from other classes, thereby inheriting fields and methods from
those classes:class Sub extends Sup {
…
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть





















![4. Java OOP. 4. Inheritance and Polymorphism Hiding Static Methods (3 of 6)public static void main(String[] args) { Animal](/img/tmb/15/1445022/241573593c36bdea2a1b655cb5ad5756-720x.jpg)

![4. Java OOP. 4. Inheritance and Polymorphism Hiding Static Methods (5 of 6)public static void main(String[] args) { Animal](/img/tmb/15/1445022/6311a69cf86039a0047175dda9e8ae1c-720x.jpg)


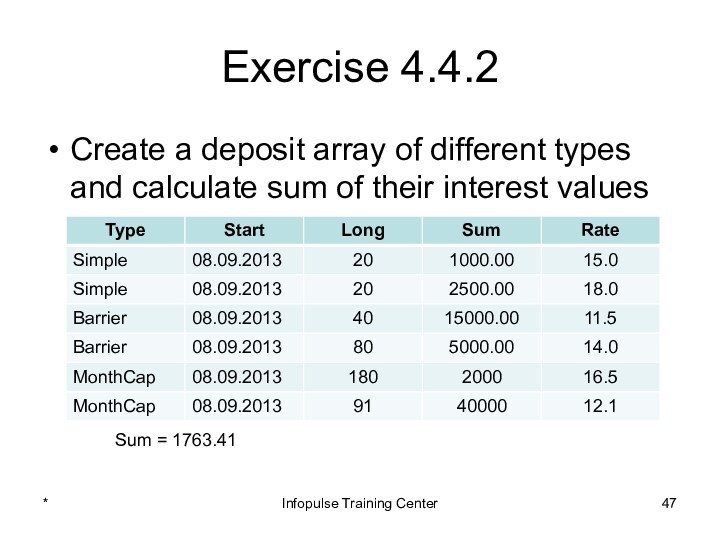
![4. Java OOP. 4. Inheritance and Polymorphism Exercise: Interest Values SumDate start = new GregorianCalendar(2013, Calendar.SEPTEMBER, 8).getTime();DepoBase[] depo =](/img/tmb/15/1445022/8e05507010855bbb7c665ba861c11cd3-720x.jpg)









*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
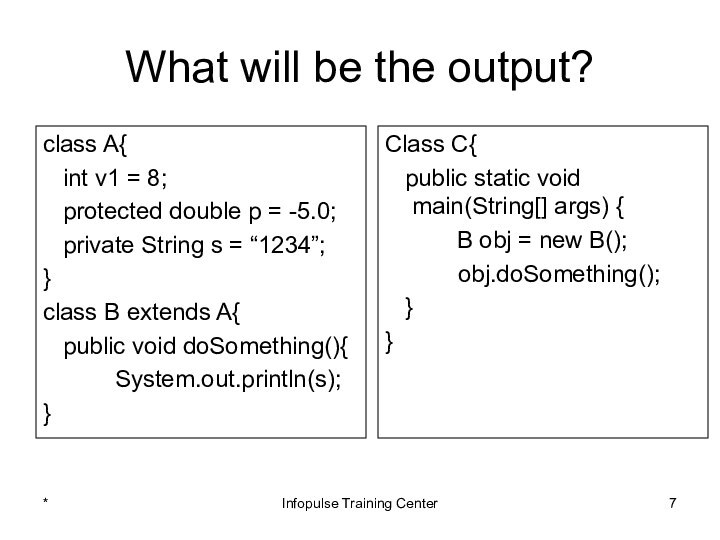
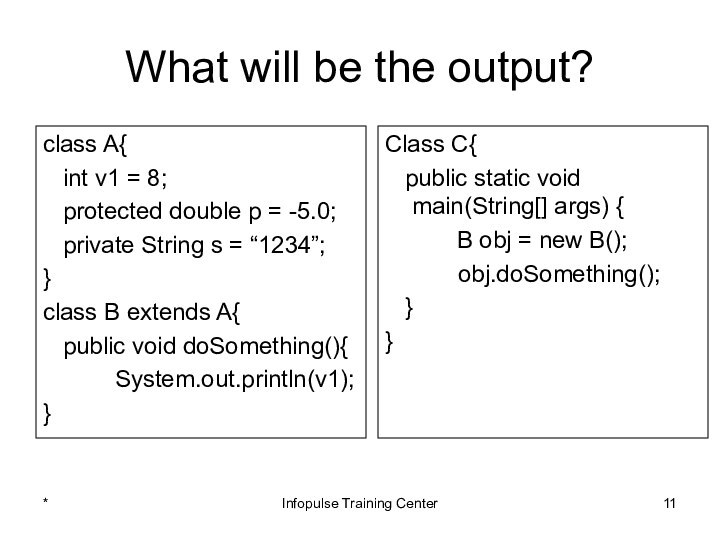
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
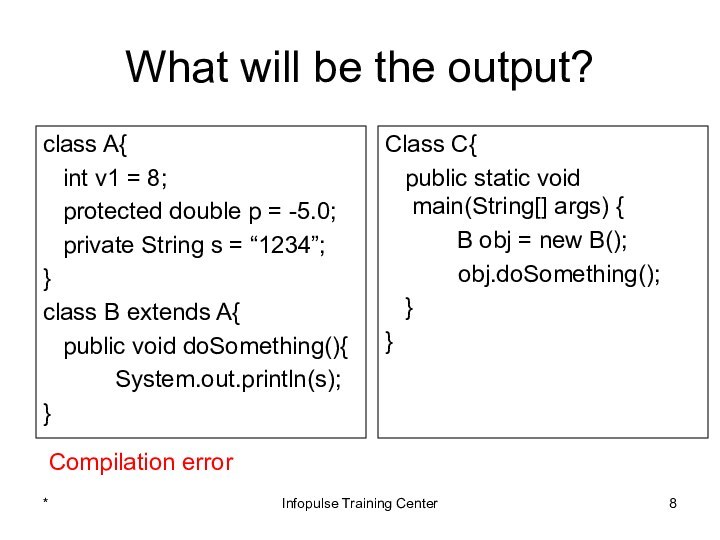
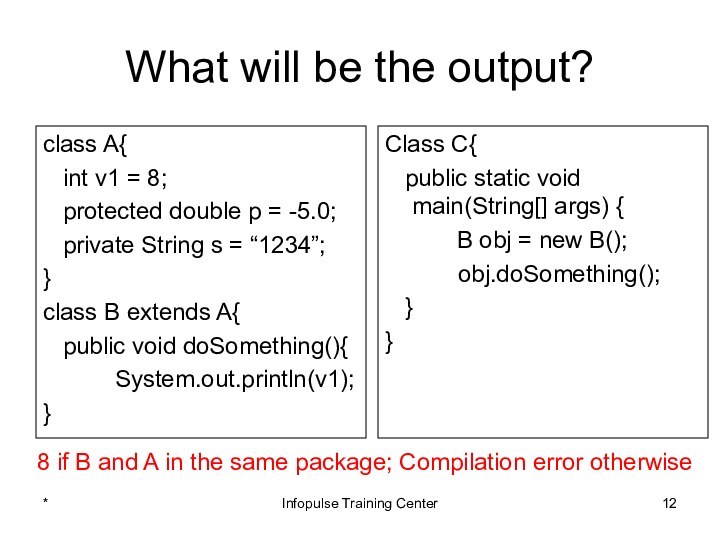
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
Compilation error
*
Infopulse Training Center
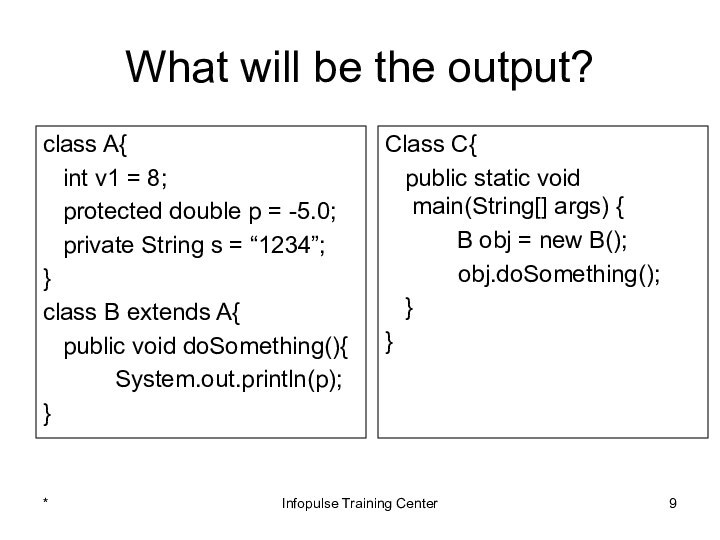
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
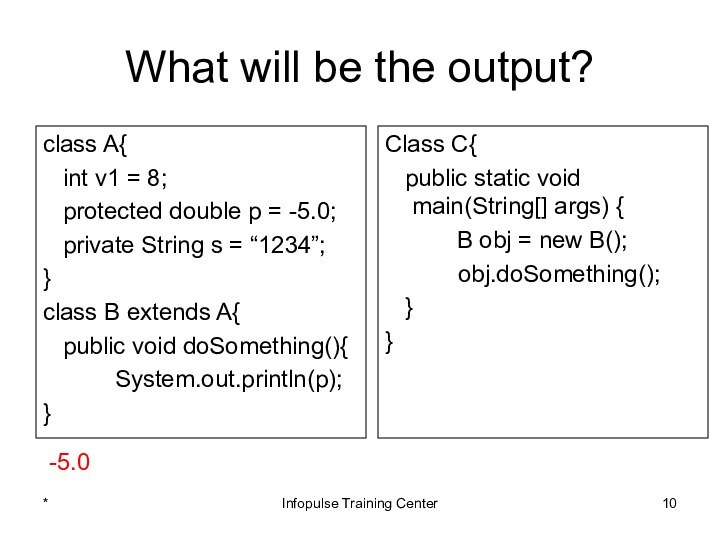
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
-5.0
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
8 if B and A in the same package; Compilation error otherwise
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
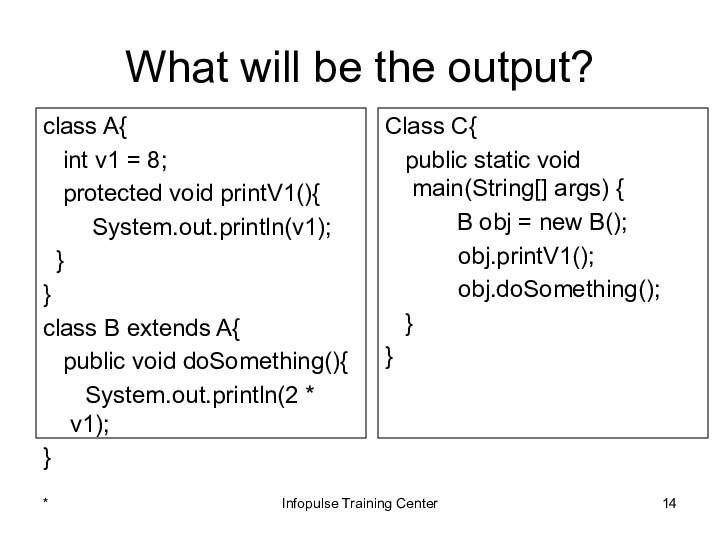
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
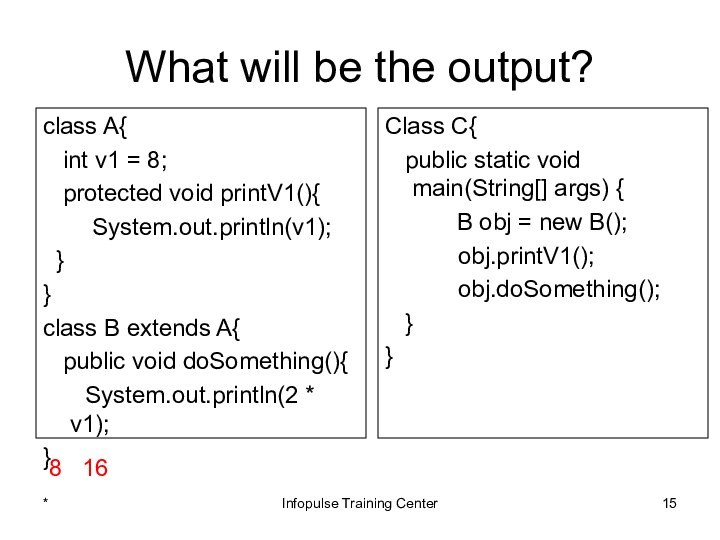
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
8 16
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
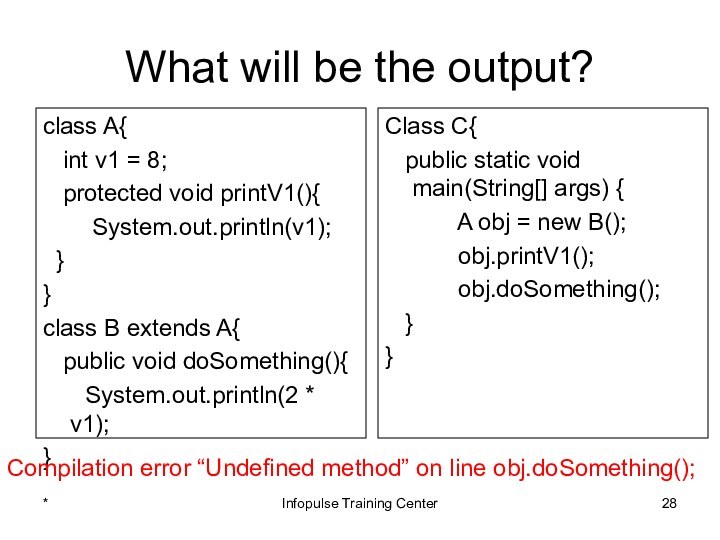
Compilation error “Undefined method” on line obj.doSomething();
*
Infopulse Training Center
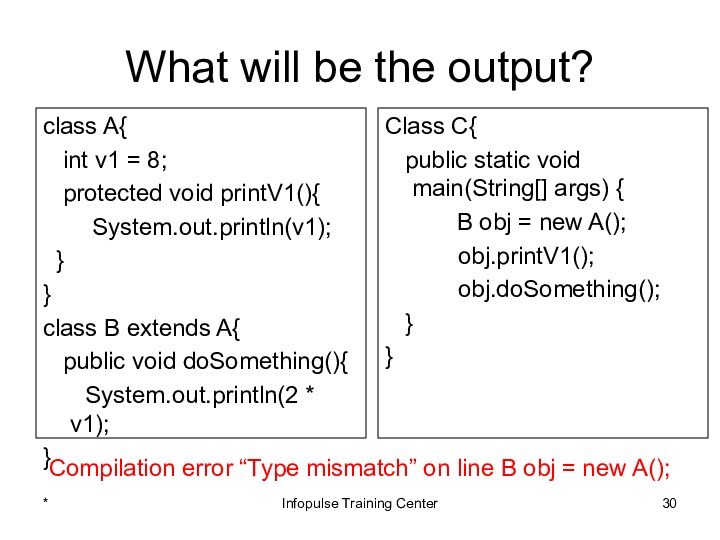
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new A();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new A();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
Compilation error “Type mismatch” on line B obj = new A();
*
Infopulse Training Center
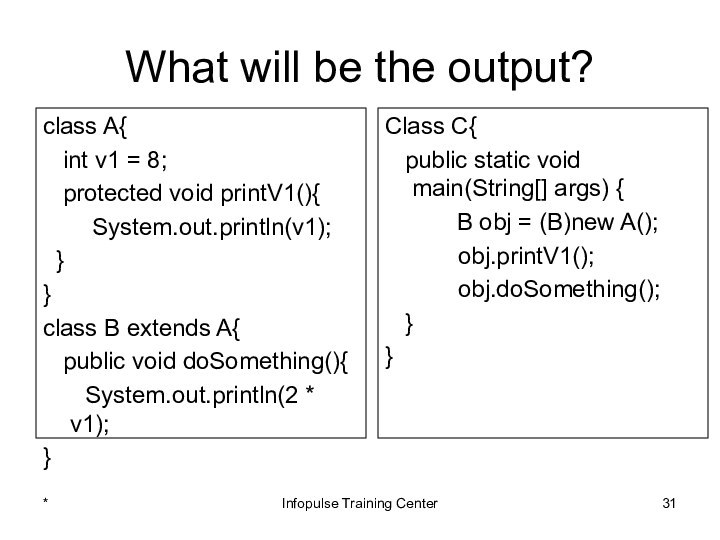
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = (B)new A();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
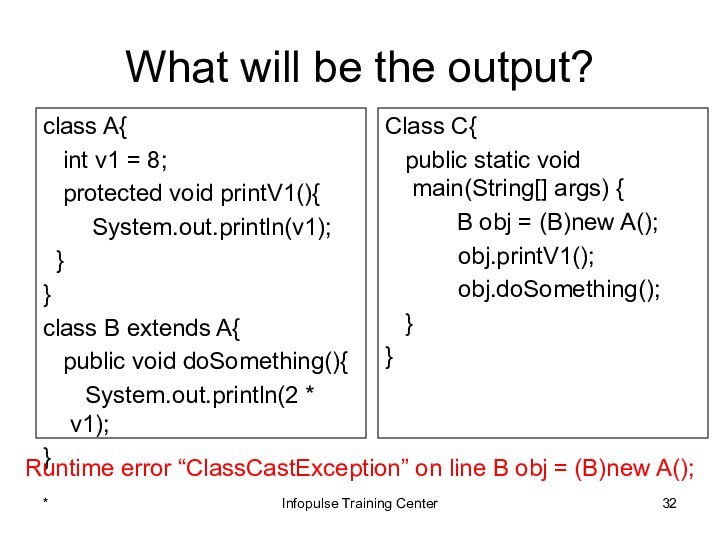
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = (B)new A();
obj.printV1();
obj.doSomething();
}
}
Runtime error “ClassCastException” on line B obj = (B)new A();
*
Infopulse Training Center
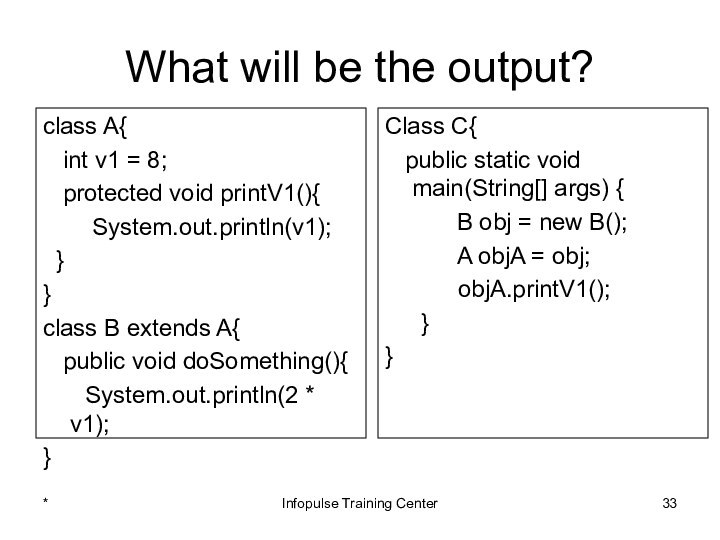
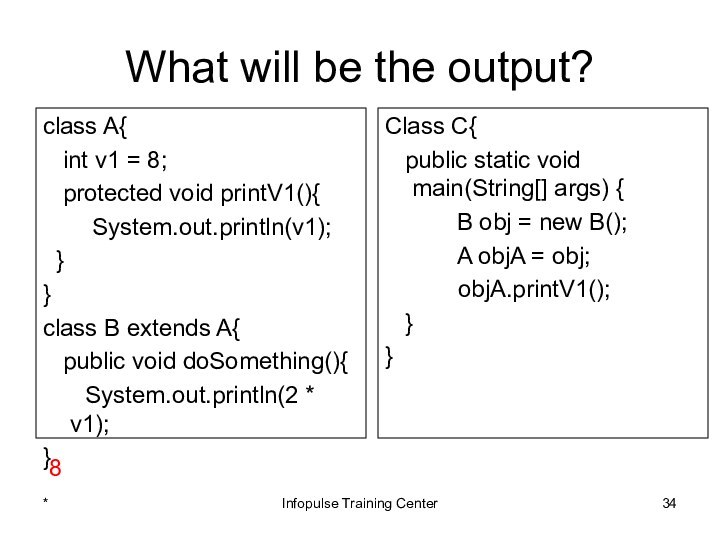
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
A objA = obj;
objA.printV1();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
A objA = obj;
objA.printV1();
}
}
8
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
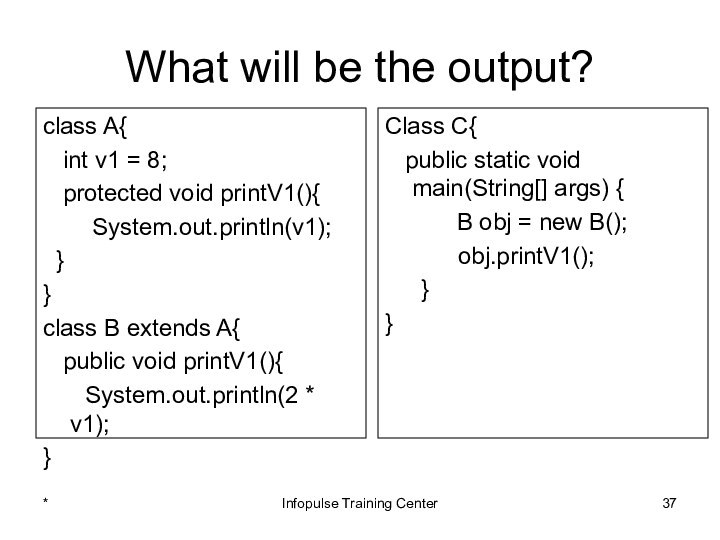
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
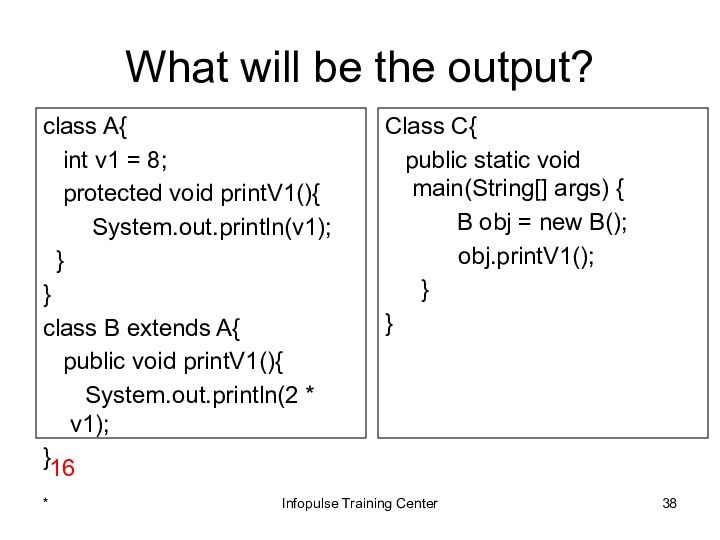
Class C{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B();
obj.printV1();
}
}
16
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center
*
Infopulse Training Center