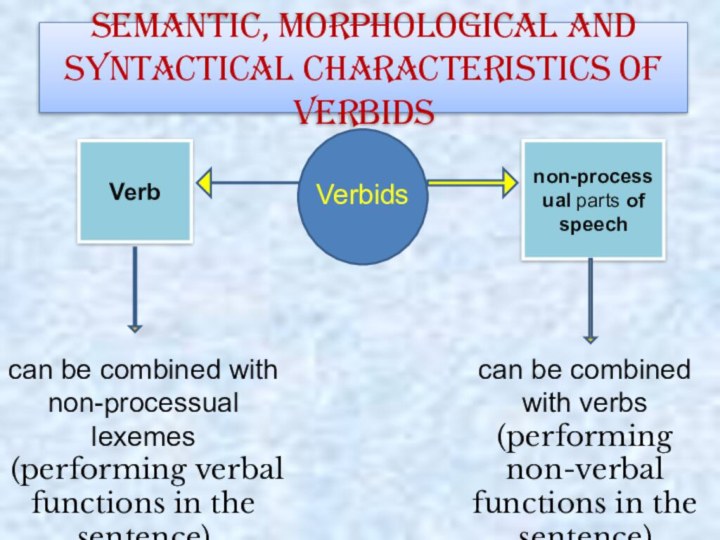
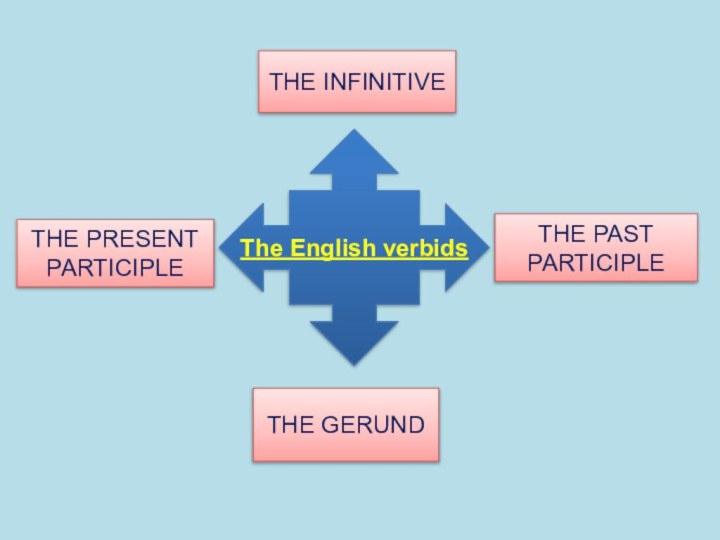
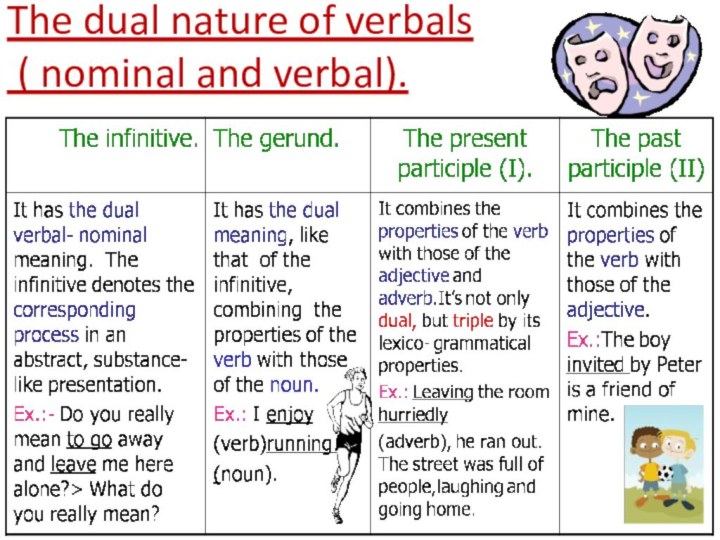
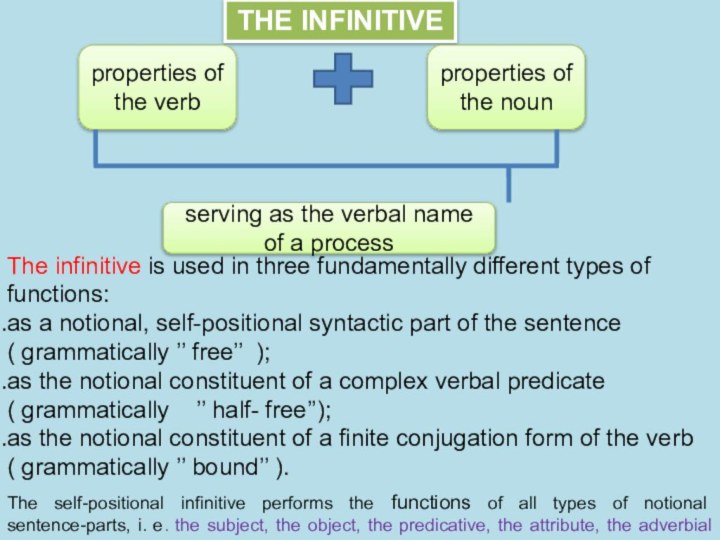
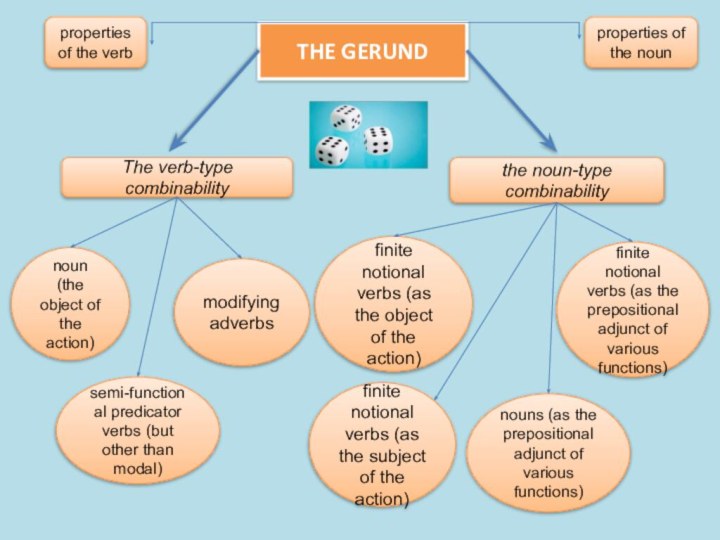
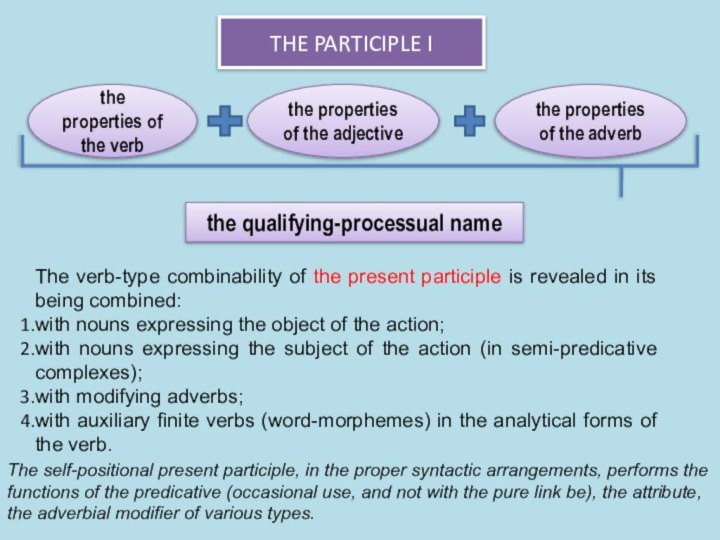
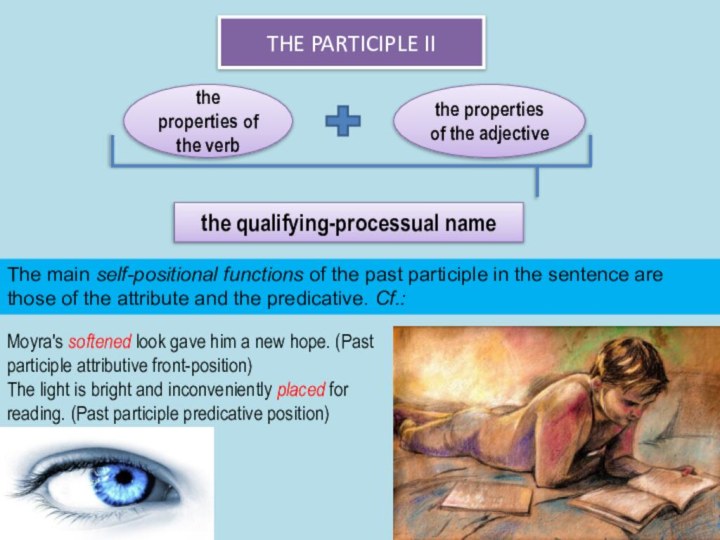
the functions of all the types of notional sentence-parts,
i.e. the subject, the object, the predicative, the attribute, the adverbial modifier.
the aspective category of retrospective coordination (perfect in opposition);
the category of voice (passive in opposition).
The gerund is a categorically changeable form; it distinguishes the two grammatical categories:
the simple active - the perfect active;
the simple passive - the perfect passive.
E.g.: taking — having taken;
being taken — having been taken.
The categorial paradigm of the gerund of the objective verb includes four forms:
The perfect forms of the gerund are used, as a rule, only in semantically strong positions, laying special emphasis on the meaningful categorial content of the form.
E.g.: going — having gone.
The gerundial paradigm of the non-objective verb, correspondingly, includes two forms: