30.5 kJ
P
Check your neighbors work!
Just a few ways living things use ATP.
An amoeba eating food phagocytosis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6rnhiMxtKU
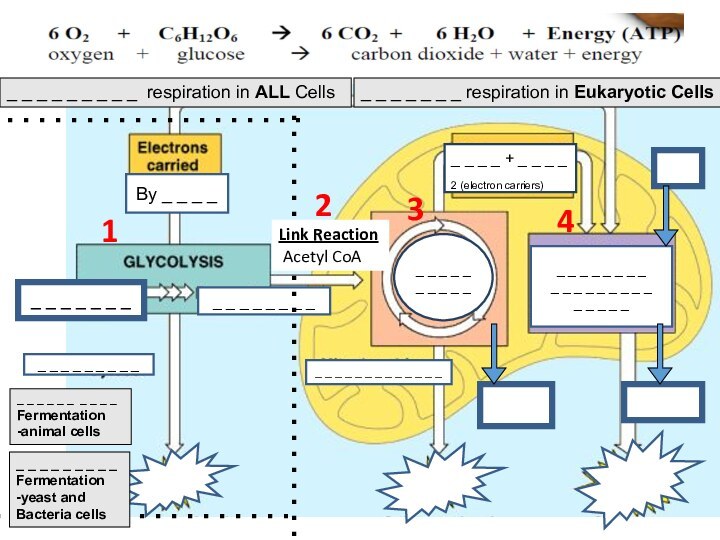
_ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
By _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ respiration in Eukaryotic Cells
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ respiration in ALL Cells
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
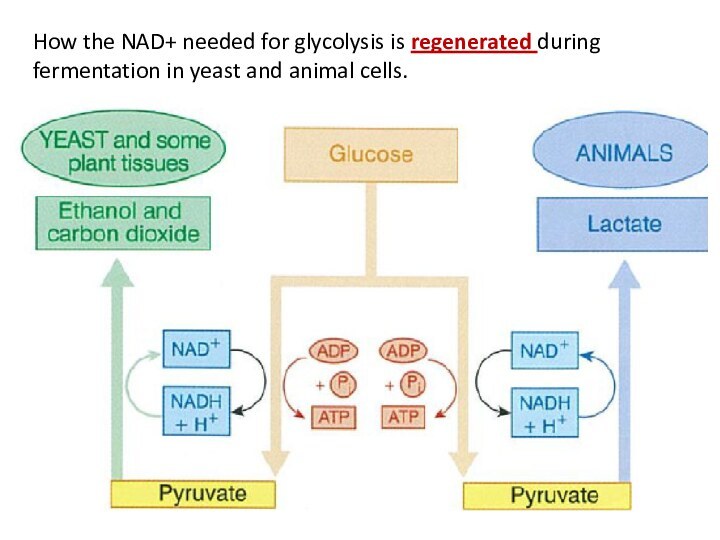
Fermentation
-animal cells
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Fermentation
-yeast and
Bacteria cells
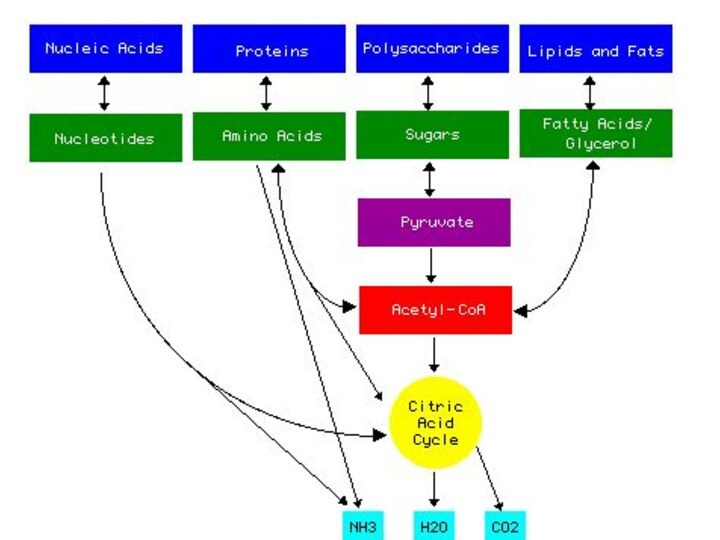
Link Reaction
Acetyl CoA
1
2
3
4
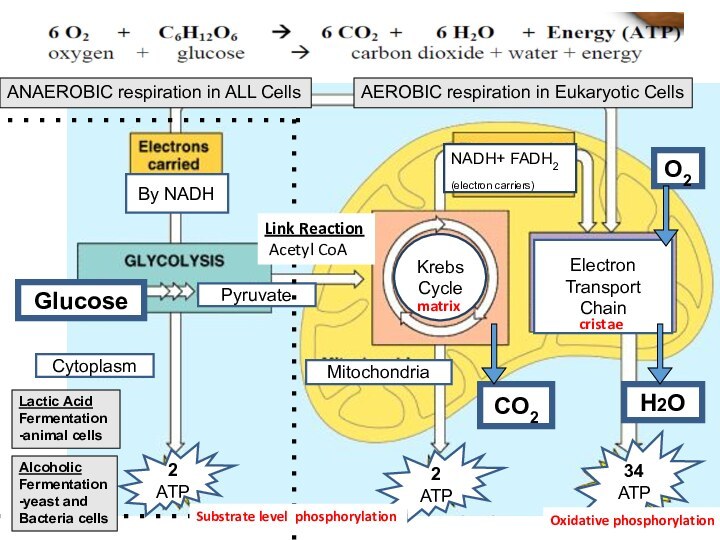
AEROBIC respiration in Eukaryotic Cells
ANAEROBIC respiration in ALL Cells
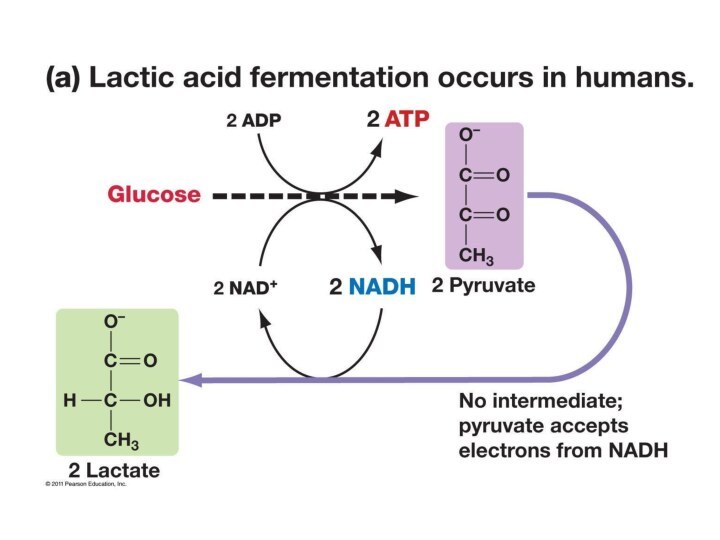
Lactic Acid
Fermentation
-animal cells
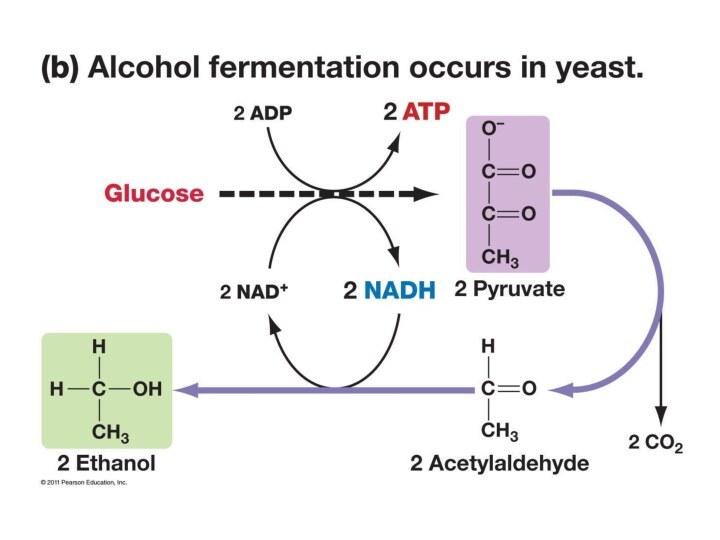
Alcoholic
Fermentation
-yeast and
Bacteria cells
O2
H2O
CO2
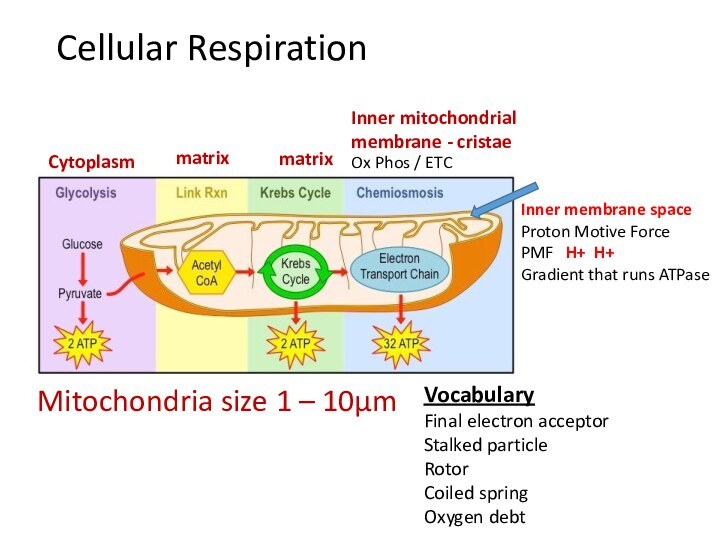
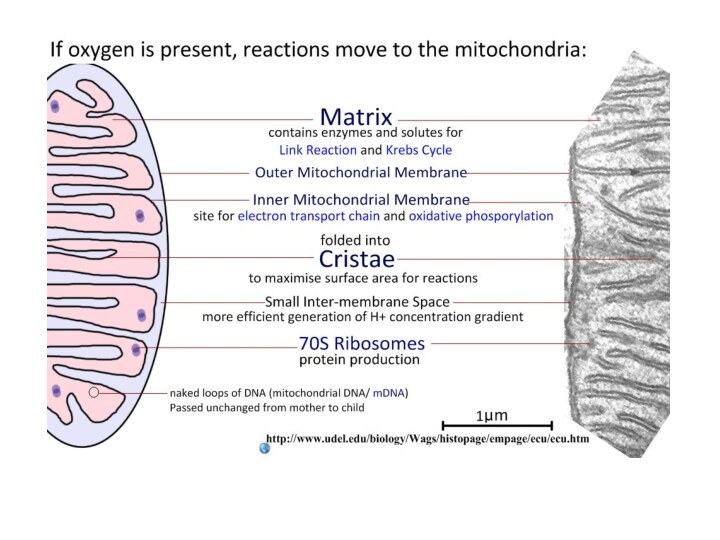
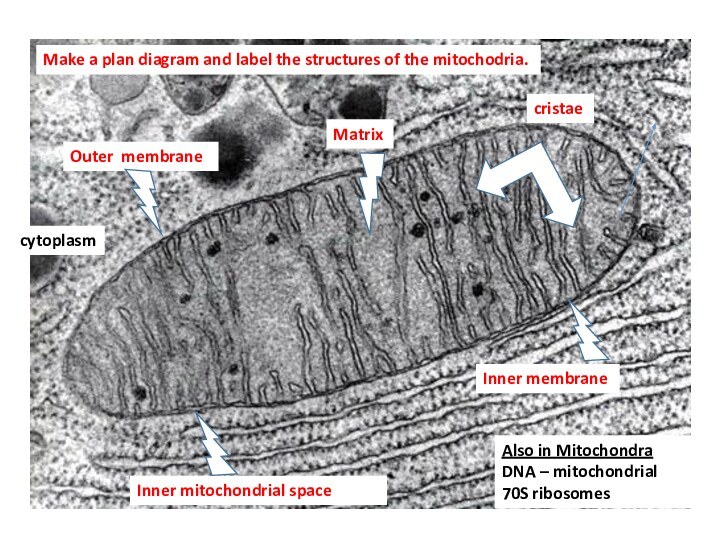
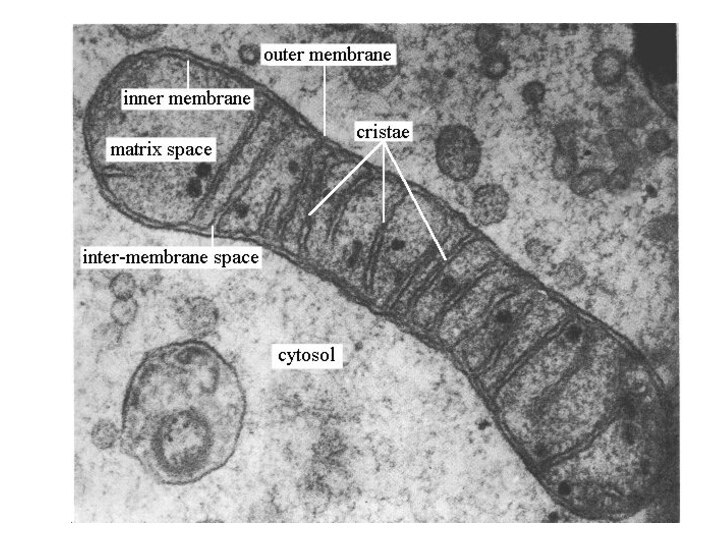
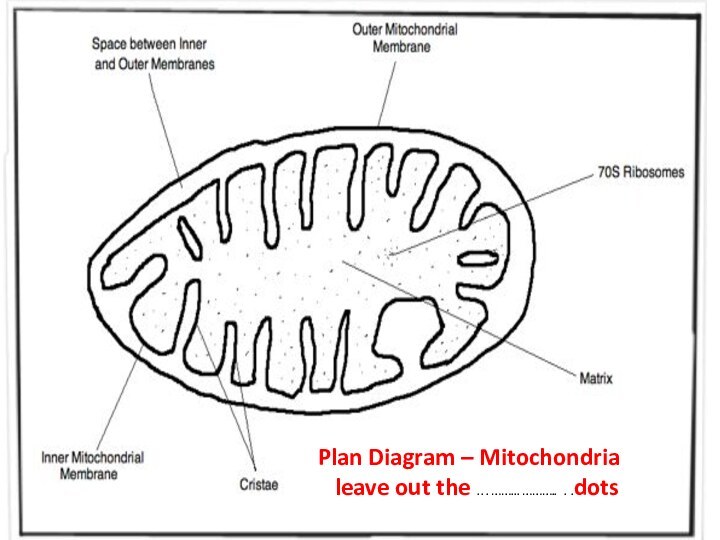
matrix
cristae
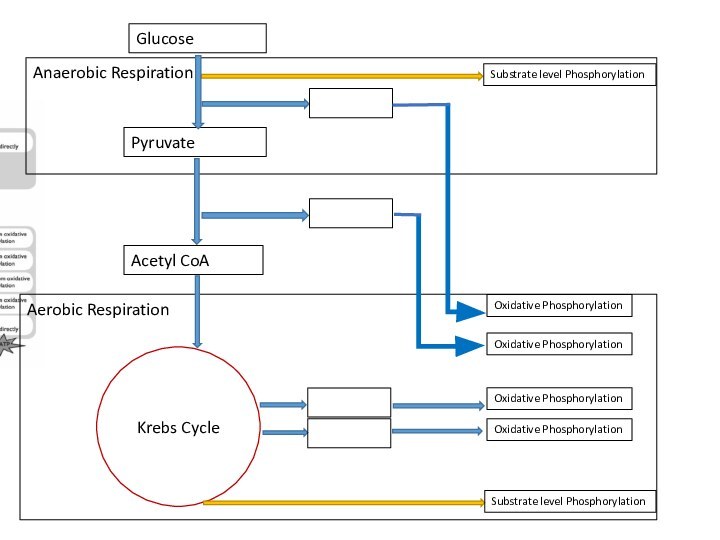
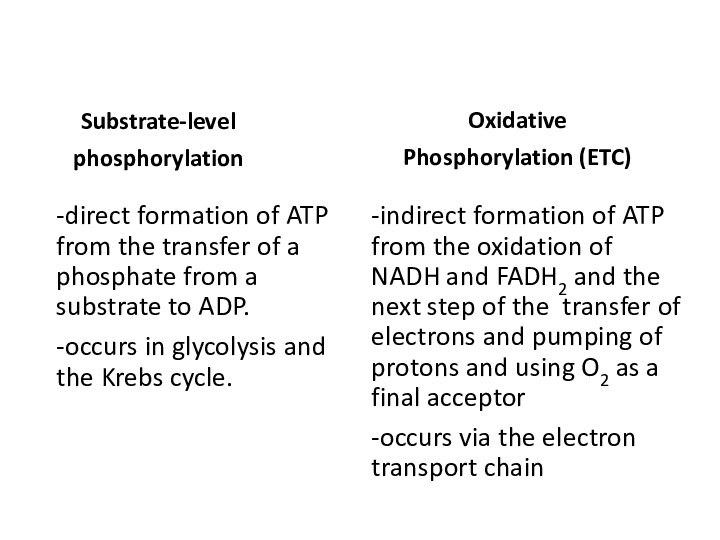
Substrate level phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Link Reaction
Acetyl CoA
Ox Phos / ETC
Inner membrane space
Proton Motive Force
PMF H+ H+
Gradient that runs ATPase
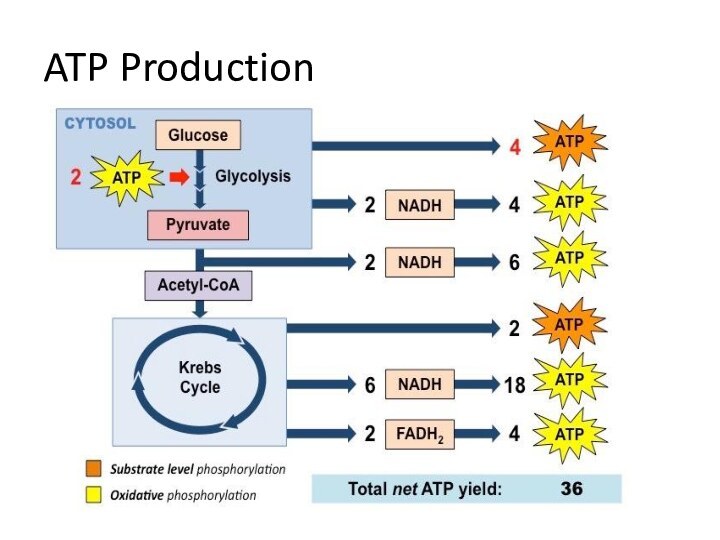
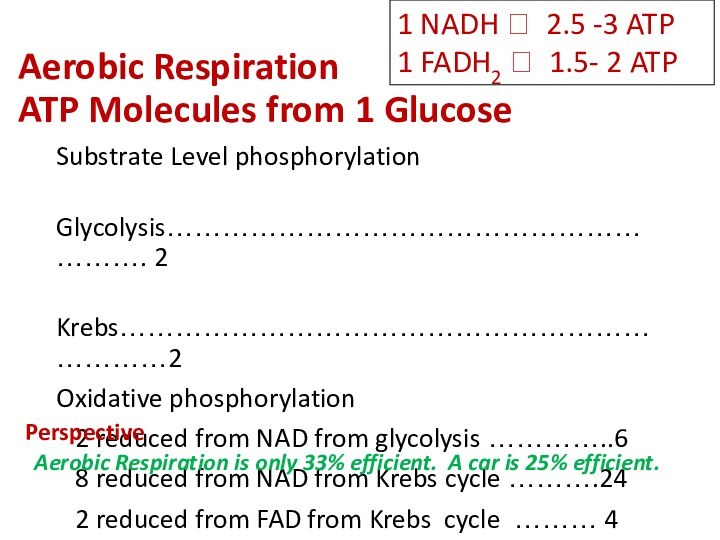
1 NADH ? 2.5 -3 ATP
1 FADH2 ? 1.5- 2 ATP
Aerobic Respiration is only 33% efficient. A car is 25% efficient.
Perspective
Oxidative
Phosphorylation (ETC)
-indirect formation of ATP from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 and the next step of the transfer of electrons and pumping of protons and using O2 as a final acceptor
-occurs via the electron transport chain
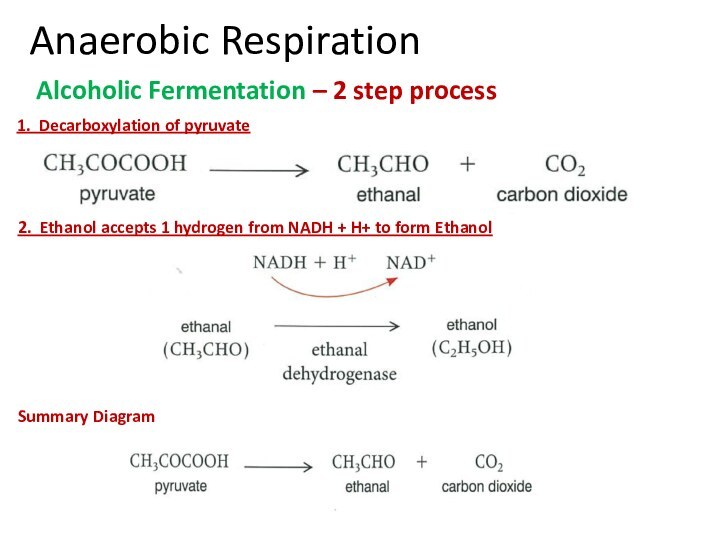
Summary Diagram
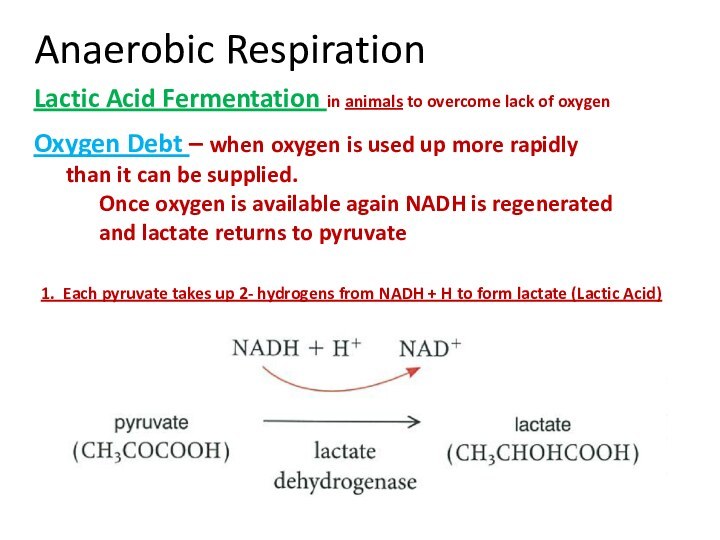
1. Each pyruvate takes up 2- hydrogens from NADH + H to form lactate (Lactic Acid)
Created by P Comte NIS 16-17