Слайд 2
Why Study Money, Banking, and Financial Markets
To examine
how financial markets
such as bond, stock and foreign
exchange markets work
To examine how financial institutions such as banks and insurance
companies work
To examine the role of money in
the economy
Слайд 3
Main Topics
What is money?
Who controls the money supply?
Why is money important?
Why is inflation a problem?
How do
banks make “money” (profits)?
Why are banks important?
How does the government regulate banks and why?
Financial Markets and financial instruments
What is monetary policy?
How does the Fed conduct monetary policy?
How are interest rates determined?
Слайд 4
Money
Money is the stock of items widely used
to make payment for goods and services.
Money, or
the money supply, includes:
currency and coins in circulation,
checking accounts in depository institutions, and
other items, such as Certificates of Deposit (CDs), when measured more broadly.
Слайд 6
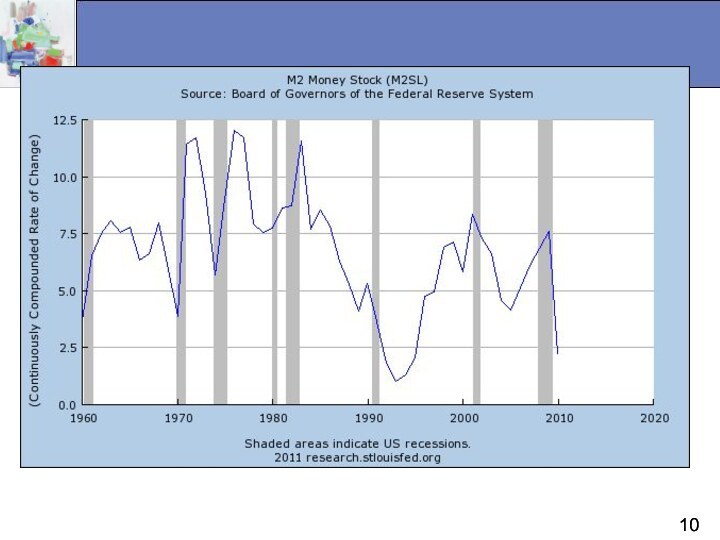
What Determines The Money Supply?
The central bank
is responsible for the trend or long-run behavior of
the money supply.
Banks and non-bank public also play important roles in determining the aggregate money supply.
In the United States, the central bank is the Federal Reserve System (the Fed).
The Fed conducts monetary policy.
Monetary Policy refers to the management of money supply and interest rates.
Слайд 7
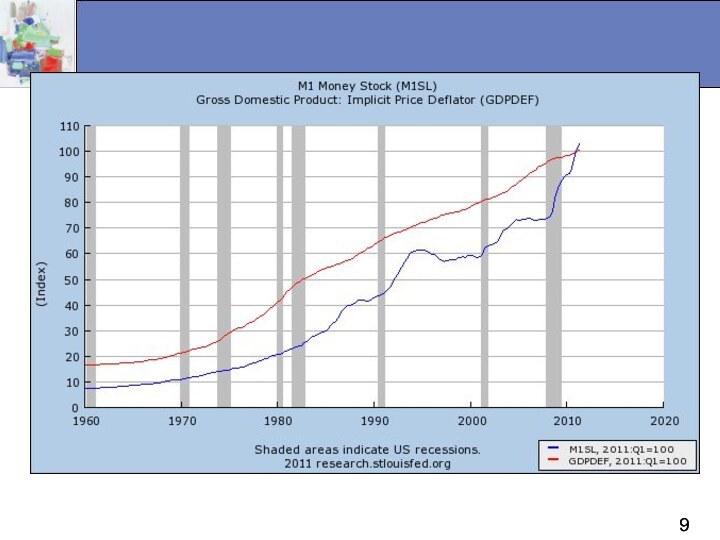
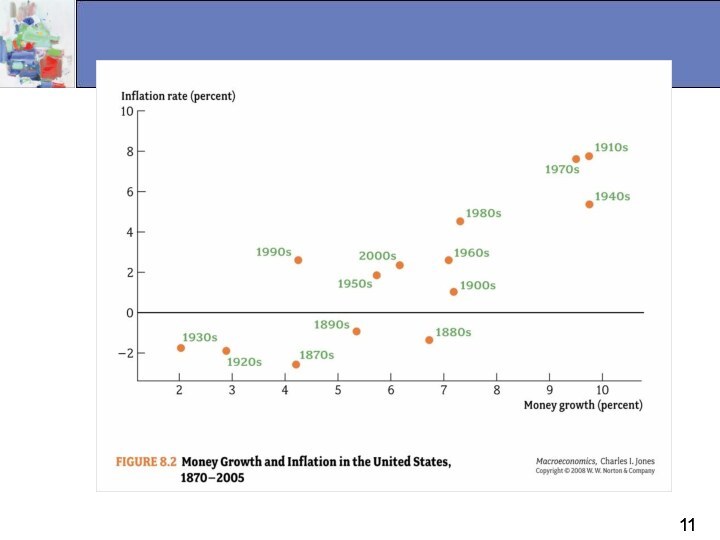
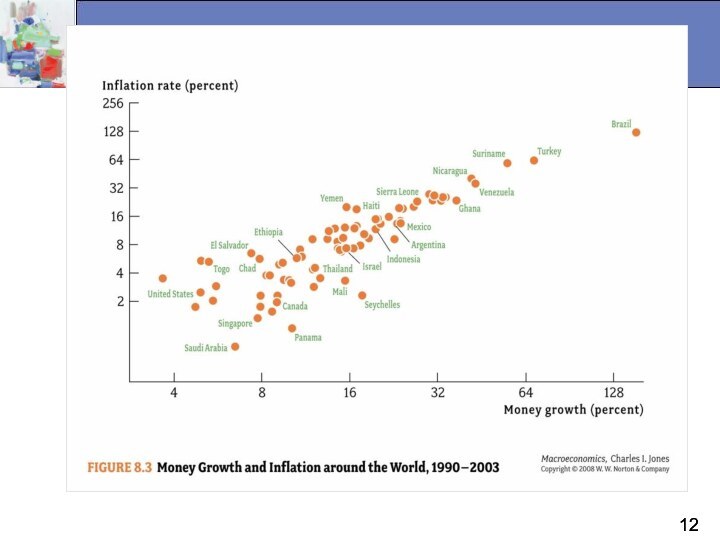
Money, Inflation, and Deflation
When the money supply
increases more rapidly than the output of goods and
services, inflation occurs.
Why is Inflation a problem?
Deflation is a continuing decline in prices and is more damaging to a nation's economic health than inflation.
Why is deflation a problem?
Inflation targeting occurs when a central bank announces an explicit inflation range it pledges to maintain and enforces policies consistent with that goal.
Слайд 8
Money and Business Cycles
Evidence suggests that money
plays
an important role in generating
business cycles
Recessions (unemployment) and
booms (inflation) affect all of us
Monetary Theory ties changes in the money supply to changes in aggregate economic activity and the price level
Слайд 13
Key Financial Markets
The stock market
The bond market
The foreign exchange (ForEx) market
Markets in which funds
are transferred from people who have an excess of available funds to people who have a shortage of funds
Слайд 14
The Bond Market and Interest Rates
A security (financial
instrument) is a claim on the issuer’s future income
or assets
A bond is a debt security that promises to make payments periodically for a specified period of time
Bondholders are lenders; stockholders are owners.
An interest rate (or yield) is the cost of borrowing or the price paid for the rental of funds and are determined by market forces of supply and demand.
Слайд 15
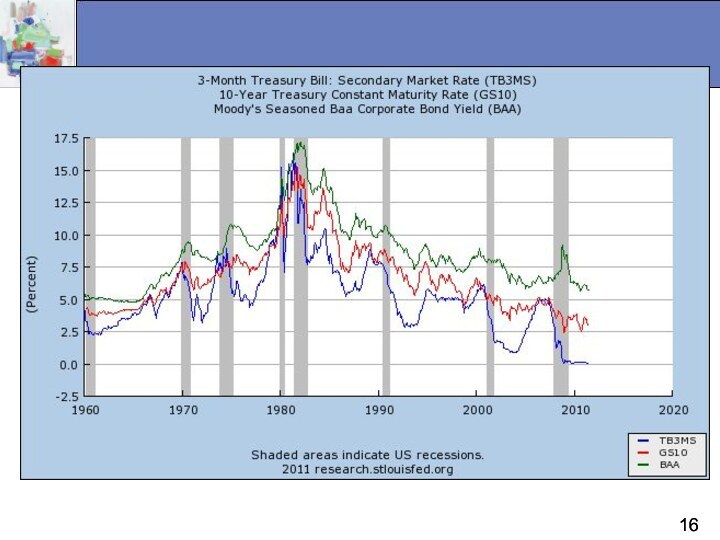
Facts about interest rates
There are many different interest
rates.
Interest rates tend to move together.
Sometimes we ignore the
differences among interest rates and focus on the interest rate level.
The interest rate level is determined in the bond market or loanable funds market.
There are intimate relationships among different interest rates.
Слайд 17
The Stock Market
Common stock represents a share of
ownership in a corporation
A share of stock is a
claim on the earnings and assets of the corporation
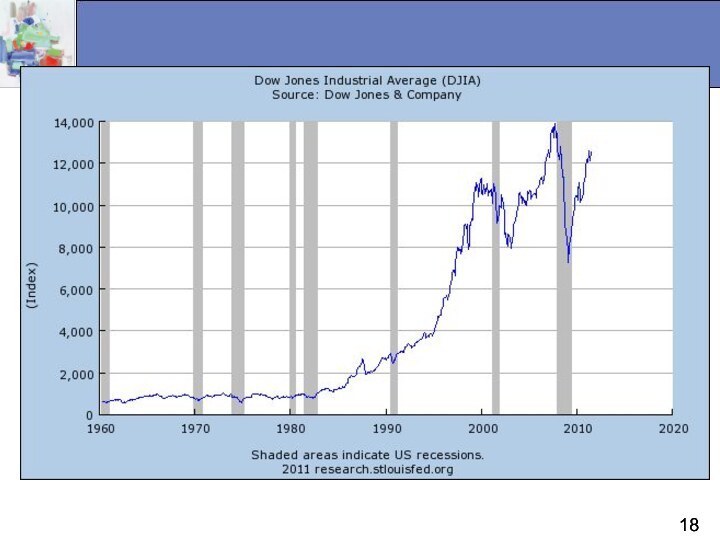
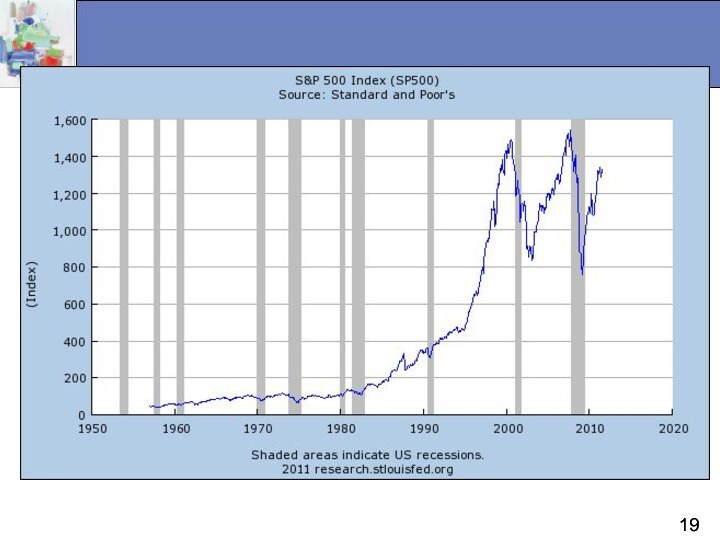
A company’s stock share price reflects the opinion of the market about the company's economic value, which ultimately depends on its future profitability.
Major indexes reflect changing sentiment about the nation's economic prospects.
Dow-Jones Industrials Average (DJIA)
Standard and Poor's 500 Average (S&P 500)
Слайд 20
The Foreign Exchange Market
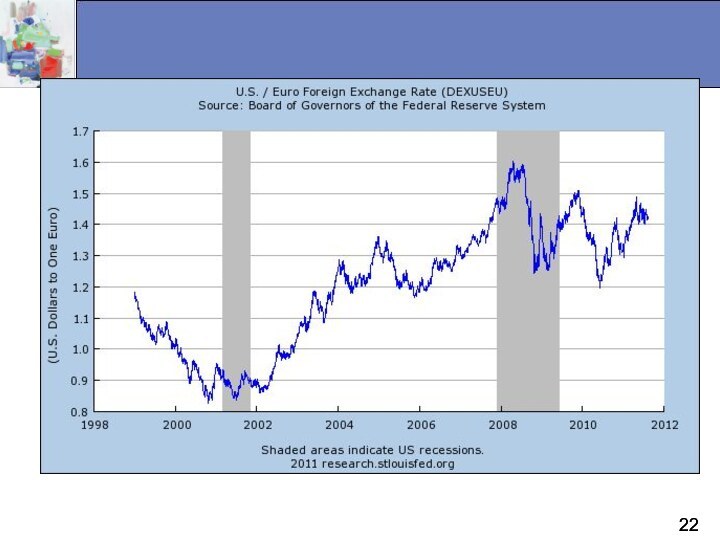
The foreign exchange market is
where funds are converted from one currency into another
The
foreign exchange rate is the
price of one currency in terms of
another currency
The foreign exchange market determines the foreign exchange rate
Слайд 21
Foreign Exchange and Trade
Appreciation is an increase in
the value of one nation’s currency relative to another
nation’s currency.
Depreciation is the opposite.
Appreciation causes:
higher prices to foreign buyers of exports,
lower prices to domestic consumers of imports, and
a trade deficit (or a reduction in the trade surplus).
Depreciation causes:
lower prices to foreign buyers of exports,
higher prices to domestic consumers of imports, and
a trade surplus (or a reduction in the trade deficit.)
Слайд 23
Banking and Financial Institutions
Financial Intermediaries—institutions that borrow funds
from people who have saved and make loans to
other people
Banks—institutions that accept deposits and make loans
Other Financial Institutions—insurance companies, finance companies, pension funds, mutual funds and investment banks
Financial Innovation—in particular, the advent of the information age and e-finance
Слайд 24
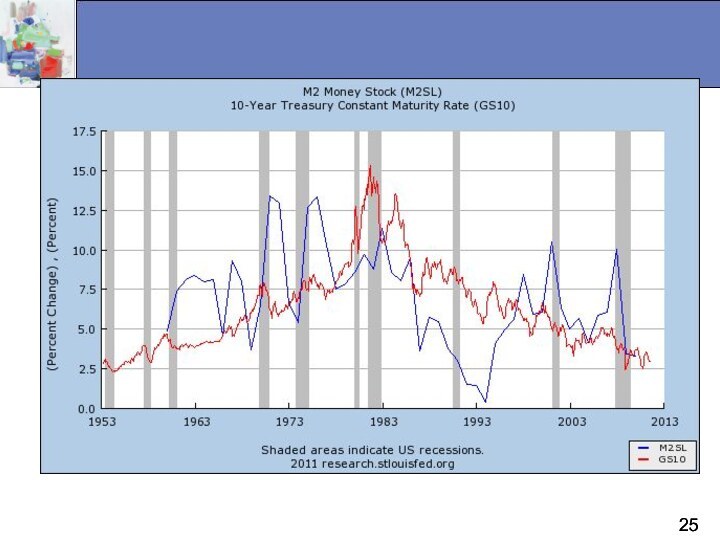
Money and Interest Rates
Interest rates are the price
of money
Prior to 1980, the rate of money growth
and the interest rate on long-term Treasure bonds were closely tied
Since then, the relationship is less clear but still an important determinant of interest rates
Слайд 26
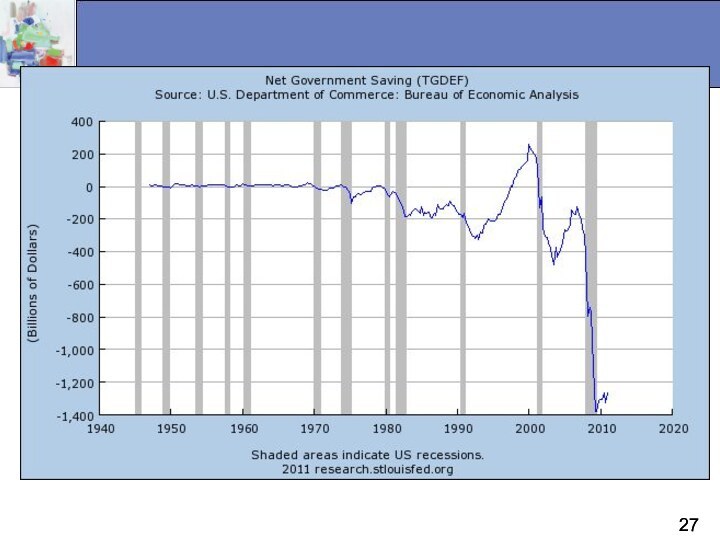
Monetary and Fiscal Policy
Monetary policy is the management
of the money supply and interest rates
Conducted in the
U.S. by the Federal Reserve Bank (Fed)
Fiscal policy is government spending
and taxation
Budget deficit is the excess of expenditures over revenues for a particular year
Budget surplus is the excess of revenues over expenditures for a particular year
Any deficit must be financed by borrowing