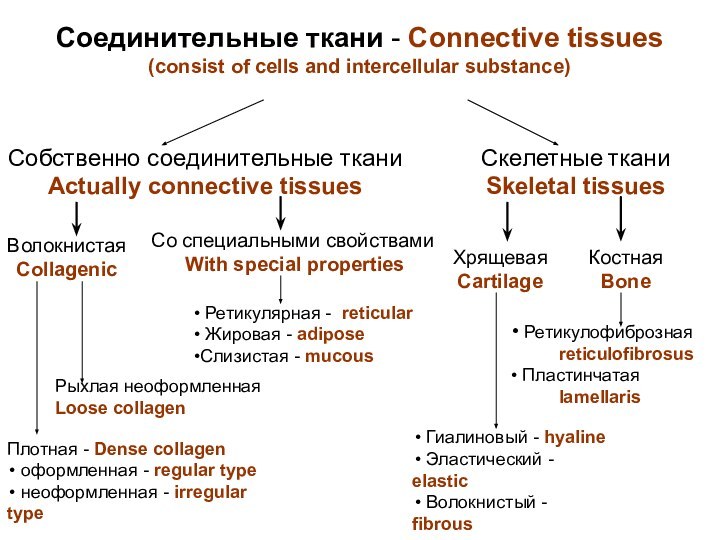
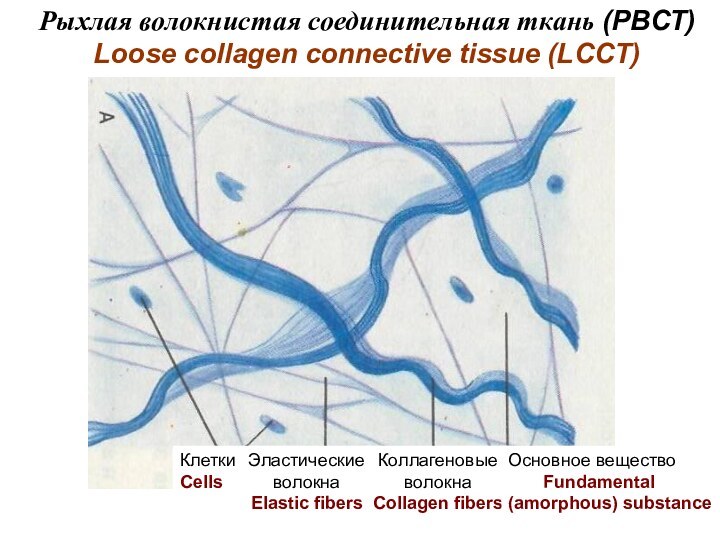
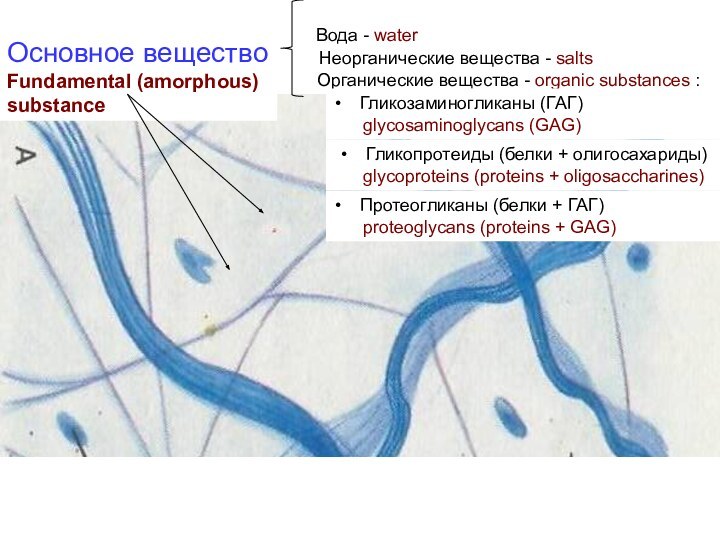
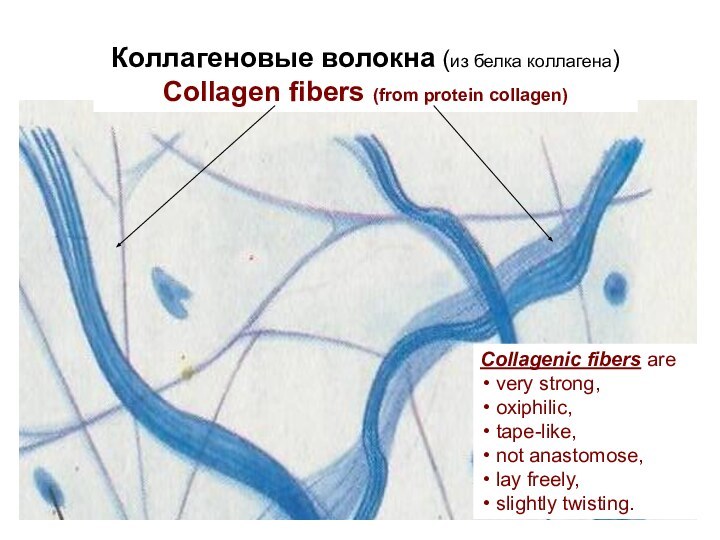
скелет)
2. Трофическая (обмен веществ между кровью и клетками)
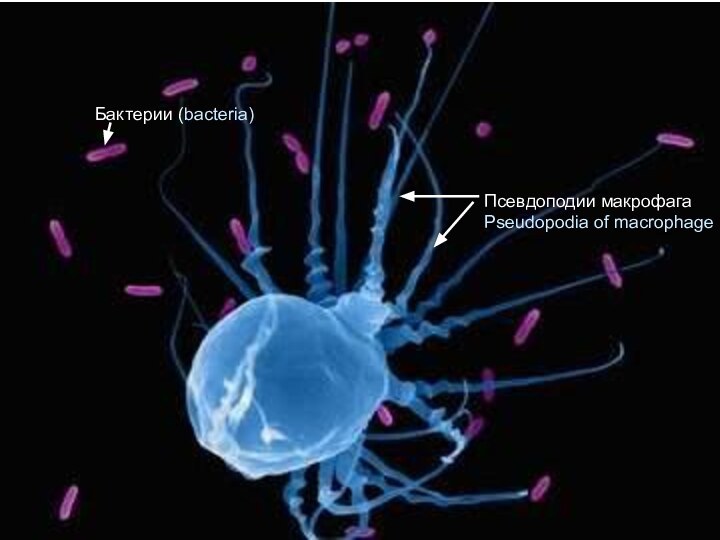
3. Защитная
(механич. защита, прочность органов, фагоцитоз макрофагами, участие в воспалении и иммунном ответе)4. Кроветворная (микроокруже-ние для клеток гемопоэза)
5. Пластическая (адаптирует к изменяющимся условиям за счёт изменения обмена веществ)
Functions of
connective tissues
Basic - make capsules of organs,
tendons, fascia, skeleton.
2. Trophic - metabolism between
blood and cells.
3. Protective - mechanical protection,
durability of organs, phagosytosis by
macrophages, participates in an
inflammation and immunity.
4. Hemopoietic - a microenvironment
for hemopoiesis cells.
5. Plastic - adapts organs at change of
conditions due to change of
a metabolism, participates in
regeneration.