Слайд 2
What are the differences between ROM and RAM?
RAM (Random Access Memory)
and ROM (Read Only Memory) are both types of solid state memory, allowing quick access
to data and not being sensitive to being moved around while in use.
In both types of memory, individual electronic switches are arranged in blocks (usually of 8, making 1 byte of memory) and binary numbers are stored as a pattern of switch positions.
Слайд 3
The differences between Random Access memory (RAM) and Read Only
Memory (ROM) are summarised below:
RAM
The contents of RAM can be
altered so a computer can both read from and write to memory addresses in RAM.
RAM is described as volatile meaning that if the power is switched off or the battery removed then the contents will be lost.
ROM
The contents of ROM cannot be altered so a computer can only read from memory addresses in ROM.
ROM is described as non-volatile meaning that if the power is switched off or the battery removed then the contents are not lost.
Слайд 4
Why is ROM needed in a computer system?
ROM
is needed for devices where programs or data must
not be lost when the power is turned off or batteries are removed etc.
Embedded computers such as those in microprocessor
controlled devices use ROM to store the software to
control the hardware, as well as data such as
cooking/washing
timings etc.
The embedded computer in a modern microwave oven would have the program settings stored on a ROM chip
Слайд 5
A typical computer uses special ROM called the BIOS (Basic Input/OutputSystem)
which permanently stores the software needed to boot up the computer
(access computer hardware such as the hard drive and then load the operating system into RAM).
Слайд 6
Why is RAM needed in a computer system?
When
a personal computer is in use the following are
loaded into RAM from the backing storage:
The Operating System (OS)
All the other programs that are running
Any data files that are in use.
RAM is needed for this task because it would be far too slow for the CPU to directly access this data from the secondary storage.
New files that are created, or changes made to files while the computer system is in use, need to be saved before the computer is switched off. This is done by copying the data from RAM to the secondary storage.
Слайд 7
How does the amount of RAM in a
personal computer affect its performance?
A modern computer might have
between 1GB and 4GB or more of RAM installed and this is easily upgraded by adding more. If the amount of RAM is increased then a computer can run more programs simultaneously, or process larger files, without being slowed down by having to use virtual memory.
SUMMARY: The more RAM installed in a personal computer, the higher the performance.
Слайд 8
What is virtual memory and why is it
needed?
If a computer system does not have enough RAM
then there will be a limitation on the number of programs that can be running at one time, or the number of files that can be loaded and processed.
However, it is possible for the OS to copy blocks of data that are not being used by the CPU from RAM to secondary storage (typically the hard drive) and copy blocks of data that are needed by the CPU into the spare RAM that is then available.
Слайд 9
What is virtual memory and why is it
needed?
If this swapping of active and inactive blocks of
data between RAM and secondary storage is managed well then it will appear to the CPU that all the programs in use are running as if there was unlimited RAM available to them, hence the term virtual memory.
This solution is a very cheap but does have its limitations. Because the read/write speed of a hard drive is so much slower than RAM, continual swapping of inactive and active data blocks will cause a delay to the execution of programs. If a computer is very low on RAM and switching between many programs then it will slow down dramatically because too much time will be spent swapping blocks of data between real and virtual memory.
Слайд 10
What is virtual memory and why is it
needed?
The area of the hard disk that acts as
the virtual memory is called a page fileand the size can set using the OS. It is usually set to be around twice the size of the RAM.
SUMMARY: Virtual memory is memory that uses secondary storage to supplement RAM, but to the CPU it appears as if the whole program is loaded and running from RAM.
Слайд 11
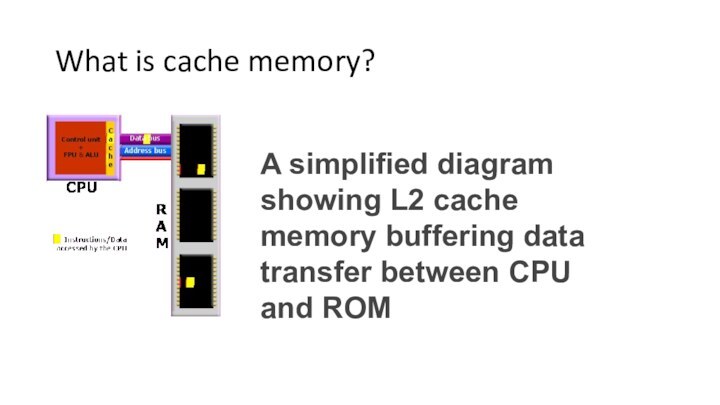
What is cache memory?
A simplified diagram showing L2
cache memory buffering data transfer between CPU and ROM
Слайд 12
What is cache memory?
Cache memory is a small
amount of very fast memory that is built into
the CPU. It acts like a buffer (a temporary store) between the CPU and RAM.
Rather than access instructions and data from RAM one at a time, whole blocks of instructions and data that are in use by the CPU are copied into the cache memory, along with the associated memory addresses.
Слайд 13
What is cache memory?
If the CPU needs to
access a memory address it first checks the cache
memory to see if there is a match. If there is then it access the contents of the cache version rather than the version stored in RAM.
When a block of data or instructions in cache memory is no longer being used by the CPU it is either deleted, or copied back to RAM if any changes have been made.
Many CPU designs have two levels of cache memory, the fastest (L1) is divided into a data cache and an instruction cache. The second (L2) cache is slightly slower and sits between the L1 cache and RAM. The L1 cache and L2 cache can be clearly seen on this enlarged labelled image of a CPU.
Слайд 14
What is cache memory?
Without cache memory the CPU
would waste clock cycles waiting while data and instructions
were exchanged with the much slower RAM.
Typical cache memory sizes range from 256KB to 4MB.
SUMMARY: Cache memory is very fast memory that is built into the CPU. The larger the cache size the less time the CPU has to spend accessing RAM so programs will execute faster.
Слайд 15
What is flash memory?
Flash memory is a special
type of RAM that, unlike
normal RAM, is non-volatile (it does
not need a power
supply to preserve the memory contents). Flash memory
cannot however replace RAM in a computer as the read/write speeds are too slow. Typical storage sizes range from 1GB to 16GB and higher.
Слайд 16
What is flash memory?
Examples of flash memory in
use:
Compact Flash™ and Secure Digital™ (SD) memory cards in
digital cameras.
Mini and Micro SD cards in Smartphones.
Memory cards in MP3 music players.
Memory cards for video game consoles.
USB memory sticks.
Solid state drives
SUMMARY: Flash memory combines the permanence of ROM with the flexibility of RAM, but not the speed.
Слайд 17
What are registers?
Registers are tiny but extremely fast
memory locations built into the CPU which are used
as temporary stores for instructions and data while instructions are being processed.
Слайд 18
Examples of registers:
The Accumulator, a register in which intermediate
arithmetic and logic results are stored as calculations (addition,
multiplication, shift, etc.) are carried out.
The Program Counter, a register that stores the address of the next instruction to be executed. After the instruction is completed it is either
incremented by the number of bits that make up an instruction, so the next sequential instruction can be accessed.
set to the memory location of a non-sequential instruction to allow programs to carry out iteration loops and conditional program execution rather than just stepping through the instructions in sequence.
The Current Instruction register which stores the instruction currently being executed.
Слайд 19
Purpose
Without such registers it would be necessary to
use cache memory or even RAM to store such
temporary data which would be impractically slow. A typical register size might be 32 or 64 bits.
Special single bit registers called flags are set to 0/1 to record true/false data, for example; if the result of a calculation is negative.
Слайд 20
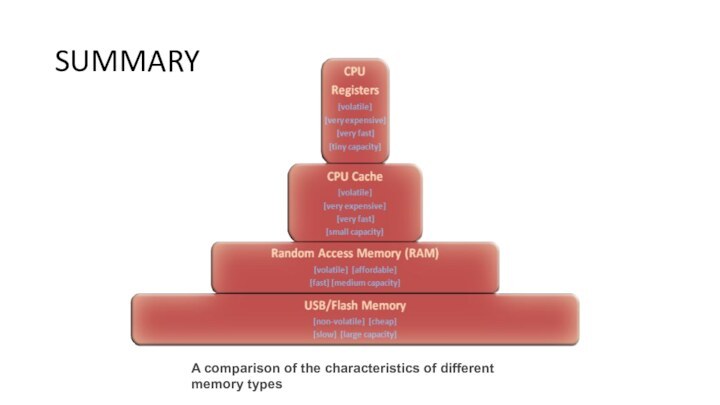
SUMMARY
A comparison of the characteristics of different memory
types
Слайд 21
How do changes in memory technologies lead to
changes in computer designs?
SUMMARY: Memory technology has developed significantly
over the years. Changes include:
Greater storage density; (the number of bits per chip has increased from almost 1 kilobit (Kb) to 2 gigabit (GB) per chip) meaning computer systems, in particular portable ones, can be much smaller.
Faster read/write times; allowing increases in the performance of computer systems, although these speed increases still lag behind the advances in processor speeds.