Слайд 2
Denial-of-service
Denial of service (DoS) an action that prevents
or impairs the authorized use of networks, systems, or
applications by exhausting resources such as central processing units (CPU), memory, bandwidth, and disk space
Attacks (overload or invalid request services that consume significant resources)
network bandwidth
system resources
application resources
Have been an issue for some time (25% of respondents to an FBI survey)
Compromise System Availability
Слайд 3
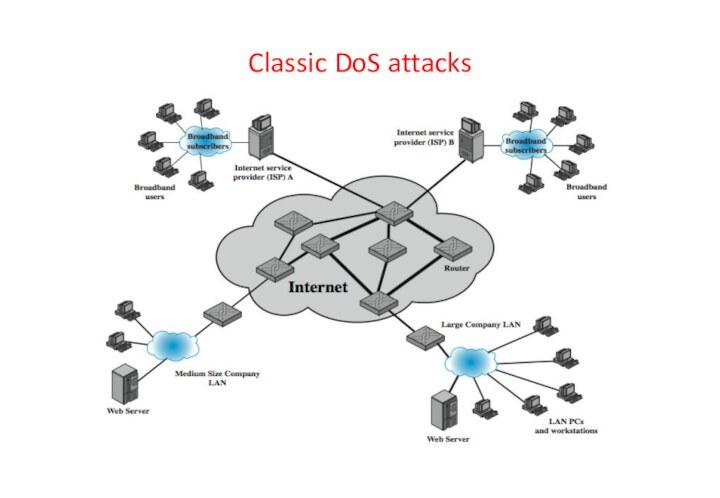
Classic DoS attacks
Flooding ping command
Aim of this attack
is to overwhelm the capacity of the network connection
to the target organization
Traffic can be handled by higher capacity links on the path, but packets are discarded as capacity decreases
Source of the attack is clearly identified unless a spoofed address is used
Network performance is noticeably affected
Слайд 5
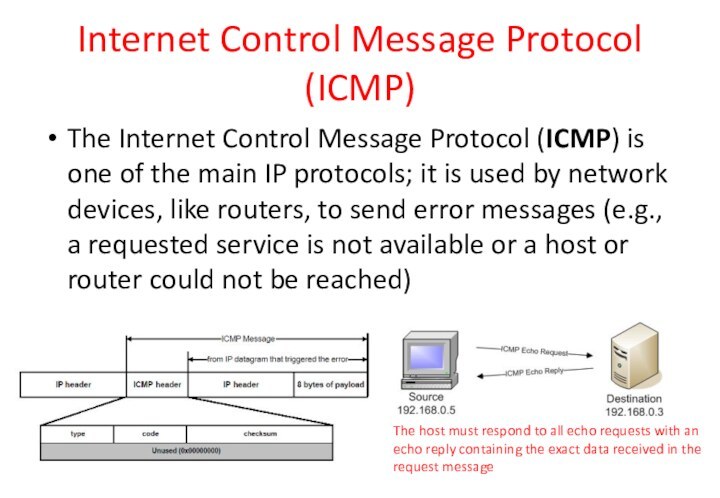
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
The Internet Control Message
Protocol (ICMP) is one of the main IP protocols;
it is used by network devices, like routers, to send error messages (e.g., a requested service is not available or a host or router could not be reached)
The host must respond to all echo requests with an
echo reply containing the exact data received in the
request message
Слайд 6
Source address spoofing
Use forged source addresses
Usually via the
raw socket interface on operating systems
Makes attacking systems harder
to identify
Attacker generates large volumes of packets that have the target system as the destination address
Congestion would result in the router connected to the final, lower capacity link
Backscatter traffic
Advertise routes to unused IP addresses to monitor attack traffic
Слайд 7
Backscatter traffic
Security researchers (Honeypot Project) advertise blocks of
unused IP addresses (no real/legit uses)
If ICMP/connection request is
made, this is most likely from attackers
Monitoring unused IP addresses provides valuable info on the type and scale of attack
Слайд 8
SYN spoofing
Common DoS attack
Attacks the ability of a
server to respond to future connection requests by overflowing
the tables used to manage them
Thus legitimate users are denied access to the server
Hence this is an attack on system resources, specifically the network handling code in the operating system
Слайд 9
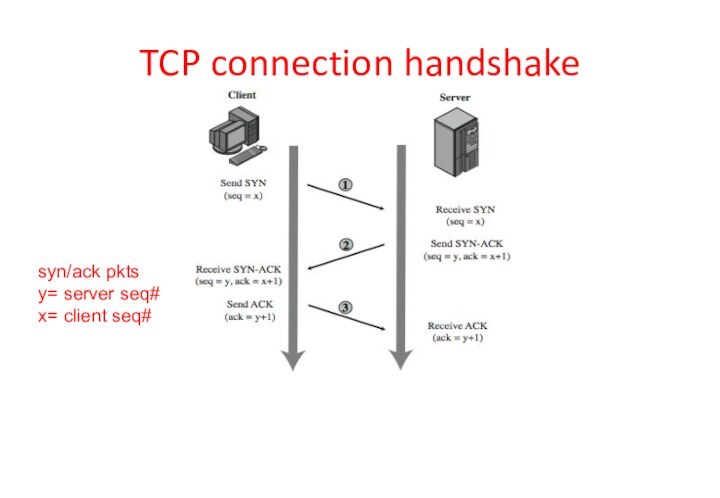
TCP connection handshake
syn/ack pkts
y= server seq#
x= client seq#
Слайд 10
SYN spoofing attack
assumption: most connections succeed and thus
table cleared quickly
Слайд 11
SYN spoofing attack: attacker’s source
Attacker often uses either
random
source addresses (addresses that may not exist)
or that of
an overloaded server (that may not send a RST)
to block return of (most) reset packets
Has much lower traffic volume
attacker can be on a much lower capacity link
Objective: uses addresses that will not respond to the SYN-ACK with a RST
Слайд 12
Types of flooding attacks
Classified according to the network
protocol used
Objective: to overload the network capacity on some
link to a server
Virtually any type of network packet can be used
ICMP Flood
Uses ICMP packets, eg ping (echo) request
Typically allowed through, some required
UDP Flood
Alternative uses UDP packets to random ports (even if no service is available, attacker achieves its goal)
TCP SYN Flood (SYN spoof vs SYN flood)
Sends TCP SYN (connection request) packets
Focuses on volume attack
Слайд 13
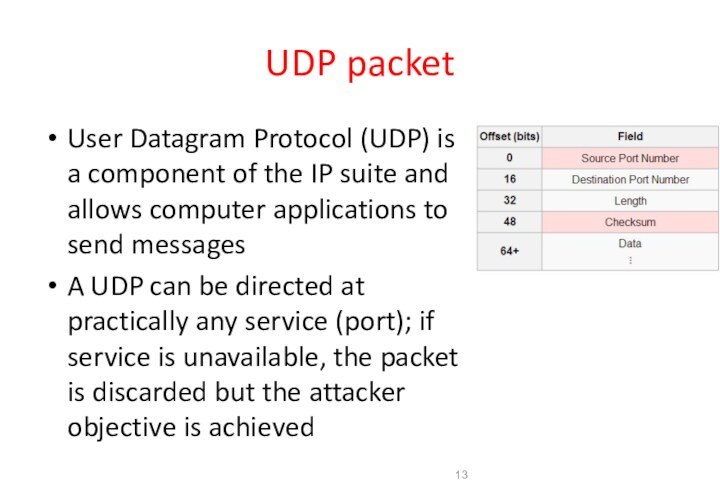
UDP packet
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a component
of the IP suite and allows computer applications to
send messages
A UDP can be directed at practically any service (port); if service is unavailable, the packet is discarded but the attacker objective is achieved
Слайд 14
Distributed DoS attacks
Have limited volume if single source
used
Multiple systems allow much higher traffic volumes to form
a distributed DoS (DDoS) attack
Often compromised PC’s/workstations
Zombies with backdoor programs installed
Forming a botnet
Example: Tribe Flood Network (TFN), TFN2K
did ICMP, SYN and UDP floods
Слайд 15
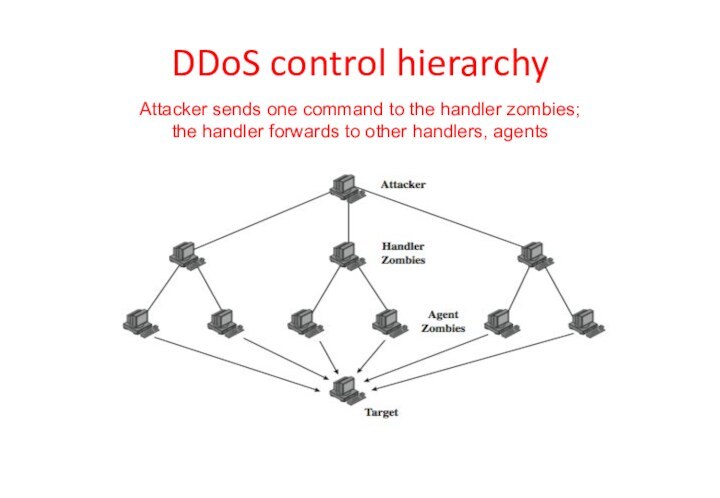
DDoS control hierarchy
Attacker sends one command to the
handler zombies;
the handler forwards to other handlers, agents
Слайд 16
Application-based bandwidth attacks
Force the victim system to execute
resource-consuming operations (e.g., searches, complex DB queries)
VoIP Session Initiation
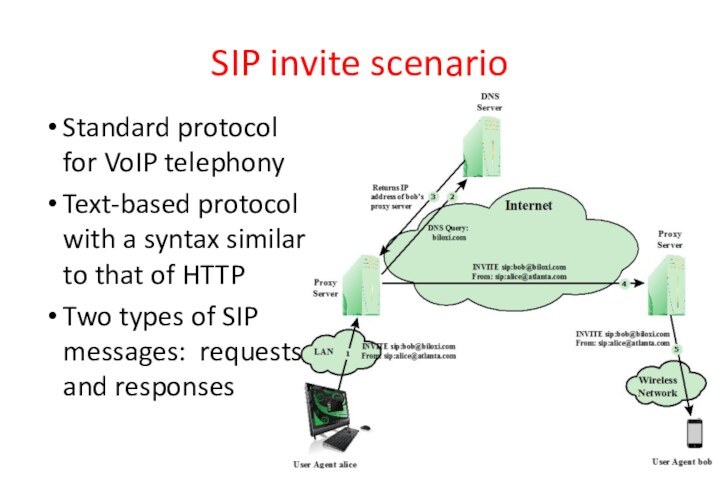
Protocol (SIP) flood (see Figure 7.5): attacker sends many INVITE requests; major burden on the proxies
server resources depleted while handling requests
bandwidth capacity is consumed
Слайд 17
SIP invite scenario
Standard protocol for VoIP telephony
Text-based protocol
with a syntax similar to that of HTTP
Two types
of SIP messages: requests and responses
Слайд 18
HTTP-based attacks
Slowloris: On each connection, it sends an
incomplete request that does not include the terminating newline
sequence. Existing intrusion detection and prevention solutions that rely on signatures to detect attacks will generally not recognize Slowloris
Attempts to monopolize by sending HTTP requests that never complete
Eventually consumes Web server’s connection capacity
Utilizes legitimate HTTP traffic
Spidering: Bots starting from a given HTTP link and following all links on the provided Web site in a recursive way
Слайд 19
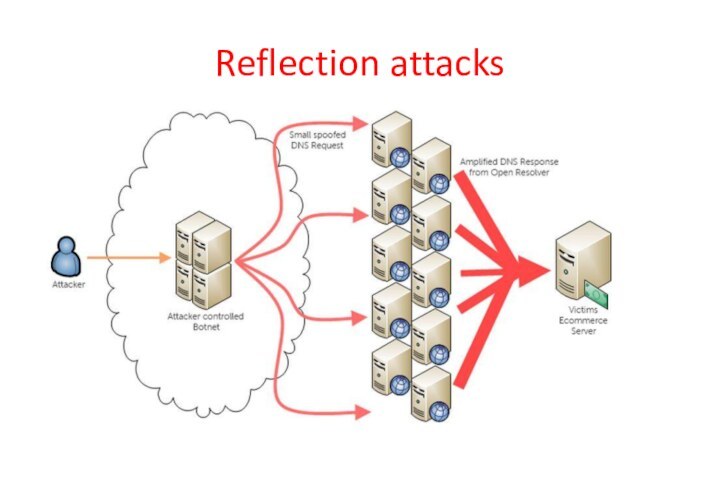
Reflection attacks
Attacker sends packets to a known service
on the intermediary with a “spoofed source address” of
the actual target system
When intermediary responds, the response is sent to the target
“Reflects” the attack off the intermediary (reflector)
Goal is to generate enough volumes of packets to flood the link to the target system without alerting the intermediary
The basic defense against these attacks is blocking spoofed-source packets
Слайд 21
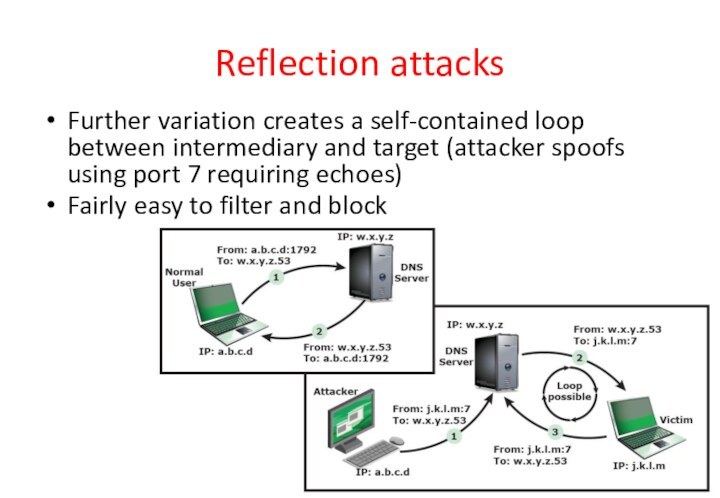
Reflection attacks
Further variation creates a self-contained loop between
intermediary and target (attacker spoofs using port 7 requiring
echoes)
Fairly easy to filter and block
Слайд 22
DNS amplification attacks
Use packets directed at a legitimate
DNS server as the intermediary system
Attacker creates a series
of DNS requests containing the spoofed source address of the target system
Exploit DNS behavior to convert a small request to a much larger response (amplification)
Target is flooded with responses
Basic defense against this attack is to prevent the use of spoofed source addresses
Слайд 23
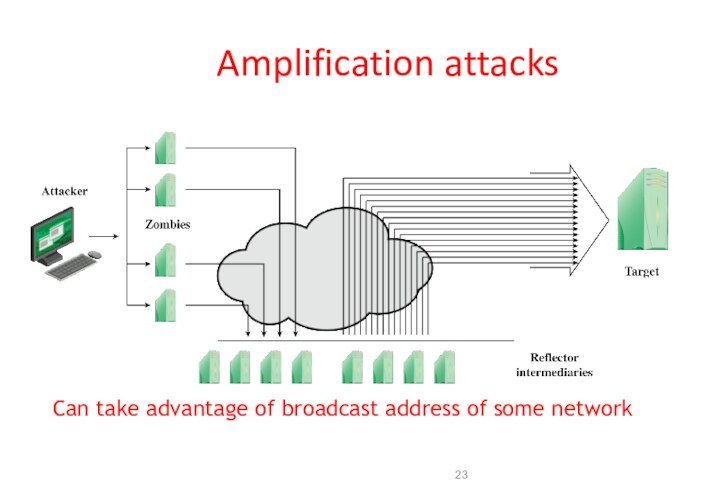
Amplification attacks
Can take advantage of broadcast address of
some network
Слайд 24
Four lines of defense against DDoS attacks
Attack prevention
and preemption (before attack)
Attack detection and filtering (during the
attack)
Attack source traceback and identification (during and after the attack)
Attack reaction (after the attack)
Слайд 25
DoS attack prevention
Block spoofed source addresses
On routers as
close to source as possible
Filters may be used to
ensure path back to the claimed source address is the one being used by the current packet
Filters must be applied to traffic before it leaves the ISP’s network or at the point of entry to their network
Use modified TCP connection handling code
Cryptographically encode critical information in a cookie that is sent as the server’s initial sequence number
Legitimate client responds with an ACK packet containing the incremented sequence number cookie
Drop an entry for an incomplete connection from the TCP connections table when it overflows
Слайд 26
Attack prevention
Rate controls in upstream distribution nets
On specific
packets types e.g. some ICMP, some UDP, TCP/SYN
Impose limits
Use
modified TCP connection handling
Server sends SYN cookies when table full (reconstruct table data from the cookie from legit clients)
Selective or random drop when table full
Слайд 27
Attack prevention
Block IP directed broadcasts
Block suspicious services and
combinations
Manage application attacks with a form of graphical puzzle
(captcha) to distinguish legitimate human requests
Use mirrored and replicated servers when high-performance and reliability is required
Слайд 28
Responding to attacks
Good incidence response plan
Details on how
to contact technical personal for ISP
Needed to impose
traffic filtering upstream
Details of how to respond to the attack
Implement anti-spoofing, directed broadcast, and rate limiting filters
Ideally have network monitors and IDS to detect and notify abnormal traffic patterns
Слайд 29
Responding to attacks
Identify type of attack
Capture and analyze
packets
Design filters to block attack traffic upstream
Or identify
and correct system/application bug
Have ISP trace packet flow back to source
May be difficult and time consuming
Necessary if planning legal action
Implement contingency plan
Switch to alternate backup servers
Commission new servers at a new site with new addresses
Update incident response plan