- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Muscle tissue
Содержание
- 2. Muscle tissue satisfy requirement of the body in movement.
- 3. Classification – The 3 types of muscle tissue:1. skeletal 2. cardiac3. smoothgroups:StriatedSmooth
- 4. Why do muscles contract?Muscle cells have contractile
- 5. Why do muscles contract?Actin and myosin form
- 6. SMOOTH MUSCLE
- 7. Locations: walls of visceral hollow organs (stomach).
- 8. SMOOTH MUSCLEUnit – spindle shaped cell --
- 9. Origin of smooth muscleSmooth muscle cells arise from mesenchymal cells.
- 10. Striated muscles
- 11. See: regular organization of the myofibrils gives
- 12. CARDIAC MUSCLE Locations: heartFunction: involuntary, rhythmic contractionUnit – cardiomyocyte (cell)
- 13. Cardiac muscle cells:3 types:Contractile, Conducting Secretory
- 14. CARDIAC MUSCLE cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical,
- 15. CARDIAC MUSCLE They are connected by special
- 17. SKELETAL MUSCLE
- 18. LocationMuscles associated with the skeleton (are connected
- 19. SKELETAL MUSCLE--- is innervated by the somatic
- 20. SKELETAL MUSCLESkeletal muscle fibers run the full
- 21. Nuclei:Skeletal muscle fibres contain many nuclei(up to several hundred ) placed beneath the plasma membrane
- 22. Myofibrils Mechanism of contraction: Sliding filaments model
- 23. Myofibrils has some bands and lines depending
- 26. Sarcomeres --are parts, smallest contractile units of
- 27. Sarcomere formula after contractionS = A(- ½ I, - ½ I, - H)
- 28. Mechanism of contraction
- 29. Origin of skeletal muscleThe myoblasts of all
- 30. 1. Myoblasts undergo frequent divisions and coalesce
- 31. Скачать презентацию
- 32. Похожие презентации
Muscle tissue satisfy requirement of the body in movement.























Слайд 3
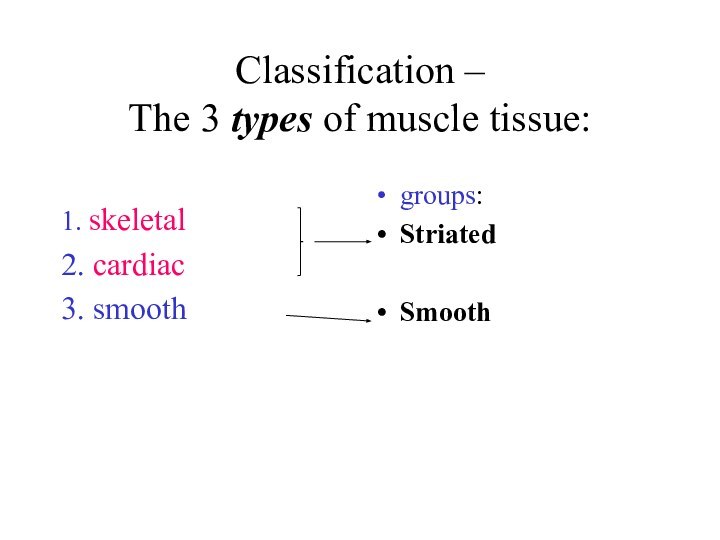
Classification –
The 3 types of muscle tissue:
1.
skeletal
2. cardiac
3. smooth
groups:
Striated
Smooth
Слайд 4
Why do muscles contract?
Muscle cells have contractile proteins
-
actin and myosin,
and some another .
The interaction
of actin and myosin mediates the contraction of muscle cells.
Слайд 5
Why do muscles contract?
Actin and myosin form myofilaments:
Myosin
- thick, dark and Anisotropic (A)
Actin – thin, light
and Isotropic (I)Actin and myosin form special organelles – myofibrils, responsible for muscle contraction.
Слайд 7
Locations: walls of visceral hollow organs
(stomach).
Functions: involuntary movement --
(peristaltics)
(The innervation -- by autonomic
nervous system)
Слайд 8
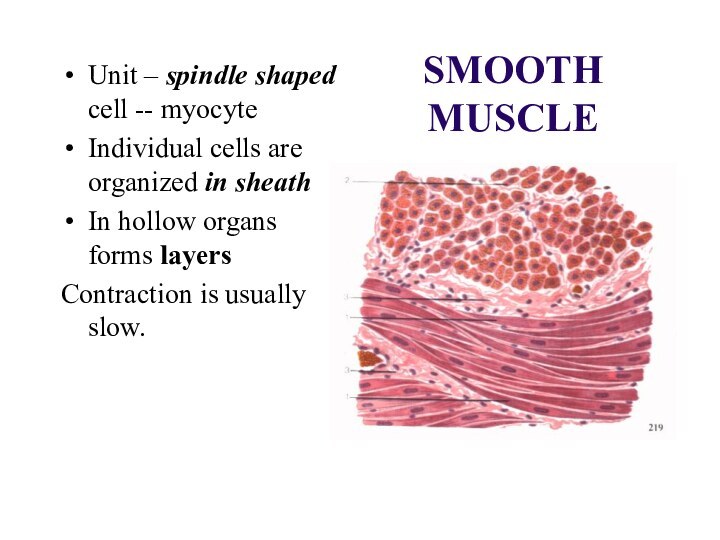
SMOOTH MUSCLE
Unit – spindle shaped cell -- myocyte
Individual
cells are organized in sheath
In hollow organs forms
layers Contraction is usually slow.
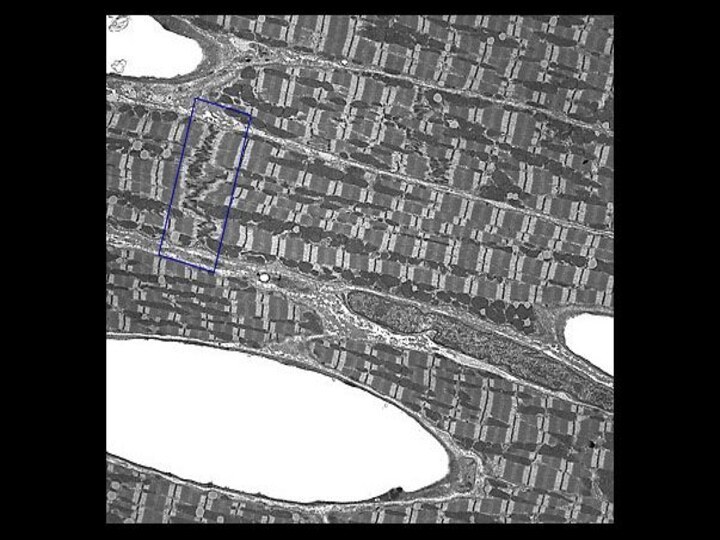
Слайд 11 See: regular organization of the myofibrils gives rise
to the cross-striation, which characterises skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Слайд 12
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Locations: heart
Function: involuntary, rhythmic contraction
Unit –
cardiomyocyte (cell)
Слайд 14
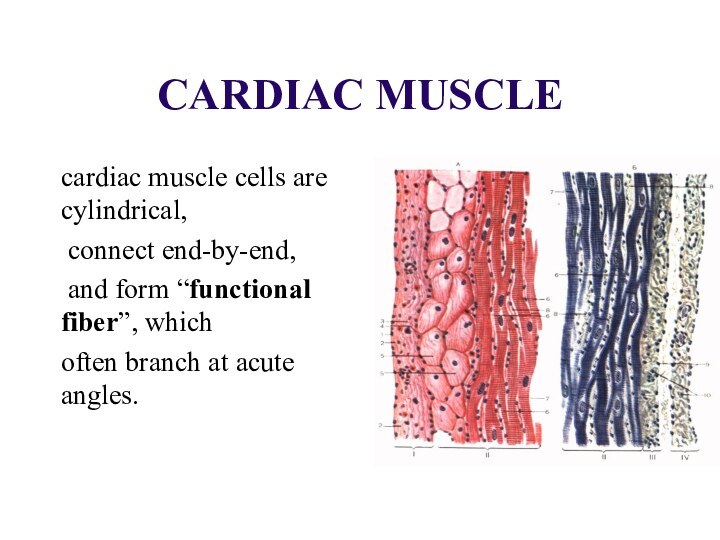
CARDIAC MUSCLE
cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical,
connect end-by-end,
and form “functional fiber”, which
often branch
at acute angles.
Слайд 15
CARDIAC MUSCLE
They are connected by special junction
-
intercalated discs – consisting of
gap junctions
and
desmosomes.
Слайд 18
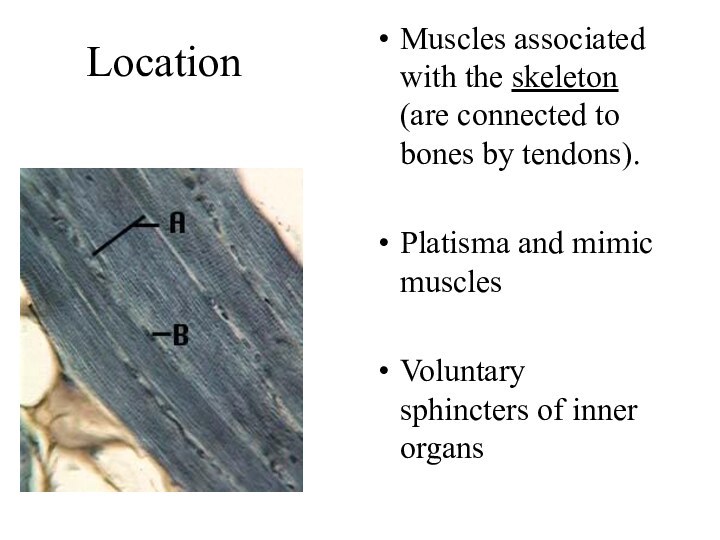
Location
Muscles associated with the skeleton (are connected to
bones by tendons).
Platisma and mimic muscles
Voluntary sphincters of
inner organs
Слайд 19
SKELETAL MUSCLE
--- is innervated by the somatic nervous
system – voluntary!!
---- consists of very long tubular
cells (also called muscle fibres).
Слайд 20
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Skeletal muscle fibers run the full length
of a muscle.
The average length of skeletal muscle
cells in humans is about 3 cm (sartorius muscle up to 30 cm, stapedius muscle only about 1 mm). Their diameters vary from 10 to 100 µm.
Слайд 21
Nuclei:
Skeletal muscle fibres contain many nuclei
(up to several
hundred )
placed beneath the plasma membrane
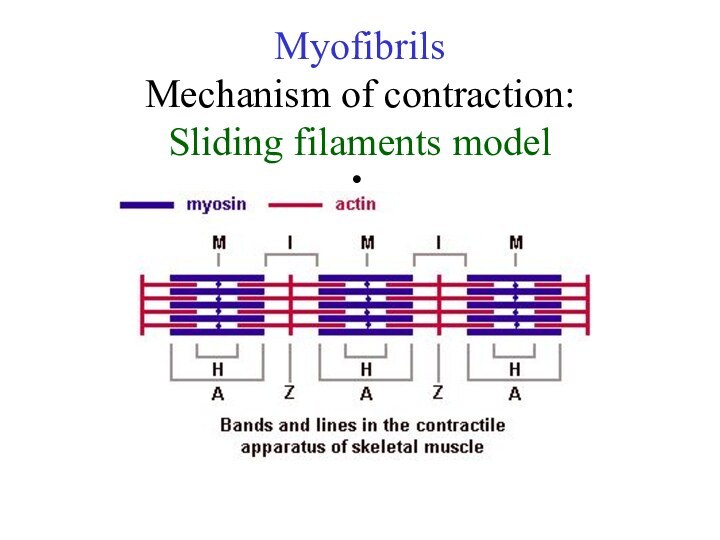
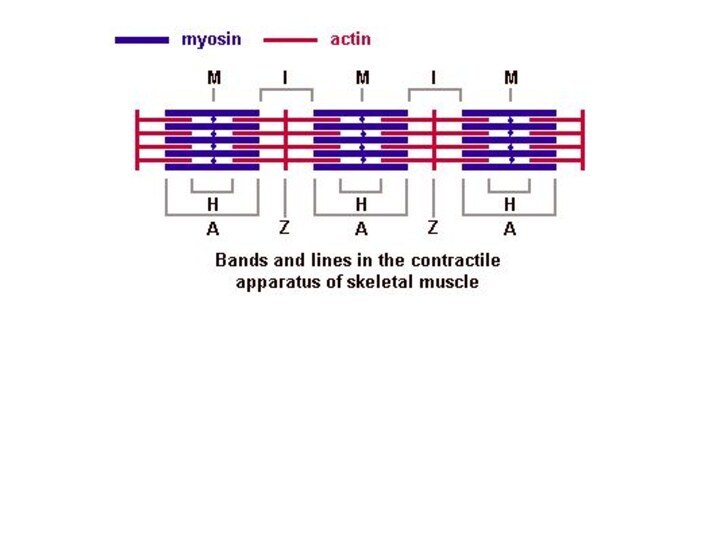
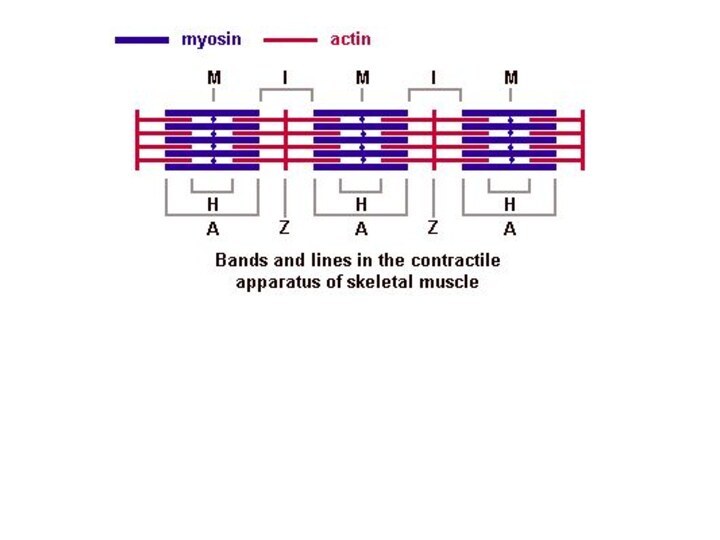
Слайд 23 Myofibrils has some bands and lines depending on
the distribution and interconnection of myofilaments -- :
I-band
- actin filaments only, A-band - myosin filaments which may overlap with actin filaments
T or Z-line -- band of connections between actin filaments; zone of apposition of actin filaments belonging to two neighboring sarcomeres;
M-line - band of connections between myosin filaments.
H-band - zone of myosin filaments only (no overlap with actin filaments) within the A-band
Слайд 26
Sarcomeres --
are parts, smallest contractile units of myofibrils.
Sarcomere
formula:
S = ½ I + A + ½
I
Слайд 29
Origin of skeletal muscle
The myoblasts of all skeletal
muscle fibres originate from the paraxial mesoderm - myotome.
Слайд 30 1. Myoblasts undergo frequent divisions and coalesce with
the formation of a multinucleated, syncytial muscle fibre or
myotube. The nuclei of the myotube are still located centrally in the muscle fibre.2. In the course of the synthesis of the myofilaments and myofibrils, the nuclei are gradually displaced to the periphery of the cell.