- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Introduction to special microbiology
Содержание
- 2. PURPOSEto study the diagnostic methods of infectious diseases and their use in dentistry
- 3. SPECIAL BACTERIOLOGYSpecial bacteriology is the branch of microbiology
- 4. VIROLOGYVirology is the study of viruses – submicroscopic, parasitic particles
- 5. PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSIS Some infectious diseases are distinctive
- 6. PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSIS Most often, therefore, it is
- 7. Laboratory procedures used in confirming a clinical
- 8. BACTERIOSCOPIC METHODBacterioscopic method is detection of microbes
- 9. BACTERIOSCOPIC METHODMaterial from the patient is visually
- 10. BACTERIOSCOPIC METHOD ADVANTAGESSimplicityAbility to quickly obtain resultsTechnical and
- 11. BACTERIOLOGICAL METHODThe bacteriological method consists in isolating
- 12. BACTERIOLOGICAL METHODIsolation of the pathogenic pure culture
- 13. BACTERIOLOGICAL METHOD ADVANTAGESHigh specificity (allows to exclude false
- 14. SEROLOGIC STUDIESSerologic studies are methods of studying
- 15. SEROLOGICAL METHOD ADVANTAGESA modern and reliable way to
- 16. ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTSare highly specific and sensitive
- 17. ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS With many infectious diseases, due
- 18. ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Identification of cellular immune response
- 19. ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Allergic diagnostic tests can diagnosetuberculosis
- 20. ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS ADVANTAGESSpecificity DISADVANTAGEScan be positive not only
- 21. BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH METHODS Biological research methods are aimed
- 22. MOLECULAR TECHIQUESMolecular techniques are based on the
- 24. MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES1.Southern blotting and nucleic acid hybridization A
- 25. MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES2. Nucleic acid amplification tests Nucleic acid
- 26. MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES2. Nucleic acid amplification tests Automated systems
- 27. POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTIONPolymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a
- 28. In the case of molecular diagnostics of
- 30. DNA POLYMERASE DNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotidesare used DNA polymerase
- 31. A strip of eight PCR tubes, each
- 32. GEL ELECTROPHORESISGel electrophoresis is a method for separation
- 33. GEL ELECTROPHORESIS Gel electrophoresis apparatus – an agarose
- 34. GEL ELECTROPHORESIS Ethidium bromide-stained PCR products after gel electrophoresis.
- 35. IMMUNOFLUORESCENCEImmunofluorescence analysis, or the reaction of immunofluorescence,
- 36. IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE
- 37. Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (FTA - ABS test)
- 38. MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS IN DENTISTRYUsed to diagnose inflammatory-destructive
- 39. MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS IN DENTISTRYPeriodontal tissues of a
- 40. An example of Gram Stained Oral Microbiota(note presence of cheek cells)http://microbio146.blogspot.ru/2011/11/lab-35-oral-microbiota.html
- 41. MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS IN DENTISTRYWhen the periodontal lesions
- 42. Скачать презентацию
- 43. Похожие презентации
PURPOSEto study the diagnostic methods of infectious diseases and their use in dentistry


































Слайд 3
SPECIAL BACTERIOLOGY
Special bacteriology is the branch of microbiology that
studies the morphology, ecology, genetics
and biochemistry of bacteria and their relation to medicine
This subdivision of microbiology involves
the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species
Слайд 4
VIROLOGY
Virology is the study of viruses – submicroscopic, parasitic particles of
genetic material contained in a protein coat – and virus-like
agentsIt focuses on the following aspects of viruses: their structure, classification and evolution, their ways to infect and exploit host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy
Virology is considered to be a subfield of microbiology or of medicine
Слайд 5
PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSIS
Some infectious diseases are distinctive enough
to be identified clinically. Most pathogens, however, can cause
a wide spectrum of clinical syndromes in humans. Conversely, a single clinical syndrome may result from infection with any one of many pathogens. Influenza virus infection, for example, causes a wide variety of respiratory syndromes that cannot be distinguished clinically from those caused by streptococci, mycoplasmas, or more than 100 other viruses.
Слайд 6
PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSIS
Most often, therefore, it is necessary
to use microbiologic laboratory methods to identify a specific
etiologic agent. Diagnostic medical microbiology is the discipline that identifies etiologic agents of disease. The job of the clinical microbiology laboratory is to test specimens from patients for microorganisms that are, or may be, a cause of the illness and to provide information (when appropriate) about the in vitro activity of antimicrobial drugs against the microorganisms identifiedСлайд 7 Laboratory procedures used in confirming a clinical diagnosis
of infectious disease with a bacterial etiology
From: Chapter 10, Principles
of DiagnosisMedical Microbiology. 4th edition.
Baron S, editor.
Galveston (TX): University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; 1996.
Слайд 8
BACTERIOSCOPIC METHOD
Bacterioscopic method is detection of microbes in
the test material; the study of their morphological and
tinctorial properties, the nature of their location in the bacteriological smear in the field of visionThe study is appointed if there is a suspicion of the patient having an infectious and purulent-inflammatory process or in the obstetric and gynecological area
Слайд 9
BACTERIOSCOPIC METHOD
Material from the patient is visually studied,
a portion is selected in which the causative agent
of the disease (lumps of mucus, purulent plugs) can be detected with the greatest probability.It is applied to a slide.
The drop is spread over the glass, dried and fixed.
The smear stains (by Gram method) and the drug is examined under a microscope.
Слайд 10
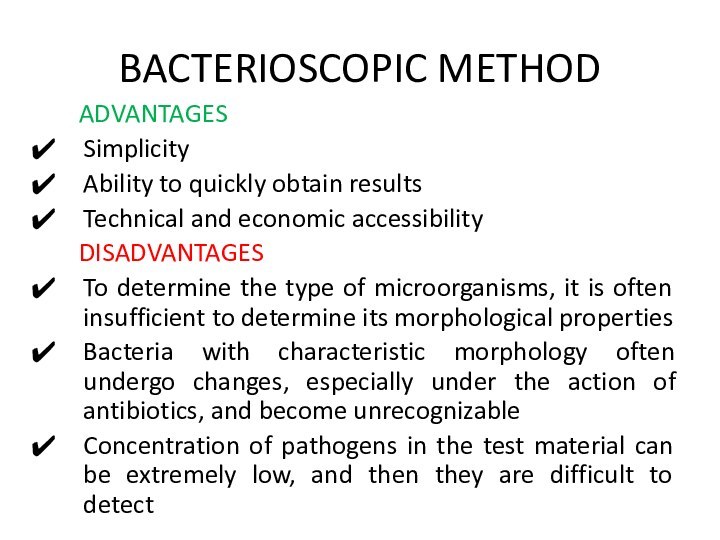
BACTERIOSCOPIC METHOD
ADVANTAGES
Simplicity
Ability to quickly obtain results
Technical and economic
accessibility
DISADVANTAGES
To determine the type of microorganisms, it is often
insufficient to determine its morphological propertiesBacteria with characteristic morphology often undergo changes, especially under the action of antibiotics, and become unrecognizable
Concentration of pathogens in the test material can be extremely low, and then they are difficult to detect
Слайд 11
BACTERIOLOGICAL METHOD
The bacteriological method consists in isolating the
pure culture of the pathogen (a population containing bacteria
of one species) and identifying this pathogenA multi-stage bacteriological study lasts 18-24 hours
Identification is the study of the properties of microorganisms so establishing a particular systematic group of bacteria (species, genus)
This method is used in to determine such dangerous diseases as tuberculosis, recurrent typhoid or gonorrhea. It is also used to study the bacterial composition of tonsils, cavities of organs
Слайд 12
BACTERIOLOGICAL METHOD
Isolation of the pathogenic pure culture (inoculation
test material on dense nutrient media, elective or differential-diagnostic
which is placed in thermostat)The study of bacterial colonies grown on a dense nutrient medium and originating from a single bacterial cell (the colony is a pure culture of the pathogen):
– cultural properties of the colonies (shape, size, color, edges and surfaces, structure, consistency)
– tinctorial and morphological properties of the selected culture and verifying at the same time its purity
Identification of the isolated pure culture of the pathogen and determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics and other chemotherapeutic drugs
Слайд 13
BACTERIOLOGICAL METHOD
ADVANTAGES
High specificity (allows to exclude false diagnose)
Helps
to apply the most effective treatment by accurately determining
the reaction of microorganisms to a particular medical deviceDISADVANTAGES
Lasts a long time
Strict requirements to test material
Strict requirements for laboratory technicians
Слайд 14
SEROLOGIC STUDIES
Serologic studies are methods of studying certain
antibodies or antigens in the blood serum of patients
based on the reactions of immunity. With their help, antigens of microbes or tissues are also identified for the purpose of their identification.The detection of antibodies to the infectious agent or the corresponding antigen in the serum of the patient allows to establish the cause of the disease.
Serological studies are also used to determine blood group antigens, tissue antigens and the level of humoral immunity.
Слайд 15
SEROLOGICAL METHOD
ADVANTAGES
A modern and reliable way to identify
such dangerous diseases as HIV, hepatitis, brucellosis, STDs
High specificity
and sensitivityMost of the reactions of this method are simple in conducting and accounting, available to a wide range of laboratories, usually safe, economical, amenable to standardization
DISADVANTAGES
the indirect nature of the result, when the etiology of the disease is judged not by the isolation of the pathogen, but by the immune response to the causative agent
the need for parenteral intervention in the patient's body
in most cases, late diagnosis, which is due to the natural dynamics of the humoral immune response
Слайд 16
ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
are highly specific and sensitive tests
of diagnosing allergic and infectious diseases, in the pathogenesis
of which the allergic component predominatesare based on the local or general reaction of the sensitized organism in response to the introduction of a specific allergen – a delayed type hypersensitivity reaction (HRT)
are used for detection of an allergen or a group of allergens that have caused a hypersensitivity state
Skin tests (application, scarification and intradermal tests) provocative tests (nasal, conjunctival, inhalation)
Слайд 17
ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
With many infectious diseases, due to
activation of cellular immunity, an increased sensitivity of the
organism to pathogens and products of their vital activity develops. This is based on allergic tests used to diagnose bacterial, viral, protozoal infections, mycoses and helminthiases. Allergic tests have specificity, but often they are positive for those who have recovered and vaccinated.
Слайд 18
ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Identification of cellular immune response -
delayed type hypersensitivity (HRT), scheme
Introduction intradermally Ag bacteria
After 48
- 72 hours there is inflammationMeasure the amount of redness and papules
Слайд 19
ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Allergic diagnostic tests can diagnose
tuberculosis (Mantoux
reaction)
brucellosis (Burne test)
tularemia (Tularin test)
anthrax (anthraxin test)
soft chancre (Duchess
reaction)leprosy (Mitsuda reaction)
differentiate tuberculoid (lepromin-positive) form from lepromatous (lepromin-negative)
Слайд 20
ALLERGY DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
ADVANTAGES
Specificity
DISADVANTAGES
can be positive not only in
infected, but also in vaccinated against these diseases, as
well as in people who have recovered many years agomany patients the method of introducing an irritant into the body is contraindicated
Слайд 21
BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH METHODS
Biological research methods are aimed at
determining the presence of pathogen toxins in the test
material and on the detection of the causative agent. Methods include infecting laboratory animals with the test material, followed by isolation of a pure pathogen culture or establishing the presence of a microbial toxin and its nature. The method is highly sensitive, can be used in the early stages of the disease, but is not always available, expensive, long-lasting, unsafe.
Слайд 22
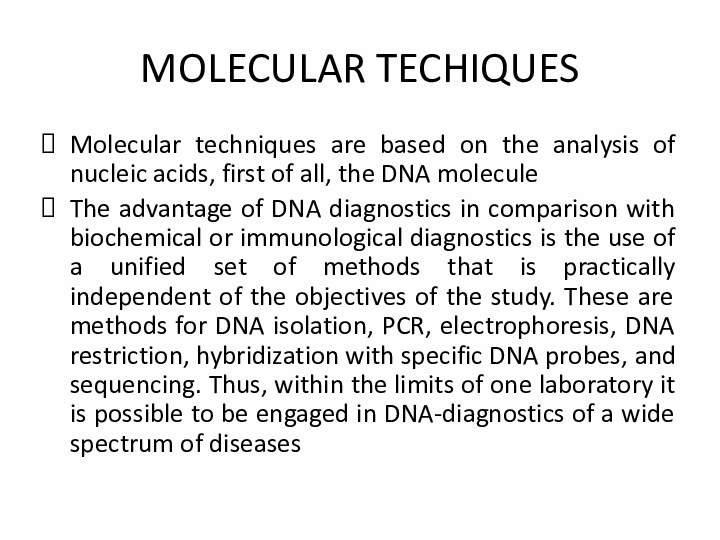
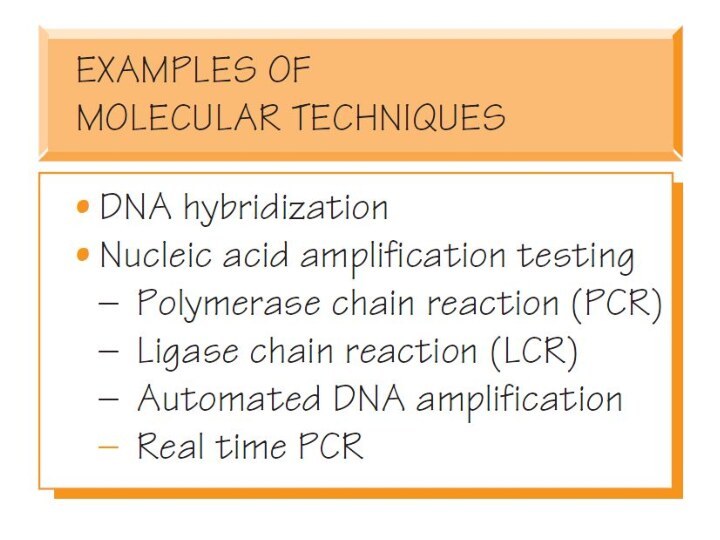
MOLECULAR TECHIQUES
Molecular techniques are based on the analysis
of nucleic acids, first of all, the DNA molecule
The
advantage of DNA diagnostics in comparison with biochemical or immunological diagnostics is the use of a unified set of methods that is practically independent of the objectives of the study. These are methods for DNA isolation, PCR, electrophoresis, DNA restriction, hybridization with specific DNA probes, and sequencing. Thus, within the limits of one laboratory it is possible to be engaged in DNA-diagnostics of a wide spectrum of diseases
Слайд 24
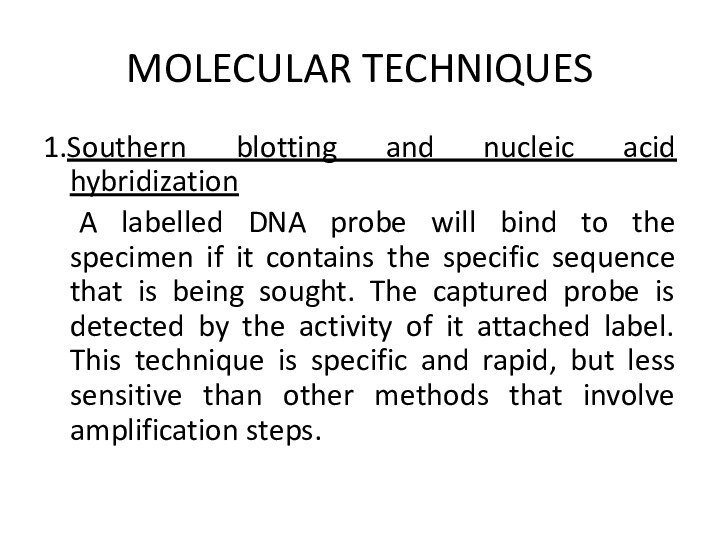
MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES
1.Southern blotting and nucleic acid hybridization
A labelled
DNA probe will bind to the specimen if it
contains the specific sequence that is being sought. The captured probe is detected by the activity of it attached label. This technique is specific and rapid, but less sensitive than other methods that involve amplification steps.
Слайд 25
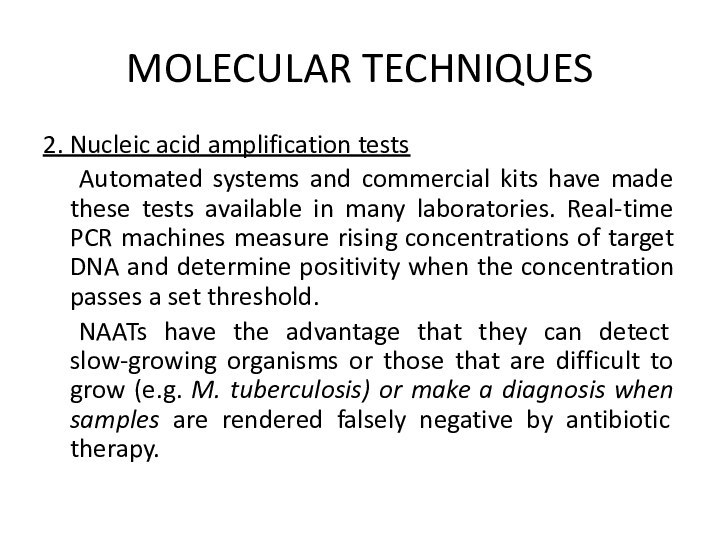
MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES
2. Nucleic acid amplification tests
Nucleic acid amplification
tests (NAATs) make the diagnosis by amplifying specific regions
of the genome from the pathogen. Although different methods are used to amplify pathogen-specific DNA or RNA the aim is the same, to produce sufficient copies for detection. For example, nucleic acid from the pathogen is separated into single strands and primers are designed to bind to targetsequences. A polymerase then catalyses synthesis of new nucleic acid and this process is repeated for multiple cycles.
Слайд 26
MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES
2. Nucleic acid amplification tests
Automated systems and
commercial kits have made these tests available in many
laboratories. Real-time PCR machines measure rising concentrations of target DNA and determine positivity when the concentration passes a set threshold.NAATs have the advantage that they can detect slow-growing organisms or those that are difficult to grow (e.g. M. tuberculosis) or make a diagnosis when samples are rendered falsely negative by antibiotic therapy.
Слайд 27
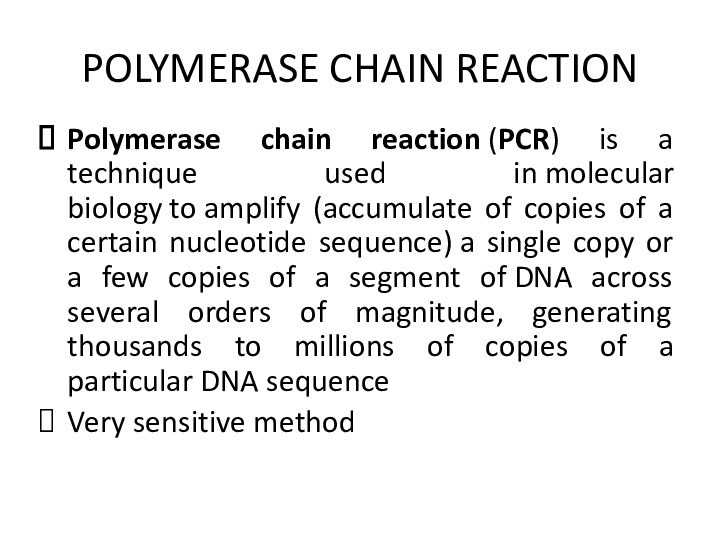
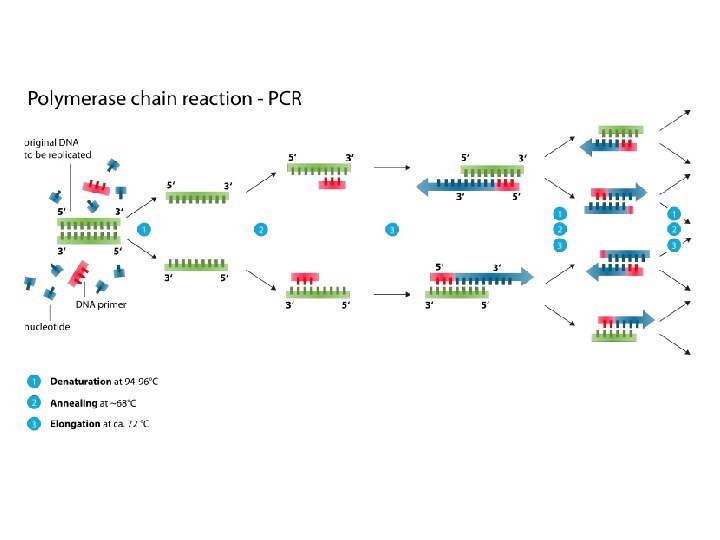
POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique
used in molecular biology to amplify (accumulate of copies of a certain
nucleotide sequence) a single copy or a few copies of a segment of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequenceVery sensitive method
Слайд 28 In the case of molecular diagnostics of infections,
a DNA fragment specific for a particular pathogen is
amplified, and then, with the help of electrophoresis and staining on DNA, the presence of this fragment, and therefore of the pathogen itself, is tested in the biological sample that was taken for analysis.POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION
Слайд 30
DNA POLYMERASE
DNA polymerases
are enzymes that synthesize DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotides
are used DNA polymerase from
thermophilic bacteria, because they are thermostable
The three-dimensional structure of
DNA-binding helical-hairpin sites in human beta-DNA polymeraseСлайд 31 A strip of eight PCR tubes, each containing
a 100 μl reaction mixture
Placing a strip of eight PCR
tubes into a thermal cycler
Слайд 32
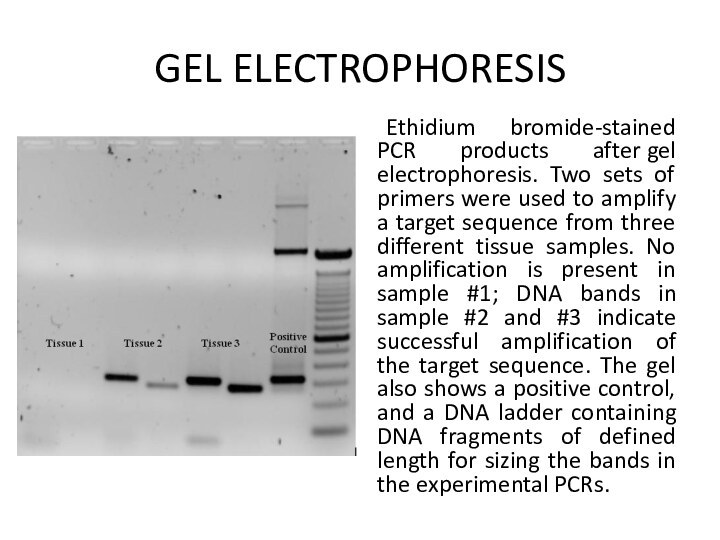
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and
analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on
their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and/or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by chargeNucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving