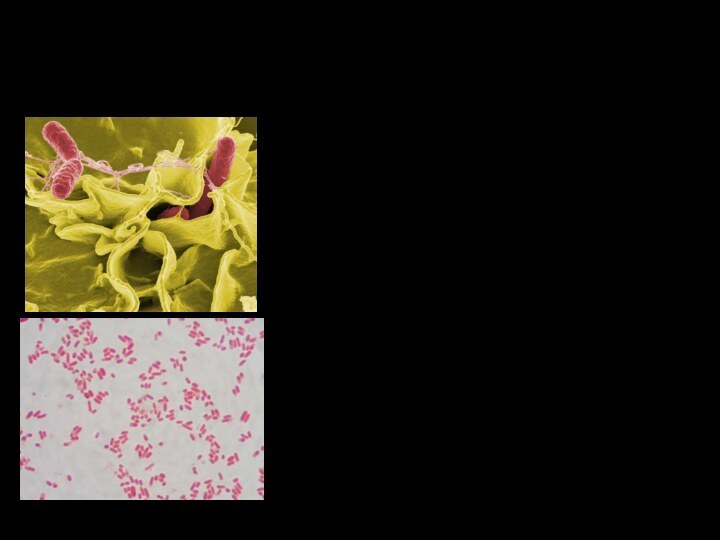
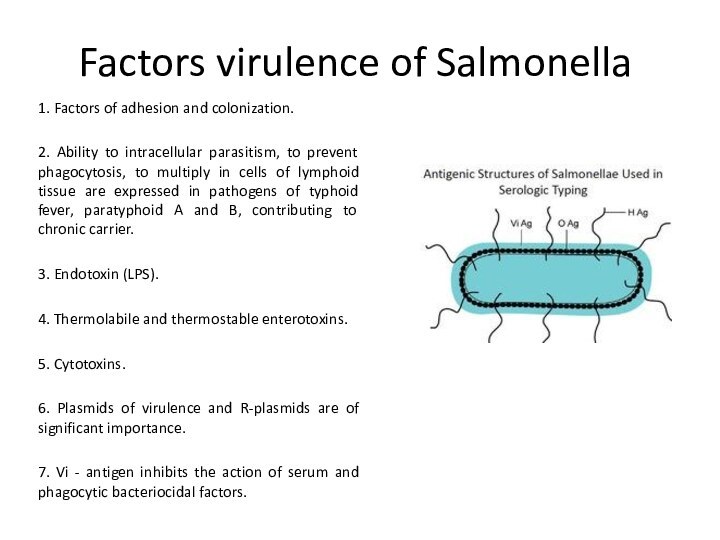
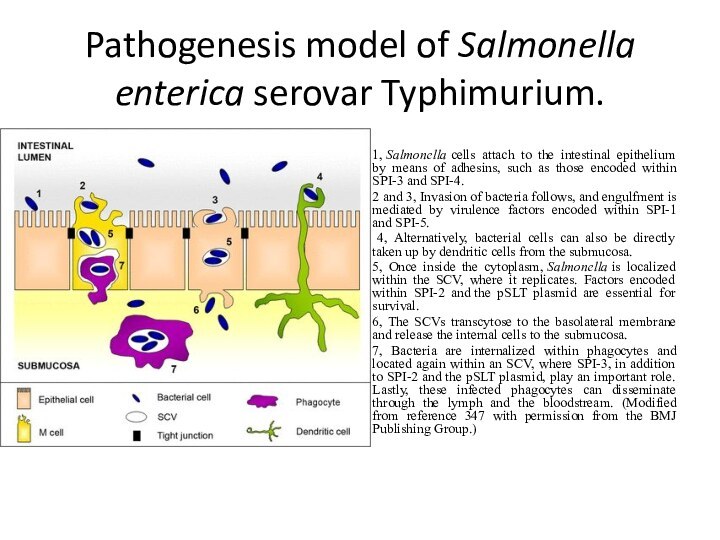
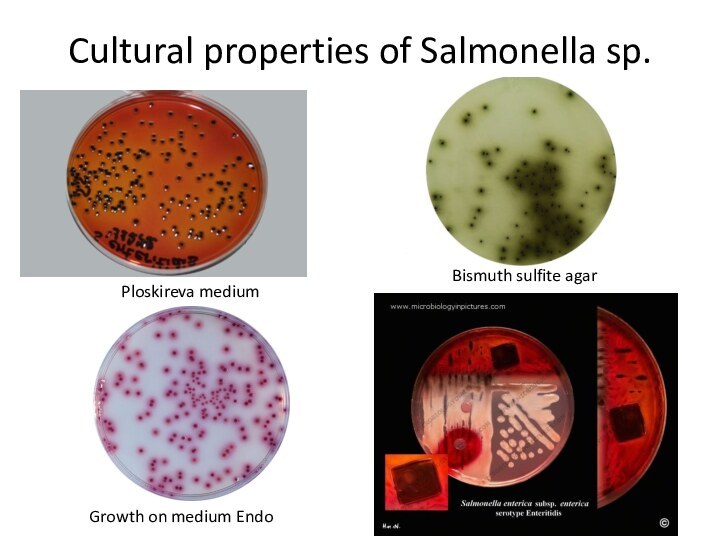
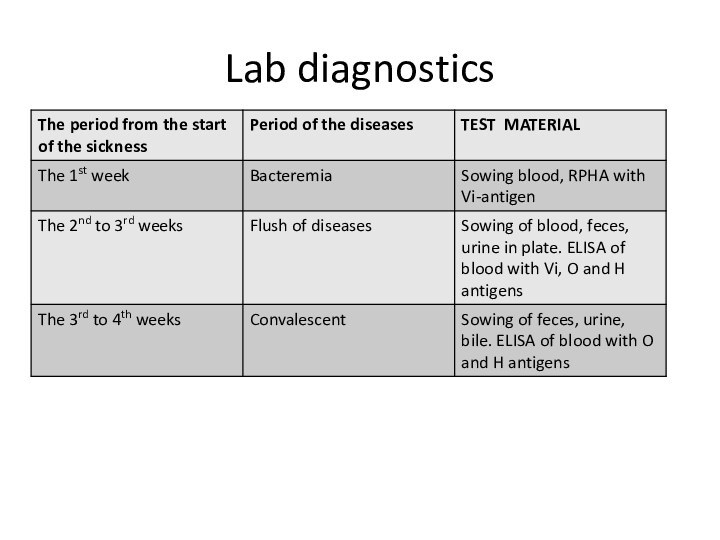
gram-negative bacillus with size 2-4 x 0,5 microns. They are
mobile due to the presence of peritrichrally located flagella.Specialty: Infectious disease
Symptoms: Diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting
Biochemical properties: Do not fermente lactose or sucrose, produce acid and gas from glucose – S. typhi is gas negative, produce H2S.
Salmonella sp. Gram stain