- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему к докладу Australian English 11 класс
Содержание
- 2. Australian English (AusE, AuE, AusEng, en-AU) is a major variety of
- 3. Most linguists (scientists who study language) split
- 4. Australian English is non-rhotic; in other words, the /r/ sound
- 5. Yod-coalescence is a process that changes the
- 6. t, d and s in the combinations
- 7. Intervocalic /nt/ in fast speech can be
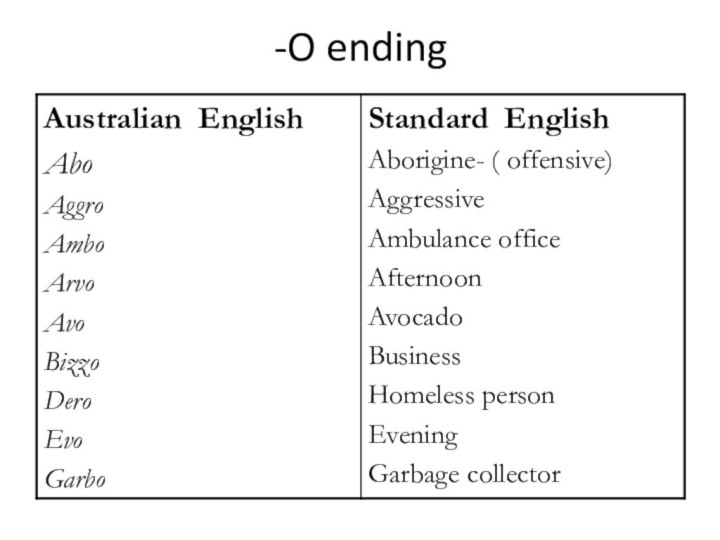
- 8. -O ending
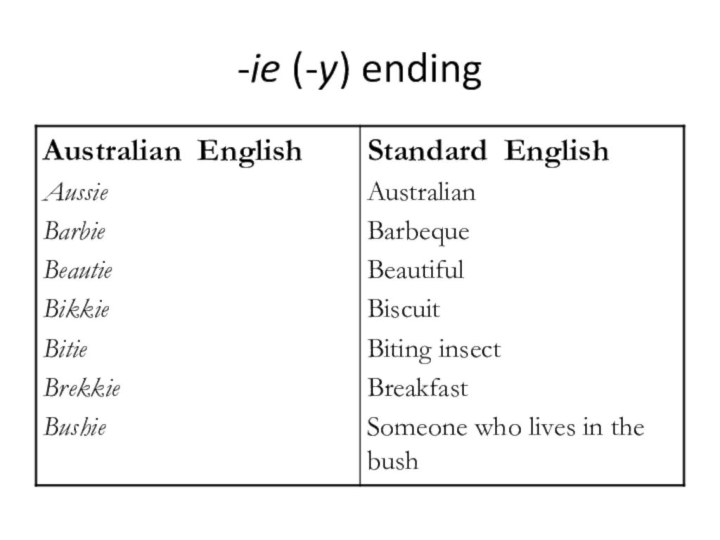
- 9. -ie (-y) ending
- 10. Some Australian English vowels sound different to
- 11. The famous Australian greeting, for example, is G'day!.
- 12. A few words have come from Australian Aboriginal languages.
- 13. Sometimes we do not know where a
- 14. Скачать презентацию
- 15. Похожие презентации
Australian English (AusE, AuE, AusEng, en-AU) is a major variety of theEnglish language and is used throughout AustraliaAustralian English is Australia's official language and is the first language of the majority of the population.




![Презентация к докладу Australian English 11 класс Yod-coalescence is a process that changes the clusters [dj], [tj], [sj] and](/img/tmb/6/555361/bcad691e19921e4b307ce05f9cbd044d-720x.jpg)

![Презентация к докладу Australian English 11 класс Intervocalic /nt/ in fast speech can be realised as [n]](/img/tmb/6/555361/3f6df23d09bbbf642071b4c8aeec8a52-720x.jpg)





Слайд 2 Australian English (AusE, AuE, AusEng, en-AU) is a major variety of theEnglish
language and is used throughout Australia
and is the first language of the majority of the population.Слайд 3 Most linguists (scientists who study language) split Australian
English up into three main kinds. These are Broad,
General, and Cultivated Australian English.Broad Australian English sounds very strongly Australian, when compared to other kinds of English.
General Australian English is the middle ground. It is used by most Australians, and can be heard in Australian-made films and television programs.
Cultivated Australian English is close to British English.
Слайд 4 Australian English is non-rhotic; in other words, the /r/ sound does
not appear at the end of a syllable or
immediately before a consonant. In Australian English the /r/ sound can only occur before a vowel. Many words which sound different in other accents sound the same in Australian English. Some examples are:caught and court
raw and roar
aunt and aren't
formally and formerly
But on the whole the consonants are approximately the same.
Слайд 5 Yod-coalescence is a process that changes the clusters
[dj], [tj], [sj] and [zj] into [dʒ], [tʃ], [ʃ]
and [ʒ] respectively:educate → /’ɛdʒu:keɪt/
nature → /’neɪtʃər/
measure → /’mɛʒər/
pressure → /’prɛʃər/
Yod-coalescence in stressed syllables occurs in Australian, Cockney, and New Zealand English resulting in :
dew → /’dʒu:/
tune → /’tʃu:n/
resume → /rə’ʒu:m/
assume → /ə’ʃu:m/
Слайд 6 t, d and s in the combinations tr,
dr and sr ( loan words only) have also
changed into /dʒ/, /ʃ/ and /tʃ/tree /tʃɹᵊi:/
draw /dʒɹɔː/
Sri Lanka /ʃɹi'læŋkə/.
Слайд 7 Intervocalic /nt/ in fast speech can be realised
as [n]
winter =
winnernineteen = nineen
ninety = niny
Say in Australian
1999!
Слайд 10 Some Australian English vowels sound different to vowels
of other kinds of English. For example, the vowel
in day starts with a very open mouth. This makes the Australian day sound close to the die of most British or American people. Days of the week, however, are often different and the day sounds like dee (usually short and sharp like the letter D).Sunday becomes Sun-dee
Monday - Mun-dee
Tuesday - Choose-dee
Wednesday - Wens-dee
Thursday - Thurs-dee
Friday - Fri-dee
Saturday - Satta-dee/Sadda-dee or even shorter Sat-dee/Sad-dee
Vowels in Australian English are more front, closer and diphthongized.
Слайд 11
The famous Australian greeting, for example, is G'day!.
A
native forest is called the bush and central Australia is called
the outback.Many words were brought to Australia from Britain and Ireland. For example, mate meaning "friend" which is still used in Britain.





























