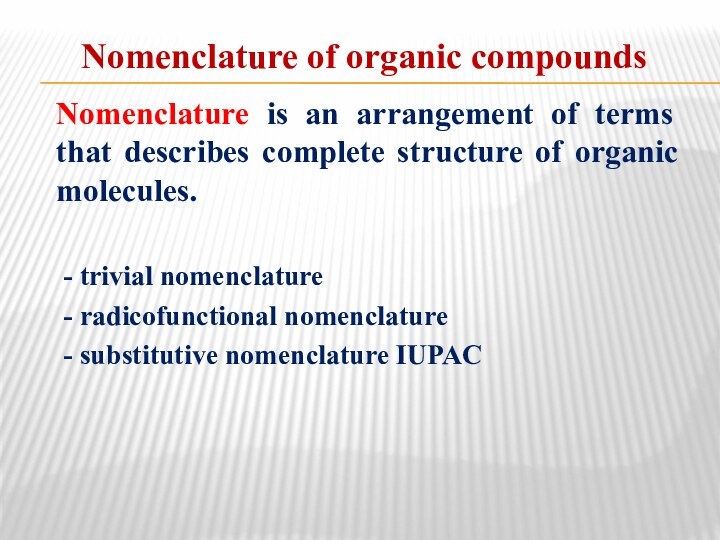
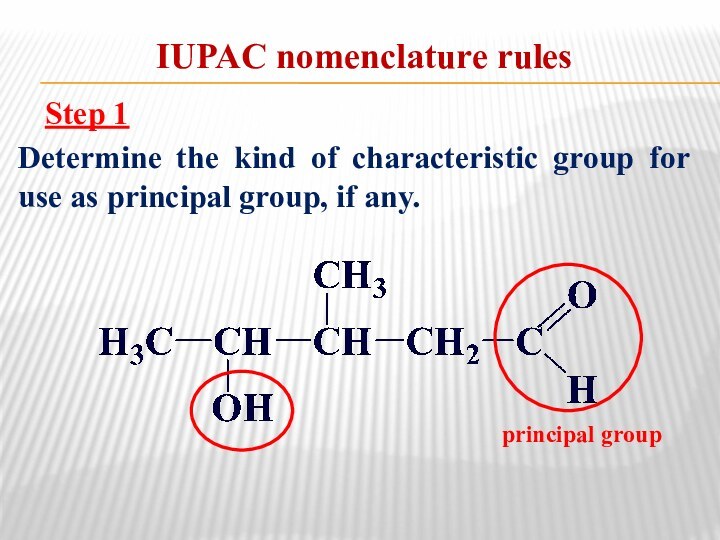
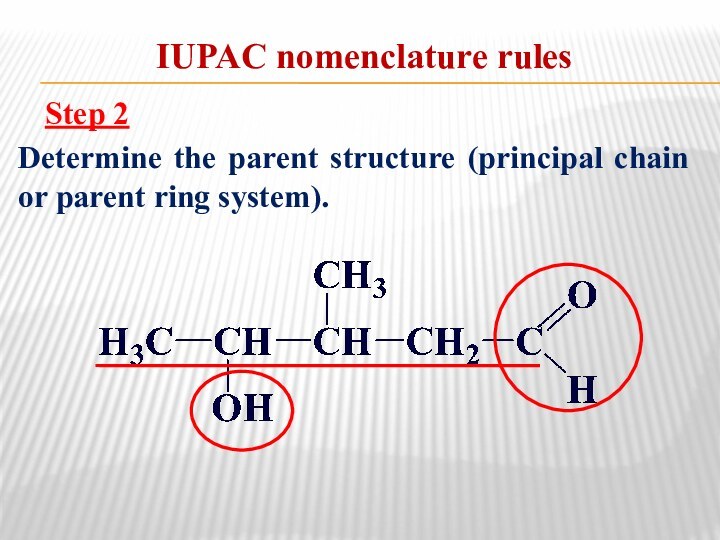
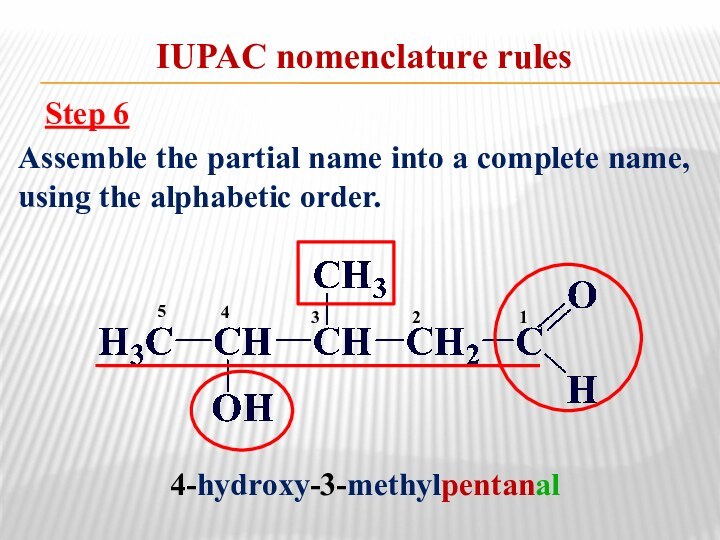
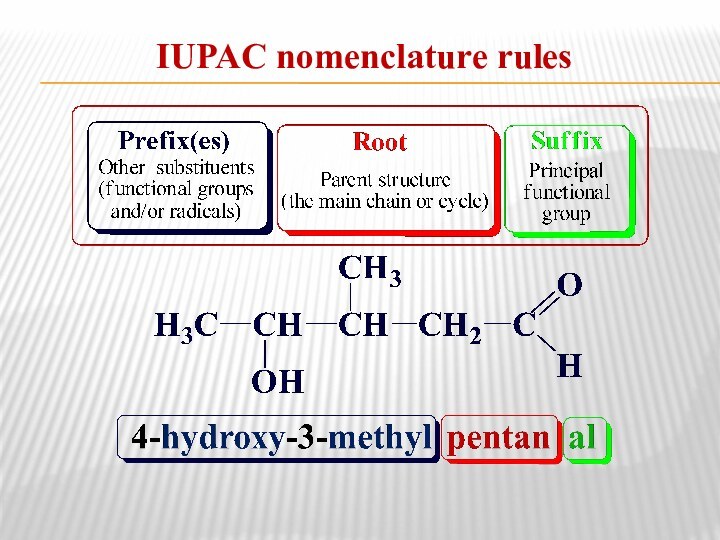
relationship between the structure of organic compounds and their
biological functions.Studyind objects
natural biologically important compounds (biopolymers, vitamins, hormones, antibiotics, pheromones, etc.);
synthetic regulators of biological processes (drugs, pesticides, etc.).