Слайд 2
Class Structure
What is ‘political culture’ and what is
Inglehart’s theory of value change?
What evidence supports the general
theory?
Potential criticisms of Inglehart?
What are the consequences for support for democracy and democratization?
Слайд 3
What is political culture?
Components:
Values and priorities
Cognitive beliefs,
attitudes, and opinions,
Social norms and practices
Gabriel Almond and
Sidney Verba’s The Civic Culture (1963) –
“Attitudes towards the political system and its various parts, and attitudes towards the role of the self in the system.”
Enduring orientation acquired due to the socialization process
Слайд 4
Claim that culture matters..
“If the democratic model is
to develop in new nations, it will require more
than the formal institutions of democracy..[it] requires as well a political culture consistent with it..the norms and values of ordinary citizens”
Almond and Verba The Civic Culture (1963)
Слайд 5
1. Ronald Inglehart’s theory
The Silent Revolution (1977)
Culture Shift
(1990)
Modernization and Post-Modernization (1997)
Inglehart & Norris Rising Tide
(2003)
Norris and Inglehart Sacred & Secular (2004)
Inglehart and Welzel Modernization, cultural change and democracy (2005)
www.worldvaluessurvey.org
Слайд 6
Theory of cultural change
“Economic, cultural and political change
go together in coherent patterns that are changing the
world in predictable ways.”
Inglehart Ch 1.
Probabilistic non-linear trajectories, but not precise predictions in all cases
Слайд 7
Premises of theory
Values = personal or social goals
Values
> attitudes > beliefs
Scarcity hypothesis
Socialization hypothesis
Maslovian value
hierarchy
Слайд 8
Maslovian Value Hierarchy
Social/ self-actualization needs (Post-Materialist)
Physical needs (Materialist)
Aesthetic
Intellectual
Belonging and esteem
Safety
Sustenance
Слайд 9
Predictions
Value change > social/political change
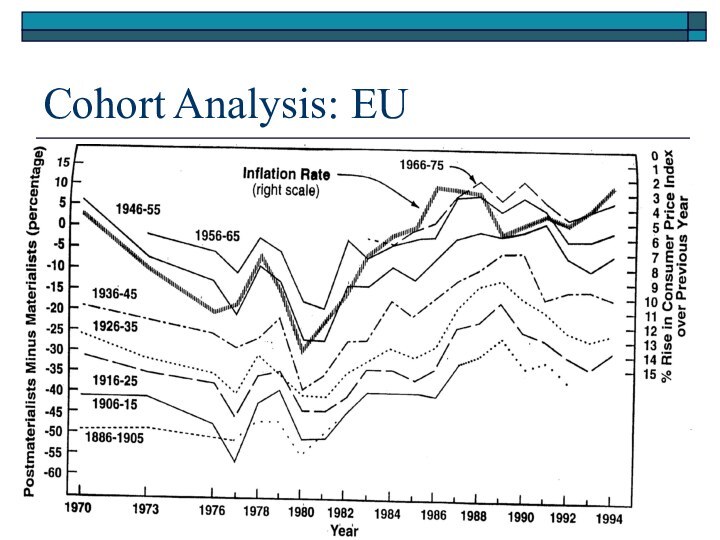
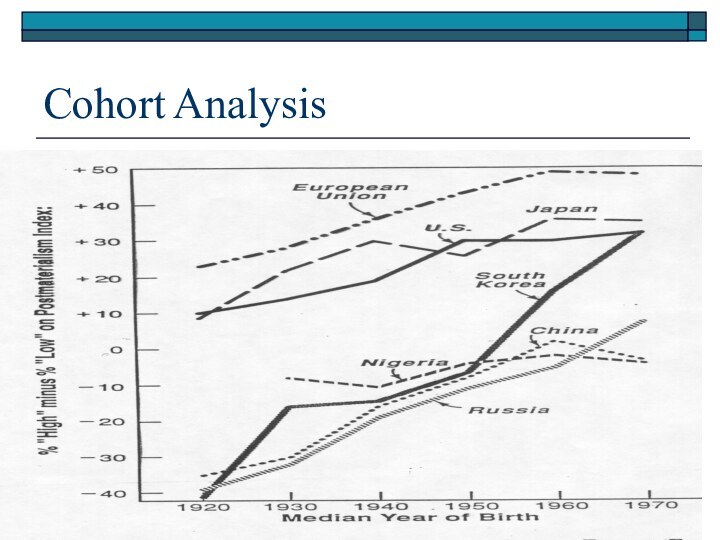
Generational patterns (pre+post
1945)
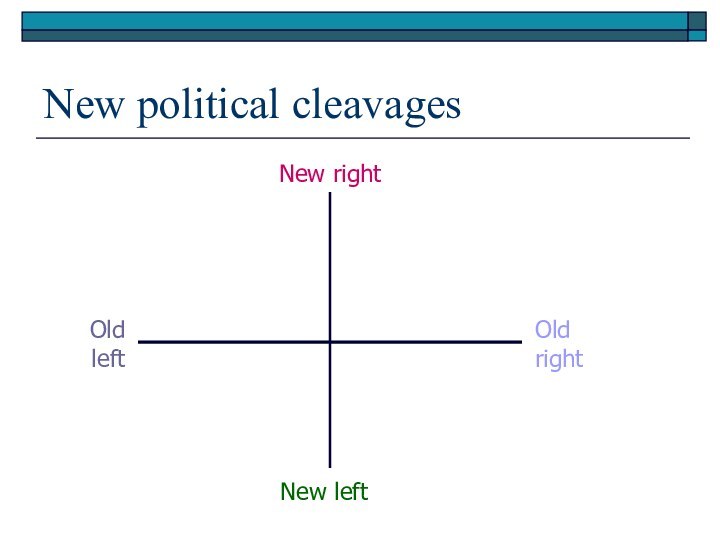
Decline of ‘old’ political cleavages
Class, region, religion
Rise of
new politics
Materialist v. post-materialist new parties eg Greens
New social movements eg women, gays, environmentalists
New public policy agenda
New demands for participation beyond elections
New ‘quality of life’ issues
New left and new right
Growing cultural demand for democratic institutions
Слайд 10
New political cleavages
Old right
Old left
New left
New right
Слайд 11
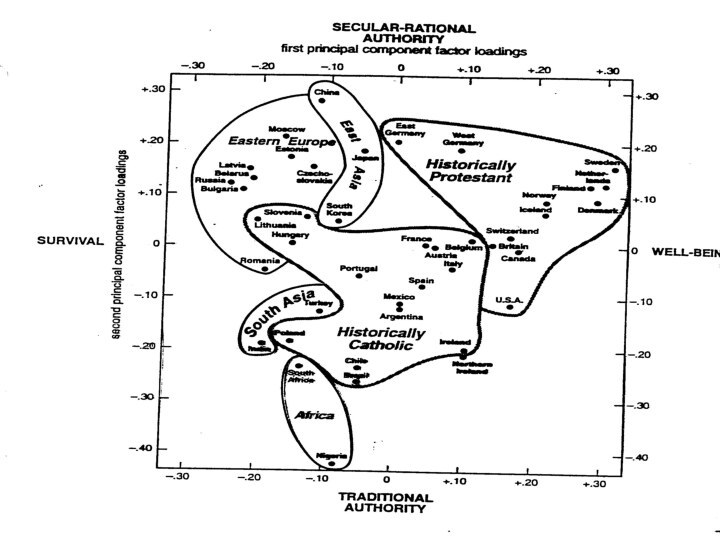
Cultural Shifts
Rational-Legal Authority
Achievement Motivation
Traditional Authority
Religious/communal values
De-emphasis of Authority
Post-materialist
Values
Post-Modernization
Modernization
Слайд 12
Process of social change
Agrarian to modern
From agriculture to
heavy industry
Rural to urban
Division church and state
Mass education and
literacy
Occupational specialization
Working class and urban bourgeoisie, decline of peasants and landed estates
Bureaucratic rational-legal authority, expansion of franchise
Basic welfare state and social protection, education/health
From extended to nuclear families
Entry more women into paid workforce
Modern to Post-modern
Service sector
Urban to suburban
Secularization & scientific authority
Higher education
Flexible careers
From ascribed to achieved status, decline in political salience of class cleavage
Growth of multilayered governance, rise of new participatory demands
Market liberalization and contracting out of social protection functions
Growth non-traditional households
Growing sex equality in the home and workplace
Слайд 13
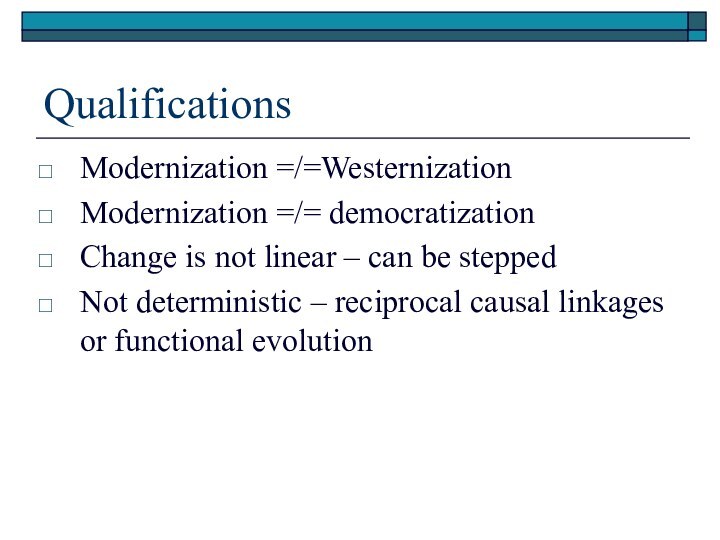
Qualifications
Modernization =/=Westernization
Modernization =/= democratization
Change is not linear –
can be stepped
Not deterministic – reciprocal causal linkages or
functional evolution
Слайд 14
2: Evidence
“There is a lot of talk these
days about what the aims of the country should
be for the next ten years. On this card are listed some of the goals which different people would give as top priority. Would you please say which of these you consider the most important? And which would be the next most important?
Maintaining order in the nation
Giving people more say in important government decisions
Fighting rising prices
Protecting freedom of speech”
Mat
Mat
PM
PM
Слайд 15
Questions about the evidence
Is economic development linked with
cultural values?
Do values cluster in predictable patterns?
How does
region and religion influence cultural values?
Слайд 16
89 Nations in the WVS 1980-2007
Слайд 17
WVS -Waves
1980-1984 - 22 nations
1990-1993 - 42 nations
1995-1997
- 53 nations
1999-2002 - 79 nations
2006-2007 – 42 nations
to date
Representative surveys per nation 1000
New sources www.globalbarometer.org
Africa, Latin America, Asia, C&E Europe
Слайд 22
3. Potential criticisms?
Measure of post-materialism?
Diverse patterns across societies
e.g. environmental movement, green parties
Economic-cultural determinism?
Prospects for democracy in
agrarian societies
e.g. Can agrarian societies like India be democratic?
Слайд 23
4. Implications for democratic support
Inglehart and Welzel’s theory
Self-expression
values influence subsequent democratic institutions (not vice versa)
Direct attitudes
towards democracy are less important than self-expression values
Слайд 24
Why does development strengthen self-expression values?
Socio-economic development increases:
Financial capital and economic resources (income and wealth)
Human capital
and cognitive resources (access to information and education), and
Social capital (diversifying human interaction and networks)
Reduces constraints (widens objective capacity of people to act according to their own choices)
Leads towards self-expression values (subjective aspirations for choice)
In turn, self-expression values lead towards greater demand for entitlement to choice, including civil and political liberties, and demand for democratic institutions
Слайд 25
Measuring self-expression values
Post-materialist values
R gives priority to post-materialist
values (4-item index)
Life satisfaction and subjective well-being
R describes self
as ‘very’ or ‘rather’ happy
Tolerance of other’s liberty
R agrees that homosexuality is justifiable (10-pt scale)
Elite-challenging civil activity
R would sign a petition
Generalized interpersonal trust:
R agrees ‘most people can be trusted most of the time’
Is the measure valid, reliable, and robust?
Слайд 26
Measuring self-expression values
Post-materialist values
R gives priority to post-materialist
values (4-item index)
Life satisfaction and subjective well-being
R describes self
as ‘very’ or ‘rather’ happy
Tolerance of other’s liberty
R agrees that homosexuality is justifiable (10-pt scale)
Elite-challenging civil activity
R would sign a petition
Generalized interpersonal trust:
R agrees ‘most people can be trusted most of the time’
Is the measure valid, reliable, and robust?
Слайд 27
Factor analysis loadings
R gives priority to post-materialist values
(4-item index) .87
R describes self as ‘very’ or
‘rather’ happy .81
R agrees that homosexuality is justifiable (10-pt scale) .77
R would sign a petition .74
R agrees ‘most people can be trusted most of the time’ .46
25% cross-national variations in ‘survival’ v. ‘self-expression’ values
(Aggregate-level analysis WVS 78 societies 1981-2001)
Слайд 28
Defining and measuring democracy
Constitutional democracy (exec constraints, etc)
Polity
IV 20-pt democracy-autocracy scale
Electoral democracy
Vanhanen 100-pt scale (Turnout*party competition)
Formal
democracy
Civil and political liberties
Freedom House 12-pt scale
Regime change = 4+ pt FH scale change per year
Major watershed 1987-1996
Effective democracy
How far power-holders follow legal norms
FH scores * WB anticorruption scores
Слайд 29
Direction of causality?
Impact of values (X) on democracy
(Y)
Test for:
Temporal order
X t1 leads to Y t2…
Spuriousness
Control for Z (economic development)
Autocorrelations
Measure of Y t1 leads to Y t2
Слайд 30
Self-expression values & democracy
Слайд 31
Models: 61 nations
Self-expression values, early-1990s
Socio-econ resources, early-1990s
Democracy, FH
1997-2002
Democracy, FH 1981-1986
Self-expression values, early-1990s
Socio-econ resources, early-1990s
.49**
.81***
A.
B.
.26
.11
Слайд 32
Why not reverse causality?
Living under democracy leads to
values?
Democratic institutions encourage tolerance, trust, etc?
Examine historical development in
specific cases e.g.
post-Communist countries
Singapore
Germany
India
What of direct attitudes towards democratic ideals and practices?
Слайд 33
Critique?
Robert W. Jackman and Ross A. Miller Before
Norms: Institutions & Civic Culture U. Michigan Press 2005
Слайд 34
3. Jackman and Miller critique
“We believe there is
no systematic evidence that links cultural values either to
the longer-term viability of democratic institutions or even to shorter-term transitions to democracy.”
Robert W. Jackman and Ross A. Miller p.129
Claims driven by one or more enigmatic empirical decisions, without which the argument fails.
Слайд 35
Jackman and Miller critique
What counts as ‘culture’?
Post-materialist values
Self-expression
values?
Levels of social trust?
Support for democratic ideals or practices?
Tendency
towards ex post explanation
Eg Confucianism ‘explains’ economic growth of the Asian tigers?
Problems of a few influential cases driving general results
Слайд 36
Jackman and Miller critique
“These problems taken as a
whole generate a set of non-cumulative results and thereby
signify an empirical research program grounded on a set of ad hoc assumptions.”
Jackman and Miller p.131
More plausible to treat values as endogenous i.e. a response to the conditions within which people find themselves.
Eg national wealth and degree of democracy lead towards self-reported life satisfaction
Eg performance of government institutions leads towards political trust and confidence in them
Political and economic circumstances > values
Not values leading to economic and political outcomes