Слайд 2
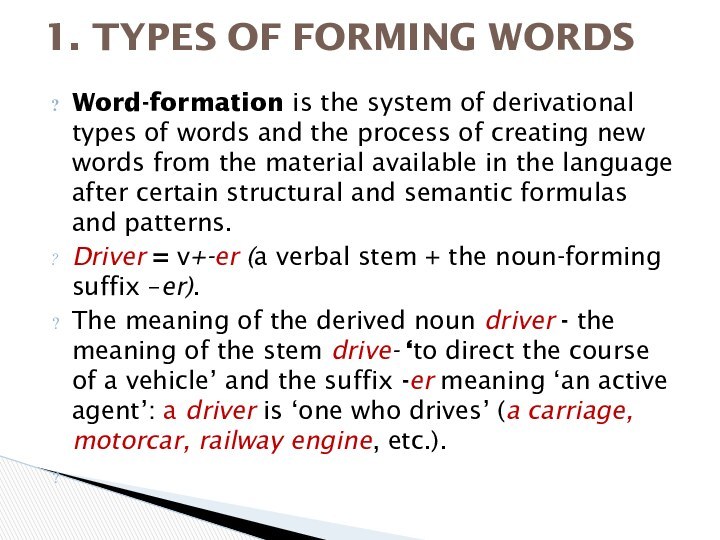
Word-formation is the system of derivational types of
words and the process of creating new words from
the material available in the language after certain structural and semantic formulas and patterns.
Driver = v+-er (a verbal stem + the noun-forming suffix –er).
The meaning of the derived noun driver - the meaning of the stem drive- ‘to direct the course of a vehicle’ and the suffix -er meaning ‘an active agent’: a driver is ‘one who drives’ (a carriage, motorcar, railway engine, etc.).
1. TYPES OF FORMING WORDS
Слайд 3
I. Word-derivation in morphology is a word-formation process
by which a new word is built from a
stem with the addition of an affix that changes the word class and / or basic meaning of the word.
The basic ways of forming words in word-derivation are:
1. Affixation is the formation of a new word with the help of affixes: pointless (from point).
2. Conversion is the formation of a new word by bringing a stem of this word into a different formal paradigm: a fall (from to fall), a cut (from to cut).
II. Word-composition is the formation of a new word by combining two or more stems which occur in the language as free forms: door-bell, house-keeper.
1.1. Main Types of Forming Words
Слайд 4
shortening is the formation of a word by
cutting off a part of the word.
a) initial
(or aphesis):fend (v) < defend, phone < telephone;
b) medial (orsyncope): specs < spectacles, fancy < fantasy;
c) final (or apocope): lab – laboratory, exam – examination;
d) both initial and final: flu < influenza, fridge < refrigerator;.
1.2. Minor Types of Forming Words
Слайд 5
blending is the formation of a new word
by combining parts of two words:
a) additive type:
smog – sm(oke) and (f)og; b) restrictive type: telecast – television + broadcast.
acronymy (or graphical abbreviation) is the formation of a word from the initial letters of a word combination. :
a) acronyms which are read as ordinary English words:UNESCO – [ju:'neskəu] the United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization;
b) acronyms with the alphabetic reading: BBC – [,bi:bi:'si:] the British Broadcasting Corporation;
Слайд 6
sound-interchange is the formation of a word due
to an alteration in the phonetic composition of its
root. Sound-interchange falls into 3 groups:
a) vowel-interchange (or ablaut): full − to fill, blood − to bleed, food – to feed. In some cases vowel-interchange is combined with suffixation: long − length, strong − strength, broad − breadth;
b) consonant-interchange: advice – to advise.
c) combined forms: life – to live;
Particular cases of sound-interchange:
[k] — [t∫]: to speak — speech,
[s] — [d]: defence — to defend; offence — to offend;
[s] — [t]: evidence — evident, importance — important, etc.
Слайд 7
sound imitation (or onomatopoeia) is the naming of
an action or a thing by a more or
less exact reproduction of the sound associated with it, cf.: cock-a-doodle-do (English) – ку-ка-ре-ку (Russian).
Groups:
a) words denoting sounds produced by human being in the process of communication or expressing their feelings: mumble, babble;
b) words denoting sounds produced by animals, birds, insects: mew, croak, buzz;
c) words imitation the sound of water, the noise of metallic things, a forceful motion, movement: splash, clink, bang.
Слайд 8
back-formation is the formation of a new word
by subtracting a real or supposed suffix from the
existing words. The process is based on analogy: the word to butle ‘to act or serve as a butler’ is derived by subtraction of –er from a supposedly verbal stem in the noun butler;
distinctive stress is the formation of a new word by means of the shift of the stress in the source word, cf.: export (n) — to ex´port; ´import (n) — to im´port; ‘
Слайд 9
is that branch of Lexicology which studies the
derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on
which the English language, builds new words.
Word-formation can deal only with words which are analysable both structurally and semantically, i.e. with all types of Complexes.
2. Word-formation as the Subject of Study
Слайд 10
Synchronically – investigation of the existing system of
the types of word-formation. The derived word is regarded
as having a more complex structure than its correlated word regardless of the fact whether it was derived from a simpler base or a more complex base;
Diachronically – chronological order of formation of one word from some other word that is relevant.
Word-formation may be studied:
Слайд 11
In the history of the English language there
are cases when a word structurally more complex served
as the original element from which a simpler word was derived =>
back-formation (or back-derivation) :
cf. beggar — to beg; editor — to edit; chauffeur — to chauff
The fact that historically the verbs
to beg, to edit, etc. were derived from the corresponding agent-nouns is of no synchronous relevance.
Слайд 12
Affixation is the formation of words by adding
derivational affixes to different types of bases.
An affix
is not-root or a bound morpheme that modifies the meaning and / or syntactic category of the stem in some way.
Affixes are classified into prefixes and suffixes.
3. AFFIXATION
Слайд 13
Zero - degree of derivation is ascribed to
simple words, i.e. words whose stem is homonymous with
a word-form and often with a root-morpheme, e.g. atom, haste, devote, anxious, horror, etc.
First - derived words whose bases are built on simple stems and thus are formed by the application of one derivational affix, e.g. atomic, hasty, devotion, etc.
Second - derived words formed by two consecutive stages of coining, e.g. atomical, hastily, devotional, etc.
Degrees of Derivation
Слайд 14
Distinction is naturally made between prefixal and suffixal
derivatives according to the last stage of derivation, which
determines the nature of the ICs of the pattern that signals the relationship of the derived word with its motivating source unit, cf.
unjust (un-+just),
justify, (just++ -ify),
arrangement (arrange + -ment),
non-smoker (non- + smoker).
Affixation=suffixation+prefixation
Слайд 15
Affixation is subdivided into suffixation and prefixation.
Distinction
is naturally made between prefixal and suffixal derivatives according
to the last stage of derivation, which determines the nature of the ICs of the pattern that signals the relationship of the derived word with its motivating source unit, cf.
unjust (un-+just),
justify, (just++ -ify),
arrangement (arrange + -ment),
non-smoker (non- + smoker).
Слайд 16
reappearance, unreasonable, denationalise
This qualification is relevant only in
terms of the constituent morphemes such words are made
up of, i.e. from the angle of morphemic analysis.
From the point of view of derivational analysis such words are mostly either suffixal or prefixal derivatives, e.g.
sub-atomic = sub- + (atom + + -ic), unreasonable = un- + (reason + -able), denationalise = de- + + (national + -ize), discouragement = (dis- + courage) + -ment.
Prefixal-suffixal derivatives:
Слайд 17
Suffixation is mostly characteristic of noun and adjective
formation.
Prefixation is mostly typical of verb formation.
The distinction also
rests on the role different types of meaning play in the semantic structure of the suffix and the prefix.
The part-of-speech meaning has a much greater significance in suffixes as compared to prefixes which possess it in a lesser degree.
A prefix may be confined to one part of speech, e.g. enslave, encage, unbutton or may function in more than one part of speech as, e.g., over- in overkind a, to overfeed v, overestimation n
Слайд 18
Suffixes as a rule function in any one
part of speech often forming a derived stem of
a different part of speech as compared with that of the base, e.g. careless a — cf. care n; suitable a — cf. suit v, etc.
A suffix closely knit together with a base forms a fusion retaining less of its independence than a prefix which is as a general rule more independent semantically, cf. reading — ‘the act of one who reads’; ‘ability to read’; and to re-read — ‘to read again.'
Слайд 19
Suffixation is the formation of words with the
help of suffixes, which usually modify the lexical meaning
of the base and transfer words to a different part of speech.
Some suffixes do not shift words from one part of speech into another, but usually transfer a word into a different semantic group, e.g. a concrete noun becomes an abstract one, e.g. child — childhood, friend — friendship, etc.
A suffix is a derivational morpheme following the root and forming a new derivative in a different word class (-en, -y, -less in heart-en, heart-y, heart-less).
3.1. SUFFIXATION.
CLASSIFICATION OF SUFFIXES
Слайд 20
According to the lexical-grammatical character of the base
suffixes are usually added to, they may be:
deverbal suffixex
(those added to the verbal base): -er (builder); -ing (writing);
denominal suffixes (those added to the nominal base): -less (timeless); -ful (hopeful); -ist (scientist); -some (troublesome);
deajectival suffixes (those added to the adjectival base): -en (widen); -ly (friendly); -ish (whitish); -ness (brightness).
Suffixes can be classified into different types in accordance with different principles:
Слайд 21
According to the part of speech formed suffixes
fall into several groups:
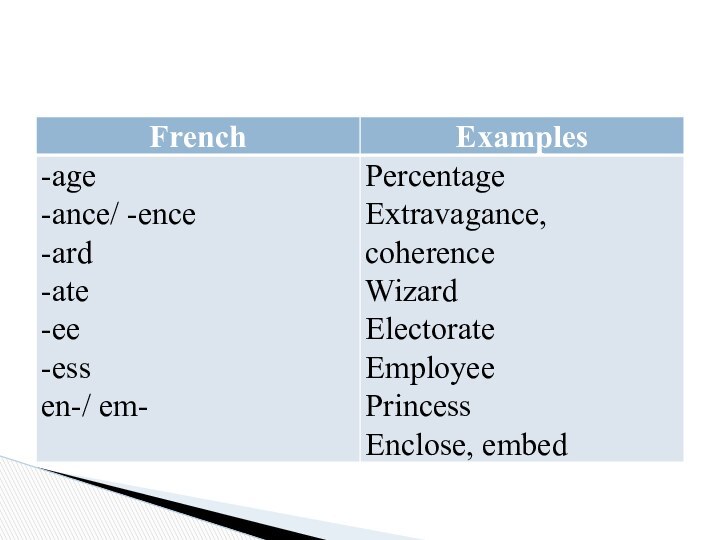
noun-forming suffixes: -age (breakage, bondage); -ance/-ence
(assistance, reference); -dom (freedom, kingdom); -er (teacher, baker); -ess (actress, hostess); -ing (building, wasing);
adjective-forming suffixes: -able/-ible/-uble (favourable, incredible, soluble); -al (formal, official); -ic (dynamic); -ant/-ent (repentant, dependent);
numeral-forming suffixes: -fold (twofold); -teen (fourteen); -th (sixth); -ty (thirty);
verb-forming suffixes: -ate (activate); -er (glimmer); -fy/-ify (terrify, specify); -ize (minimize); -ish (establish);
adverb-forming suffixes: -ly (quickly, coldly); -ward/-wards (backward, northwards); -wise (likewise).
Слайд 22
Semantically suffixes fall into:
Monosemantic:the suffix -ess has only
one meaning ‘female’ – tigress, tailoress;
Polysemantic: the suffix -hood
has two meanings:
‘condition or quality’ – falsehood, womanhood;
‘collection or group’ – brotherhood.
Слайд 23
According to their generalizing denotational meaning suffixes may
fall into several groups. E.g., noun-suffixes fall into those
denoting:
the agent of the action: -er (baker); -ant (accountant);
appurtenance: -an/-ian (Victorian, Russian); -ese (Chinese);
collectivity: -dom (officialdom); -ry (pleasantry);
Diminutiveness:-ie (birdie); -let (cloudlet); -ling (wolfling).
Слайд 24
According to their stylistic reference suffixes may be
classified into:
those characterized by neutral stylistic reference: -able (agreeable);
-er (writer); -ing (meeting);
those having a certain stylistic value: -oid (asteroid); -tron (cyclotron).
These suffixes occur usually in terms and are bookish.
Слайд 25
Prefixation is the formation of words with the
help of prefixes, which are derivational morphemes, affixed before
the derivational base.
A prefix is a derivational morpheme preceding the root-morpheme and modifying its meaning (understand – mis-understand, correct – in-correct).
3.2. PREFIXATION.
CLASSIFICATION OF PREFIXES.
Слайд 26
According to the lexico-grammatical character of the base
prefixes are usually added to, they may be:
deverbal (those
added to the verbal base): re- (rewrite); over- (overdo); out- (outstay);
denominal (those added to the nominal base): - (unbutton); de- (detrain); ex- (ex-president);
deadjectival (those added to the adjectival base): un- (uneasy); bi- (biannual).
deadverbial (those added to the adverbial base): un- (unfortunately); in- independently).
Prefixes can be classified according to different principles.
Слайд 27
According to the class of words they preferably
form prefixes are divided into:
verb-forming prefixes: en-/em- (enclose, embed);
be- (befriend); de- (dethrone);
noun-forming prefixes: non- (non-smoker); sub- (sub-committee); ex- (ex-husband)
adjective-forming prefixes: un- (unfair); il- (illiterate); ir- (irregular);
adverb-forming prefixes: un- (unfortunately); up- (uphill).
Слайд 28
Semantically prefixes fall into:
Monosemantic: the prefix ex- has
only one meaning ‘former’ – ex-boxer;
Polysemantic; the prefix dis-
has four meanings:
‘not’ (disadvantage);
‘reversal or absence of an action or state’ (diseconomy, disaffirm);
‘removal of’ (to disbranch);
‘completeness or intensification of an unpleasant action’ (disgruntled).
Слайд 29
According to their generalizing denotational meaning prefixes fall
into:
negative prefixes: un- (ungrateful); non- (non-political); in- (incorrect); dis-
(disloyal); a- (amoral);
reversative prefixes: un2- (untie); de- (decentralize); dis2- (disconnect);
pejorative prefixes: mis- (mispronounce); mal- (maltreat); pseudo- (pseudo-scientific);
prefixes of time and order: fore- (foretell); pre- (pre-war); post- (post-war), ex- (ex-president);
prefix of repetition: re- (rebuild, rewrite);
locative prefixes: super- (superstructure), sub- (subway), inter- (inter-continental), trans- (transatlantic).
Слайд 30
According to their stylistic reference prefixes fall into:
those
characterized by neutral stylistic reference: over- (oversee); under- (underestimate);
un-(unknown);
those possessing quite a definite stylistic value: pseudo- (pseudo-classical); super- (superstructure); ultra- (ultraviolet); uni- (unilateral); bi- (bifocal).
These prefixes are of a literary-bookish character.
Слайд 31
The word-forming activity of affixes may change in
the course of time. This raises the question of
productivity of derivational affixes, i.e. the ability of being used to form new, occasional or potential words, which can be readily understood by the language-speakers.
Thus, productive affixes are those used to form new words in this particular period of language development.
4. PRODUCTIVE AND NON-PRODUCTIVE AFFIXES
Слайд 34
The productivity of an affix should not be
confused with its frequency of occurrence that is understood
as the existence in the vocabulary of a great number of words containing the affix in question.
An affix may occur in hundreds of words, but if it is not used to form new words, it is not productive, for instance, the adjective suffix –ful.
Слайд 35
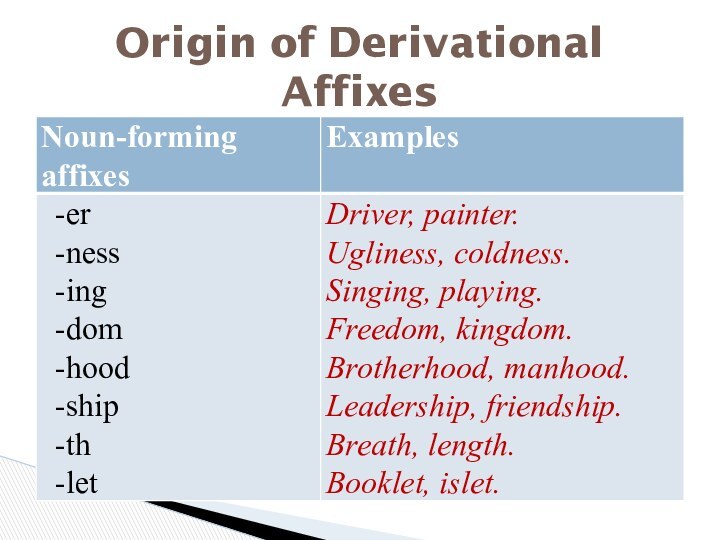
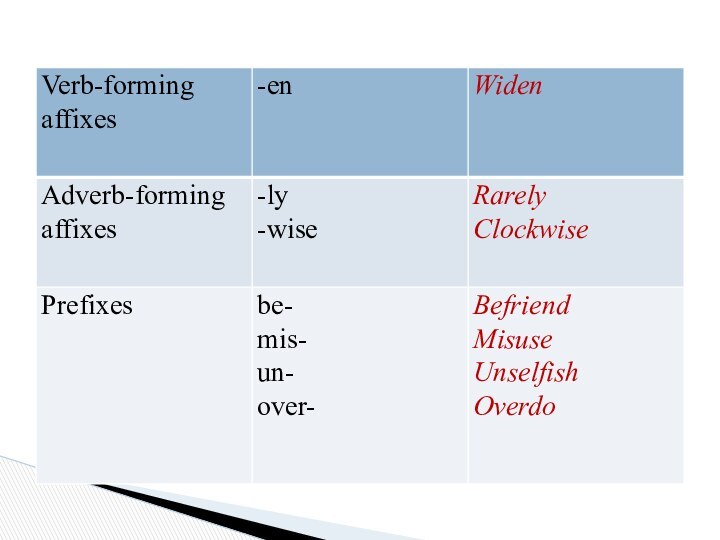
Native affixes are those in the Old English
period or were formed from Old English words.
The
change a morpheme undergoes in the course of time may be of different kinds.
A bound morpheme, e.g. may be developed from a free one. Such are the suffixes
– dom (‘fate, power’);
hood ‘state’;
-lock ‘actions or proceedings, practice’;
-ship ‘state, conduct’, and the prefixes;
over- ‘in excess, extra, upper’;
out- ‘foreign, external’, ect.
Etymology of Derivational Affixes:
Слайд 39
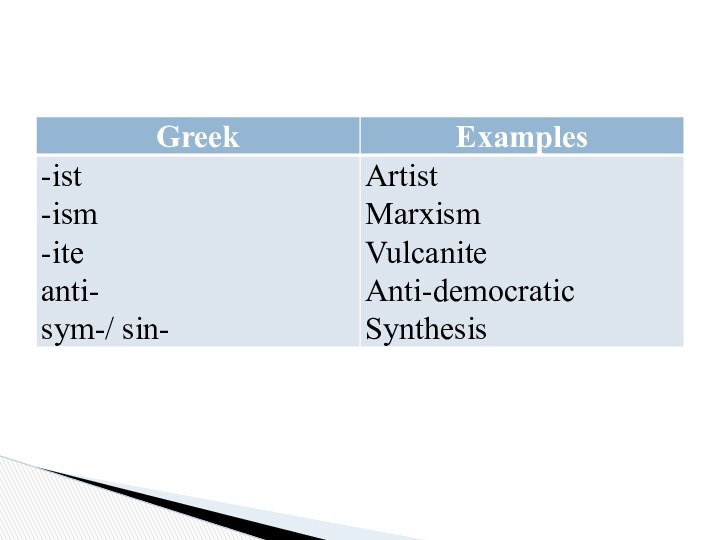
Borrowed Affixes have come to the English language
from different foreign languages. The affixes of foreign origin
are classified according to their source into:
Слайд 42
are words that are made up of elements
from two or more different languages. There are 2
basic types of forming hybrid words:
1) a foreign base is combined with a native affix, e.g. colourless, uncertain;
2) a native base is combined with a foreign affix, e.g. drinkable, ex-wife.
There are also many hybrid compounds, such as blackguard (English + French); schoolboy (greek + English).
Hybrids
Слайд 43
Valency of affixes is understood as their capability
to be combined with certain bases, e.g. adjective forming
suffixes are mostly attached to nominal bases. They are:
-en (golden),
-ful (meaningful),
-less (careless),
-ly (soldierly),
-like (childlike).
The highly productive suffix –able, however, can be combined with nominal and verbal bases alike (honorable, advisable).
VALENCY OF AFFIXES AND BASES
Слайд 44
is the possibility of a particular base to
take a particular affix. The valency of bases is
not unlimited, e.g., noun bases can be followed by:
the noun-forming suffixes, e.g. –eer (profiteer), -ful (spoonful), -ics (linguistics), -let (cloudlet);
the adjective-forming suffixes, e.g. –al (doctoral), -ary (revolutionary), -ous (spacious), -ic (historic);
the verb-forming suffixes, e.g. –en (hearten), -ize (sympathize).
Valency of bases
Слайд 45
is very important semantically because the meaning of
the derivative depends not only on the morphemes of
which it is composed but also on combinations of bases and affixes that can be contrasted with it.
Contrast is observed in the use of the same morphemes in different environment or in the use of different morphemes in the same environment, e.g., the difference in the suffixes –ity and –ism becomes clear when comparing them as combined with identical bases:
formality – formalism; reality – realism.
-ity – ‘the quality of being what corresponding adjective describes, an instant or quality’;
-ism –’ a disposition to what the adjective describes, or a corresponding type of ideology’.
Valency
Слайд 46
Word-formation is the process of creating words from
the material available in the language after certain structural
and semantic formulas and patterns.
Summary and Conclusions
Слайд 47
As a subject of study English word-formation is
that branch of English Lexicology which studies the derivative
structure of words and the patterns on which the English language builds new words. Like any other linguistic phenomenon, word-formation may be studied synchronically and diachronically.
Слайд 48
There are two types of word-formation in Modern
English: word-derivation which is divided into affixation and conversion
and word-composition. Within the types further distinction is made between the various ways and means of word-formation.
Слайд 49
There are minor types of word-formation: shortening, blending,
acronymy (graphical abbreviation), sound-interchange, sound-imitation, back-fomation and distinctive stress.
Слайд 50
Affixation (prefixation and suffixation) is the formation of
words by adding derivational affixes (prefixes and suffixes) to
bases. One distinguishes between derived words of different degrees of derivation.
Слайд 51
There are quite a number of polysemantic, homonymous
and synonymous derivational affixes in Modern English.
Слайд 52
Classifications of derivational affixes are based on different
principles such as:
1) the lexico-grammatical character of the
stem the affix is added to,
2) the part of speech formed,
3) the meaning,
4) the generalising denotational meaning,
5) the stylistic reference, etc.
Слайд 53
The productivity of derivational affixes is relative and
conditioned by various factors.
Слайд 54
Many of the Modern English derivational affixes were
at one time independent words. Others have always been
known as suffixes or prefixes within the history of the English vocabulary. Some of them are of international currency.
Слайд 55
The degree of productivity and factors favouring it
make an important aspect of synchronic description of every
derivational pattern within the two types of word-formation.
Слайд 56
Three degrees of productivity are distinguished for derivational
patterns and individual derivational affixes:
l) highly-productive,
2) productive
or semi-productive,
3) nоn-produсtive.