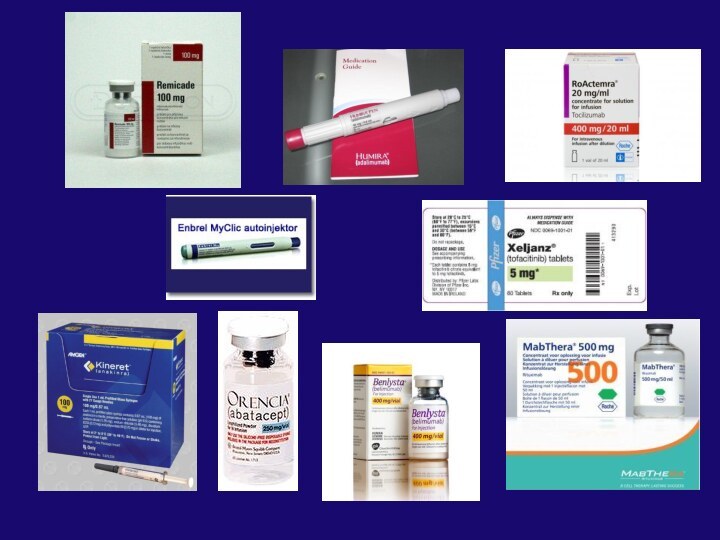
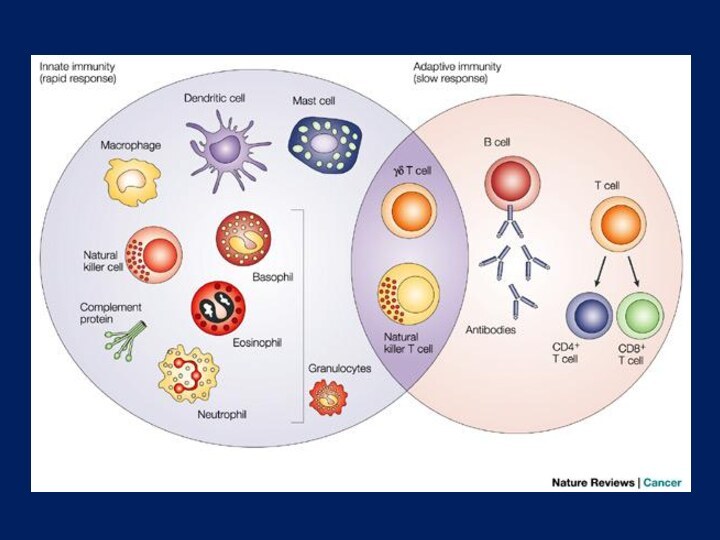
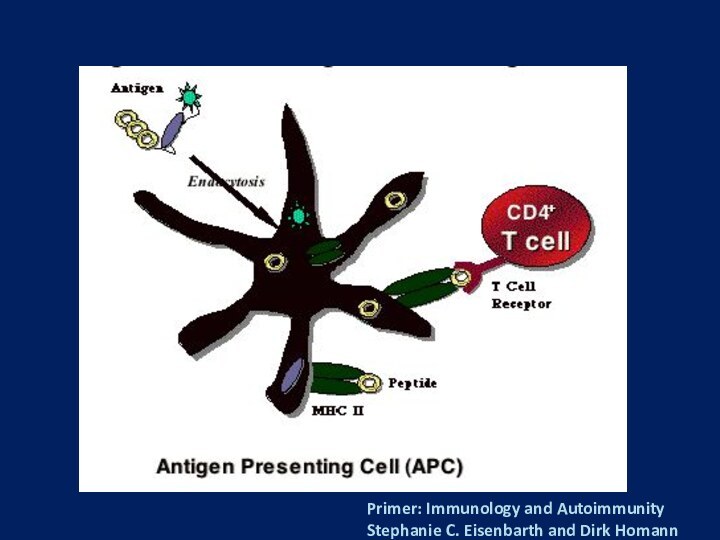
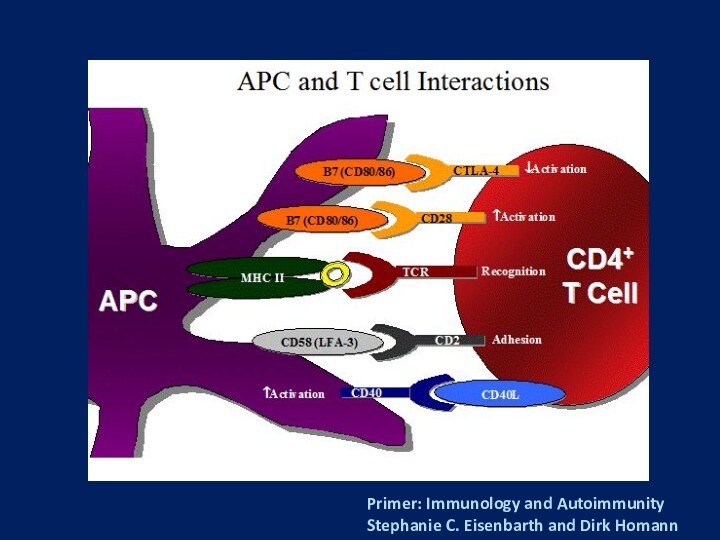
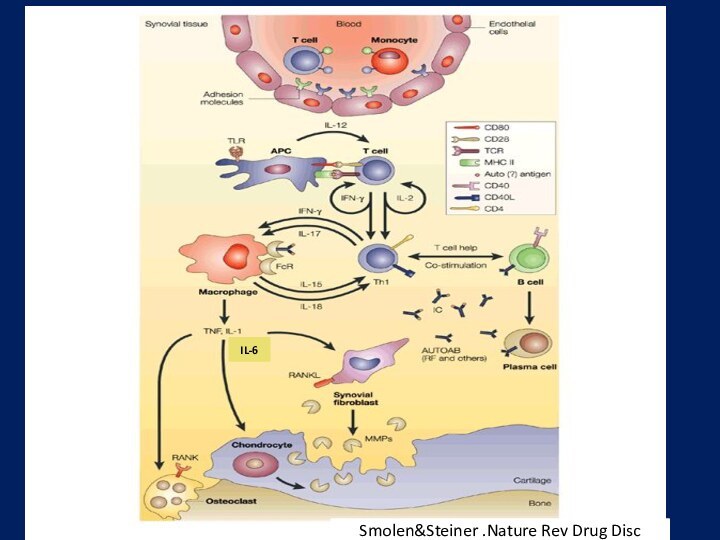
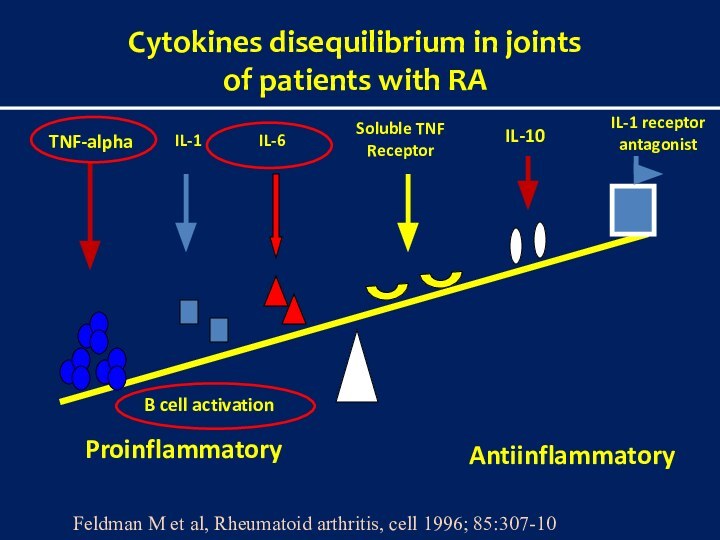
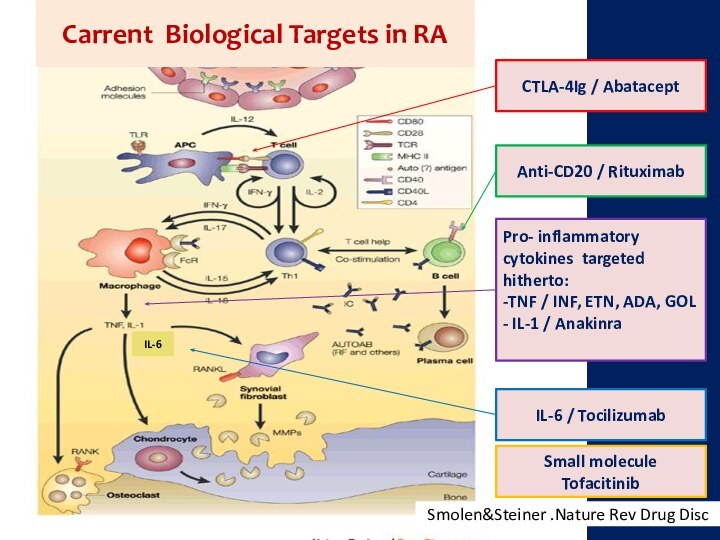
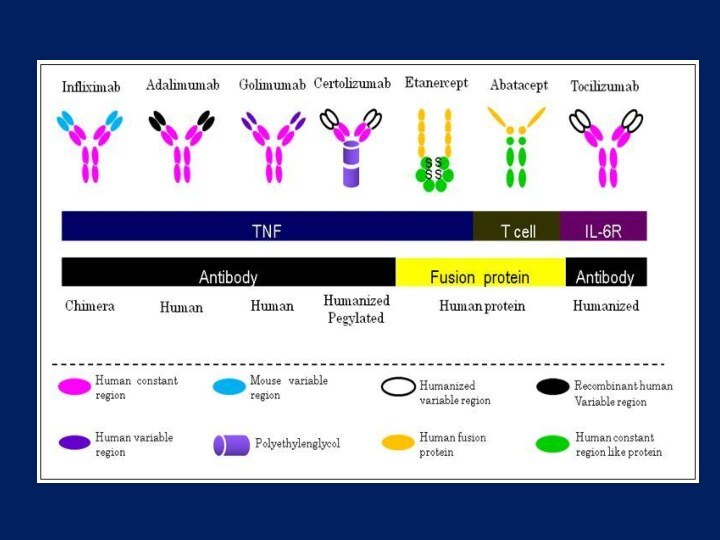
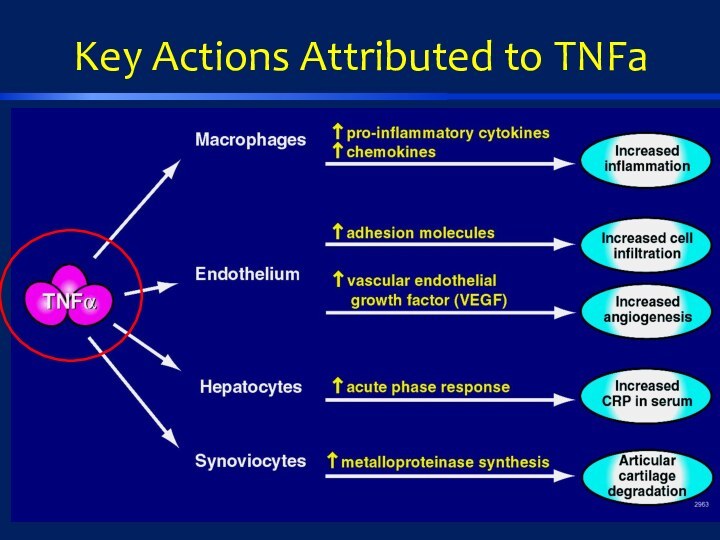
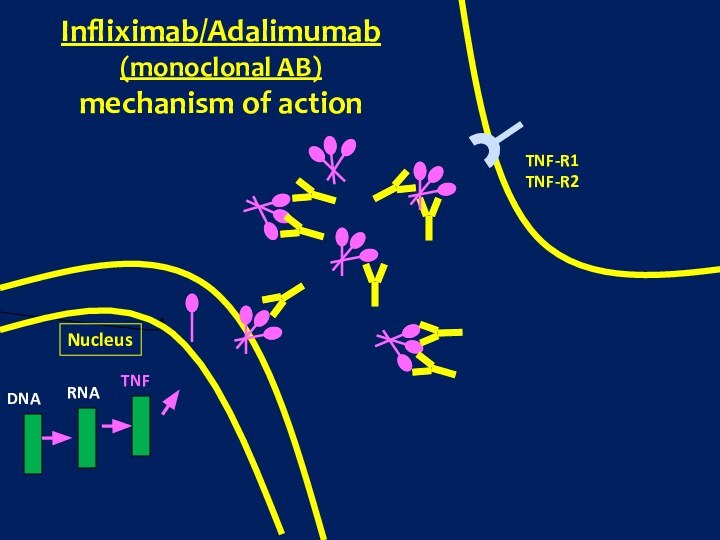
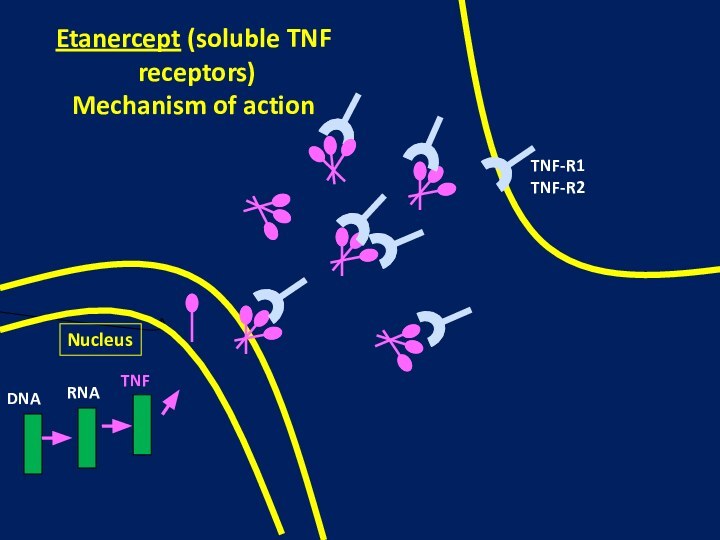
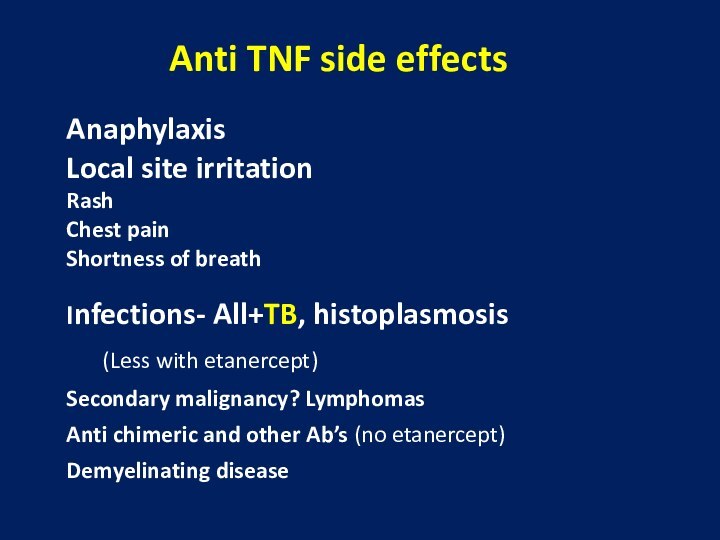
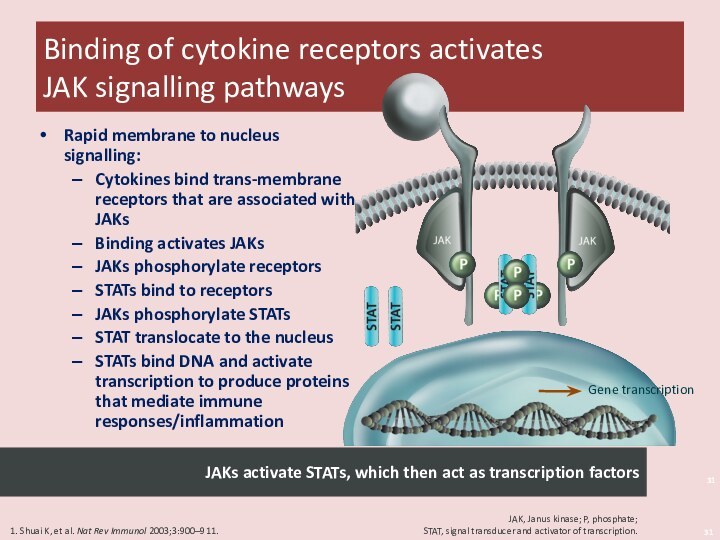
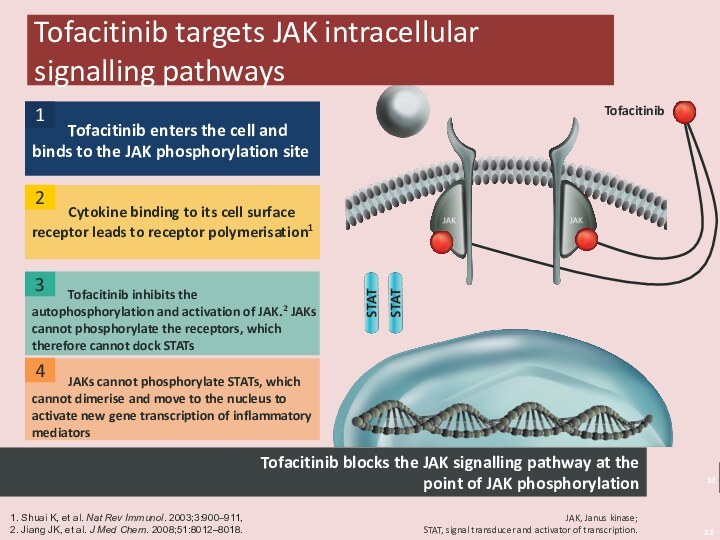
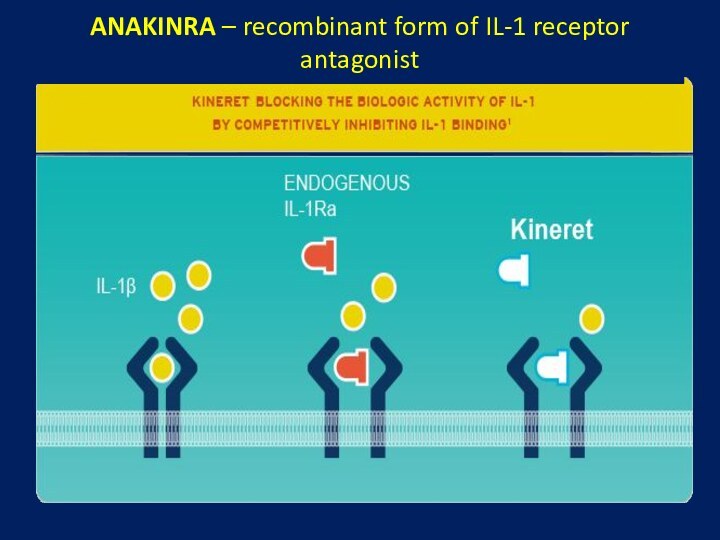
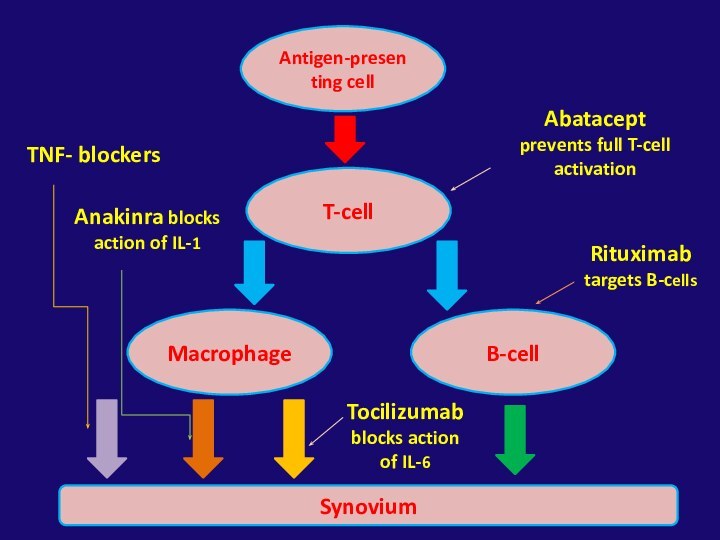
arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Psoriasis
Crohn’s d-se
Ulcerative colitis
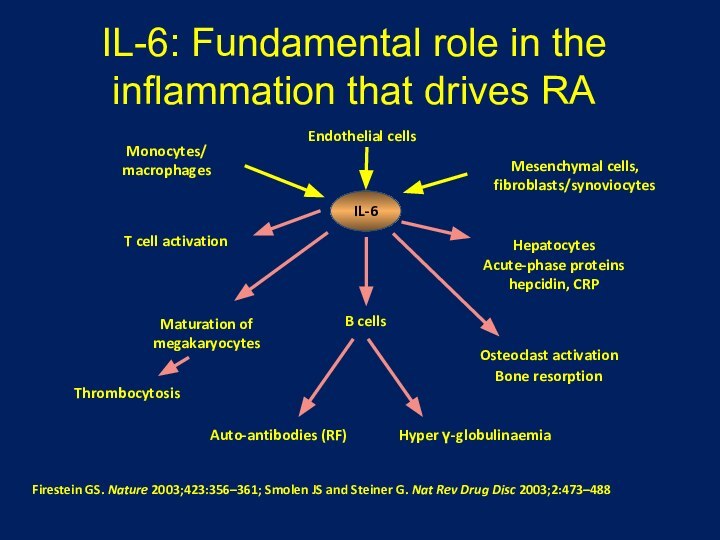
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
APLAS
Anterior uveitis
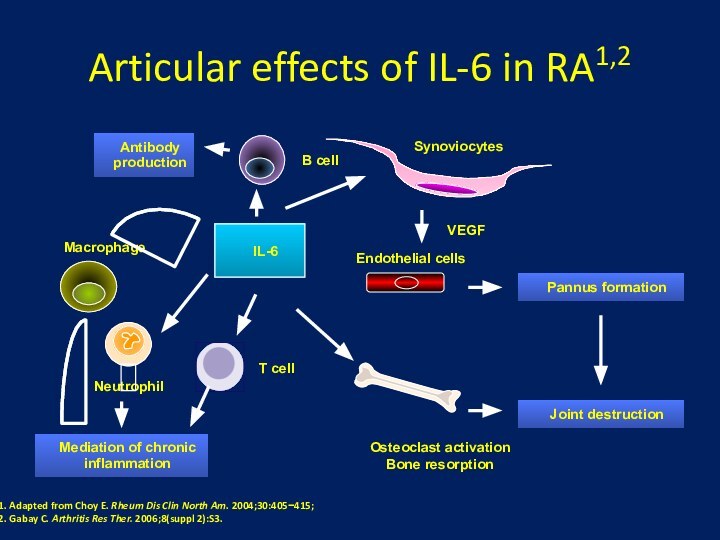
Osteoporosis
ANCA-associated granulomatous
vasculitisGiant cell arteritis
Takayasu arteritis
Behcet s-me
Adult onset Still d-se
Periodic fevers
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Gout
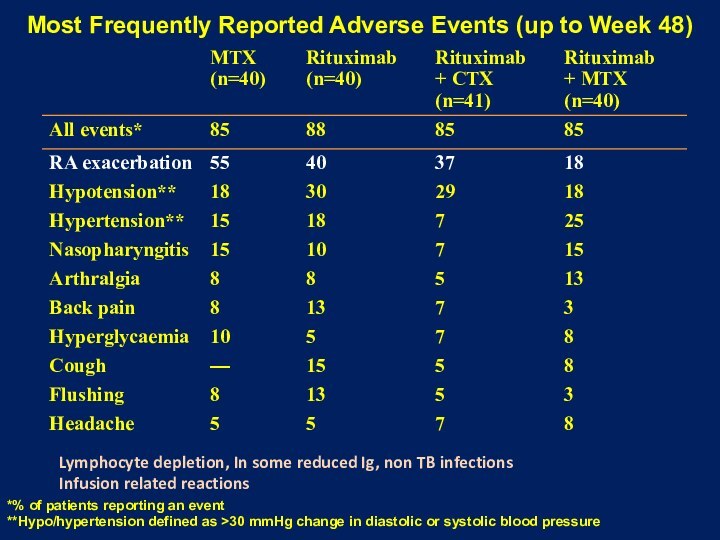
B-cell Lymphoma
Familial Mediterranean Fever