- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Antonyms
Содержание
- 2. Antonyms are words belonging to the same
- 3. Antonymsabsolute or root antonyms (late - early)derivational
- 4. 1. Negative prefixes (un-; dis-; non-) form
- 5. The antonym of the adjective with the
- 6. The difference between derivational and root antonyms
- 7. Leonard Lipka in the book Outline of
- 8. Complementarity In his classification he describes complementarity
- 9. AntonymsIt's distinguished from complementarity by being based
- 10. ConversenessConverseness is mirror-image relations or functions:e.g. husband
- 11. L.Lipka also points out non-binary contrast or
- 12. Not every word in language can have
- 13. If a word is polysemantic, it can
- 14. Скачать презентацию
- 15. Похожие презентации
Antonyms are words belonging to the same part of speech, identical in style, expressing contrary of contradictory notions.












Слайд 3
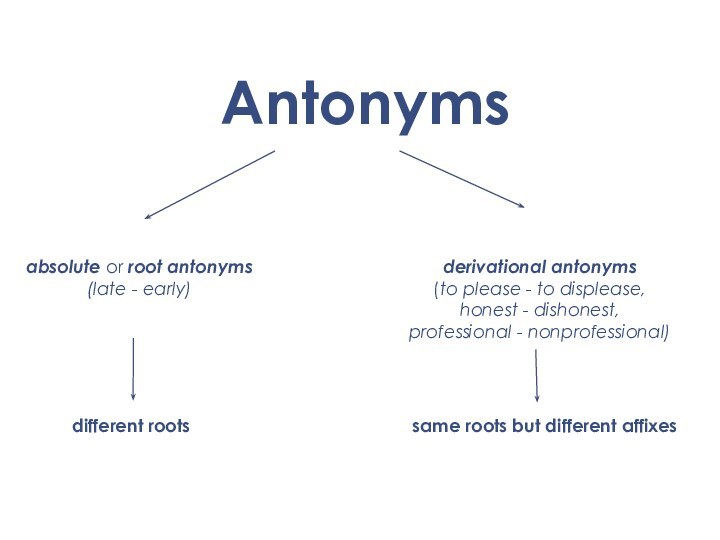
Antonyms
absolute or root antonyms
(late - early)
derivational antonyms
(to please - to displease,
honest - dishonest,
professional
- nonprofessional)different roots
same roots but different affixes
Слайд 4
1. Negative prefixes (un-; dis-; non-) form antonyms:
Un-: untrue
Dis-: dislike
Non-: nonreactive
2. Sometimes they are formed
by means of antonymous suffixes -ful and -less -ful: painful
-less: painless
Слайд 5 The antonym of the adjective with the suffix
-ful is formed by means of the prefix un-:
successful
– unsuccessfulThe antonym of the adjective with the suffix -less is formed with the help of the suffix –ish:
selfless - selfish
The same is true about antonyms with negative prefixes
e.g. to man is not an antonym of the word to unman;
to disappoint is not an antonym of the word to appoint.
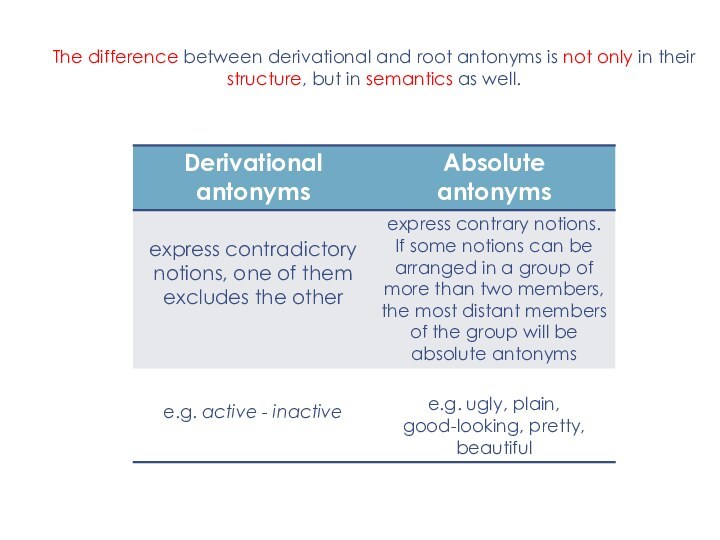
Слайд 6 The difference between derivational and root antonyms is
not only in their structure, but in semantics as
well.Слайд 7 Leonard Lipka in the book Outline of English
Lexicology describes different types of oppositeness, and subdivides them
into three types:complementarity, e.g. male - female, married – single;
antonyms, e.g. good – bad
converseness, e.g. to buy - to sell.
Слайд 8
Complementarity
In his classification he describes complementarity in
the following way: the denial of the one implies
the assertion of the other, and vice versa.John is not married = John is single
The type of oppositeness is based on yes/no decision. Incompatibility only concerns pairs of lexical units.
Слайд 9
Antonyms
It's distinguished from complementarity by being based on
different logical relationships. The assertion containing one member implies
the negation of the other, but not vice versa.John is good = John is not bad
John is not good ≠ John is bad
The negation of one term doesn't necessarily implies the assertion of the other.
An important linguistic difference from complementaries is that antonyms are always fully gradable, e.g. hot, warm, tepid, cold.
Слайд 10
Converseness
Converseness is mirror-image relations or functions:
e.g. husband –
wife, pupil - teacher, precede - follow, above -
below,before - after etc.
Jonh bought the car from Bill = Bill sold the car to John
2.. Also in the comparative form:
Y is smaller than X = X is larger than Y.
Слайд 11 L.Lipka also points out non-binary contrast or many-member
lexical sets. Here he points out serially ordered sets,
such asscales (hot, warm, tepid, cold, cool);
colour words (black, grey, white);
military ranks (marshal, general, colonel, major, captain etc.)
gradable examination marks (excellent, good ,average, fair, poor)
In such sets of words we can have outer and inner pairs of antonyms.
He also points out cycles, such as units of tie:
( spring, summer, autumn, winter)
In this case there are no outermost members.
Слайд 12 Not every word in language can have antonyms.
This type of opposition can be met in qualitative
adjective and their derivativese.g. beautiful - ugly,
to beautify - to uglify,
beauty – ugliness
It can be also met in words denoting feelings and states
e.g. respect - scorn, to live - to die,
to respect- to scorn, alive - dead,
respectful – scornful life - death
Itcan be also met among words denoting direction in space and time
e.g. here - there, up - down,
now - never, before - after
day - night, early - late etc.





























