- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему по английскому языку на тему Educational System in Britain
Содержание
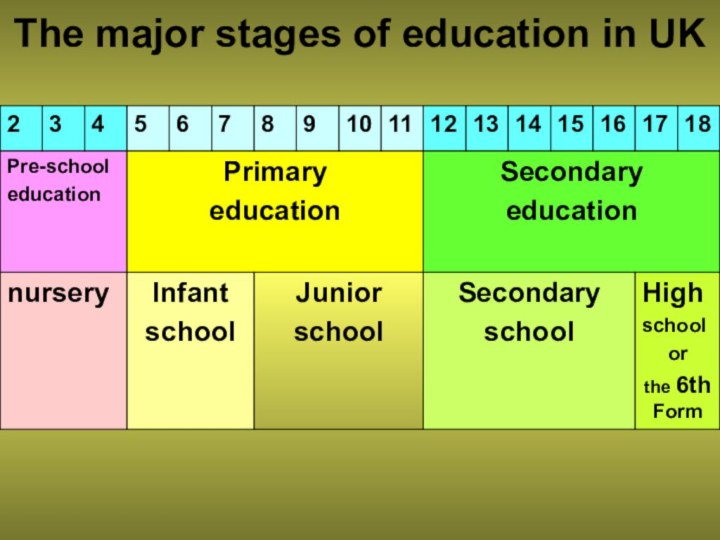
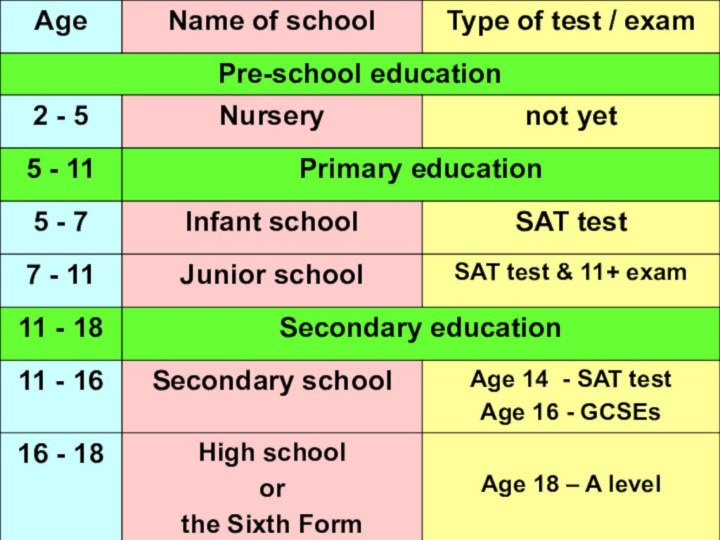
- 2. The main stages of education in BritainPre-school educationPRIMARY EDUCATIONSECONDARY EDUCATIONFURTHER EDUCATION
- 3. The major stages of education in UK
- 4. V O C A B U L
- 5. Many British children start school at the
- 6. Compulsory education begins at the age of 5, when children go to primary school.
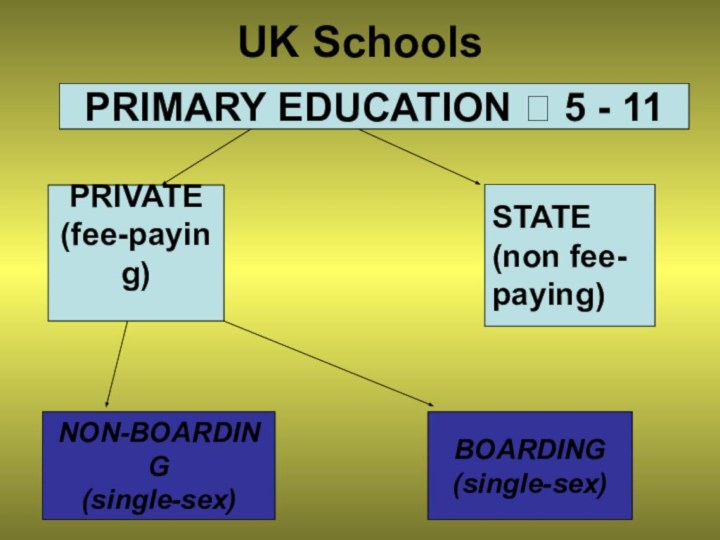
- 7. UK SchoolsPRIVATE(fee-paying)STATE(non fee-paying) PRIMARY EDUCATION ? 5 - 11NON-BOARDING(single-sex)BOARDING(single-sex)
- 8. P R I M A R Y
- 9. The usual age for transfer to secondary schools is eleven in England.
- 10. What are the main stages of education
- 11. V O C A B U L
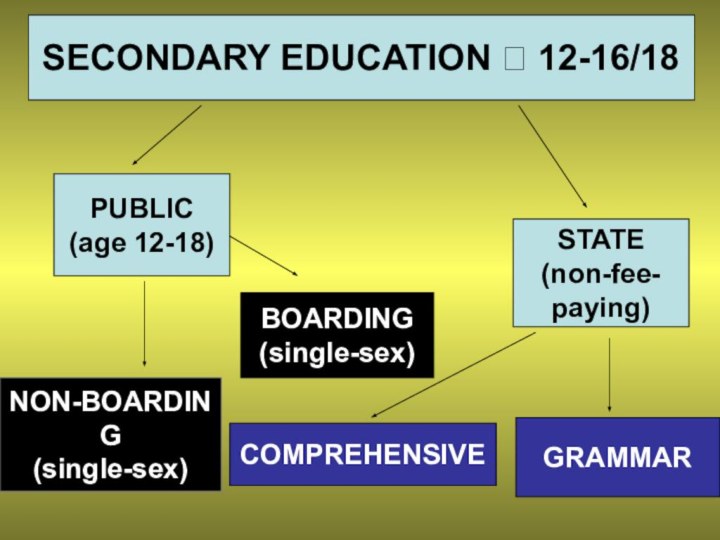
- 12. SECONDARY EDUCATION ? 12-16/18BOARDING (single-sex)STATE (non-fee-paying)NON-BOARDING(single-sex)COMPREHENSIVEGRAMMARPUBLIC (age 12-18)
- 13. STATE SCHOOL – is a non-fee-paying school
- 14. SECONDARY EDUCATION Children study compulsory (core)
- 15. SECONDARY EDUCATIONCompulsory education ends at 16.Some people
- 16. The most famous public schools in Britain
- 17. The major methods of teachingIn PRIMARY SCHOOL
- 18. When does secondary education start in Britain?What
- 19. PUBLIC EXAMS
- 21. SAT TESTSStandard Assessment Testtests that students in
- 22. 11+ (the eleven plus) examThe Eleven Plus
- 23. GCSE = General Certificate of Secondary
- 24. A Levels = Advanced LevelsHigher-level academic examsTaken
- 25. SCHOOL UNIFORMA lot of people think that
- 26. School tie – у англичан есть выражение
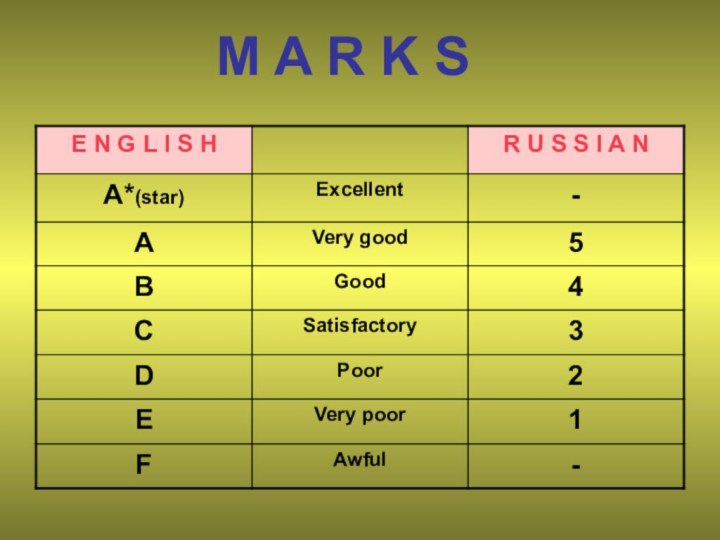
- 27. M A R K S EXELLENTVERY GOODSatisfactoryPoorVery poorAwfulGOOD
- 28. SCHOOL RULES
- 29. CHECK YOURSELF
- 30. CHECK YOURSELF1. Public school means thatThe
- 31. The organisation of a school year AUTUMN TERMCHRISTMASHOLIDAY(about 2weeks) SPRING TERMEASTERHOLIDAY(about 2weeks) SUMMER TERMSUMMERHOLIDAY(about 6weeks)
- 32. The organisation of a school dayA five-day
- 33. The School currently operates a seven day
- 34. Скачать презентацию
- 35. Похожие презентации
The main stages of education in BritainPre-school educationPRIMARY EDUCATIONSECONDARY EDUCATIONFURTHER EDUCATION





























Слайд 4 V O C A B U L A
R Y
compulsory – обязательный
free – бесплатный
fee – платный
infant –
подготовительныйjunior – младший
nursery – детский сад
primary – начальный
secondary - средний
private – частный
public - общественный
Public school – частная школа
State school – государственная школа
Boarding school – интернат
All-boys school – школа для мальчиков
Слайд 5 Many British children start school at the age
of 2 or 3 at a play school near
their house.These schools are nursery schools and they are not compulsory.
Children are taught to sing, draw, they play different creative games.
Pre-school education is often on a fee-paying basis.
Слайд 7
UK Schools
PRIVATE
(fee-paying)
STATE
(non fee-
paying)
PRIMARY EDUCATION ? 5 -
11
NON-BOARDING
(single-sex)
BOARDING
(single-sex)
Слайд 8 P R I M A R Y
E D U C A T I O N
All
children start primary school by the age of 5. Primary education lasts for six years.They attend the infant school from 5 to 7 and then junior school untill they are 11.
Some parents pay for their children to attend a private school but all children have the right to go to a state school which is free.
Private schools are called public schools.
Most of them are boarding schools.
More than 90% of British children attend state schools.
Слайд 10
What are the main stages of education in
Britain?
What age do British children start school?
How are these
schools called?Are they compulsory or optional?
What are the main stages of PRIMARY EDUCATION ?
What age does compulsory education begin?
What age does PRIMARY EDUCATION end?
What age do British children attend the infant school ?
What age do British children attend the junior school ?
What is usual age for transfer to secondary schools in England?
Слайд 11 V O C A B U L A
R Y
core – обязательный
subject - школьный предмет
courses - курсы
optional
– по выбору (факультативный)Science – предметы естественно-научного цикла
Arts –предметы гуманитарного цикла
fee-paying - платный
free-paying - бесплатный
Слайд 12
SECONDARY EDUCATION ? 12-16/18
BOARDING
(single-sex)
STATE
(non-fee-
paying)
NON-BOARDING
(single-sex)
COMPREHENSIVE
GRAMMAR
PUBLIC
(age 12-18)
Слайд 13 STATE SCHOOL – is a non-fee-paying school run
by the state
PUBLIC SCHOOL – is a long-established, with
long traditions, fee-paying school.PRIVATE/ INDEPENDENT SCHOOL – is a fee-paying school, sometimes connected with one religion
COMPREHENSIVE SCHOOL – is a state school where students of all abilities are taught together
BOARDING SCHOOL – is a school where the students live.
GRAMMAR SCHOOL – is a school for children of high academic abilities who have to pass an 11+ exam.
A SINGLE-SEX SCHOOL – is a school which is either for all boys or all girls.
Слайд 14
SECONDARY EDUCATION
Children study compulsory (core) subjects:
English,
Literature
Mathematics
IT (information technology)
Religious Education
and optional courses:
one foreign language
one science
subjectone art subject
History
Geography
PE (physical education)
Design and Technology
Слайд 15
SECONDARY EDUCATION
Compulsory education ends at 16.
Some people leave
secondary school and go to colleges for further education.
Some
choose to stay at secondary school for two years more and prepare for a university.At age sixteen pupils in England may transfer to sixth form colleges leading to A level
Слайд 16 The most famous public schools in Britain are
Eton, Harrow, Winchester.
A year at Eton costs 17,000 pounds.
It is very old, and a lot of important people used to be students there. It is an all-boys school.Prince William, the Queen’s grandson, went to Eton too.
IT'S INTERESTING
Слайд 17
The major methods of teaching
In PRIMARY SCHOOL
?
class teacher teaches all subjects
? At the ages of
7 and 11 – national tests in English, mathematics and scienceIn SECONDARY SCHOOL
? different teachers for different subjects
? regular homework
? students are separated into groups according to their abilities
Слайд 18
When does secondary education start in Britain?
What schools
are fee-paying in Britain?
What is the difference between PUBLIC
and PRIVATE/ INDEPENDENT schools?What schools are free-paying?
What are the main stages of SECONDARY EDUCATION ?
What is the difference between BOARDING and GRAMMAR schools?
How are all-boys or all-girls schools called?
What is BOARDING SCHOOL?
What courses are compulsory at secondary schools?
What courses are optional at secondary education?
What age do British children attend the secondary education?
What age do British children attend the high school?
Is High School compulsory or not in Britain?
Слайд 21
SAT TESTS
Standard Assessment Test
tests that students in schools
in Britain take at the ages of 7, 11,
and 14, to see whether they have reached the standard set by the National Curriculum.taken in all core subjects.
Слайд 22
11+ (the eleven plus) exam
The Eleven Plus is
an examination which is given to students in their
last year of primary education.The name derives from the age group of the students: 11+.
The exam came to be seen as determining whether a student went to a grammar schoolThe exam came to be seen as determining whether a student went to a grammar school or to a secondary modern (comprehensive).
Слайд 23
GCSE = General Certificate of Secondary Education
Courses are
taken in a variety of subjects
GCSEs are not compulsory
Taken
by 16-years-old in Britain in 5 subjects: 3 core (English, Maths and Science) and 2 additional (the Arts, French)Marks are given for each subject separately
System of marks is uniform ? A-G. A, B, C are regarded as “good” grades.
These examinations are taken by students of all levels of ability.
Слайд 24
A Levels = Advanced Levels
Higher-level academic exams
Taken mostly
by people around the age of 18 who wishes
to get higher educationTaken at least in 3 subjects
A-levels are graded from A to E, anything lower is unclassified (U)
A-level examinations, usually are not in more than 3 subjects. It is necessary to have A-levels in order to go to a university or other institutions of higher education
Слайд 25
SCHOOL UNIFORM
A lot of people think that school
uniforms in England are for the children from rich
families at the country’s best schools.But it isn’t always true. In fact, uniforms first came to schools for poor because they were cheaper.
Today a lot of British schools have uniforms. Usually they differ only in colours but include a blazer, a pullover, a shirt (a blouse), trousers (a skirt), tights or socks, shoes and boots, a scarf and gloves of a certain colour, a cap or a hat. School badge is on a cap and on a blazer’s pocket.
One of the most important elements of the uniform is a school tie.
Слайд 26 School tie – у англичан есть выражение ”To
be true to your school tie”- “Быть верным своему
школьному галстуку”.Это означает, что и через много лет выпускники сохраняют верность своим школьным друзьям и всегда готовы помочь им.Для выпускников престижных частных школ такой галстук является не только символом дружбы и взаимопомощи, но и пропуском в общество самых известных и влиятельных людей страны.
IT'S INTERESTING
Слайд 28
SCHOOL RULES
EVERY BRITISH SCHOOL HAS ITS RULES,
FOR EXAMPLE:Be polite
Say hello when you see a teacher
Come to school on time
Stand up when a teacher comes into the class
Wear your school uniform
Don’t eat or drink in the classroom
Don’t run in the corridors
Don’t bring mobile phones to class
Don’t talk to people in lessons
Слайд 30
CHECK YOURSELF
1. Public school means that
The school
is private
The school is for everybody
2. Boarding school means
thatStudents live there
There are only boys there
It is abroad
3. Eton is
A famous public school
A famous state school
4. Core courses are
Music, drama, home economics
English, Maths, IT.
Well done !
Read once more
Слайд 31
The organisation of a school year
AUTUMN
TERM
CHRISTMAS
HOLIDAY
(about
2
weeks)
SPRING
TERM
EASTER
HOLIDAY
(about 2
weeks)
SUMMER
TERM
SUMMER
HOLIDAY
(about 6
weeks)
Слайд 32
The organisation of a school day
A five-day week
Schools
are closed on Saturdays and Sundays
The day lasts from
9 a.m.- 3-5 p.m.Lunch break lasts about an hour-and-a-quarter
Слайд 33 The School currently operates a seven day cycle
(???) with a six period day, the timings of
which are as follows:ASSEMBLY 09:15 – 09:30
PERIOD 1 09:35 – 10:20
PERIOD 2 10:25 - 11:10
BREAK 11:10 – 11:30
PERIOD 3 11:30 – 12:15
PERIOD 4 12:20 – 13:05
LUNCH 13:05 – 14:10
PERIOD 5 14:15 – 15:00
PERIOD 6 15:05 – 15:45





























