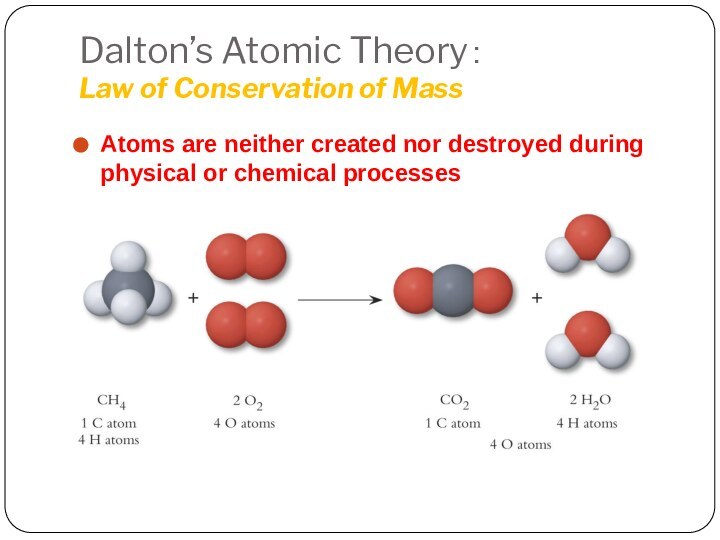
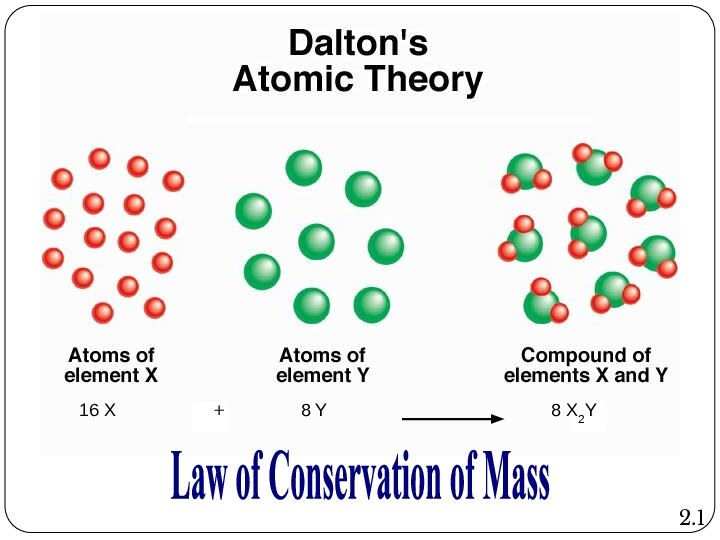
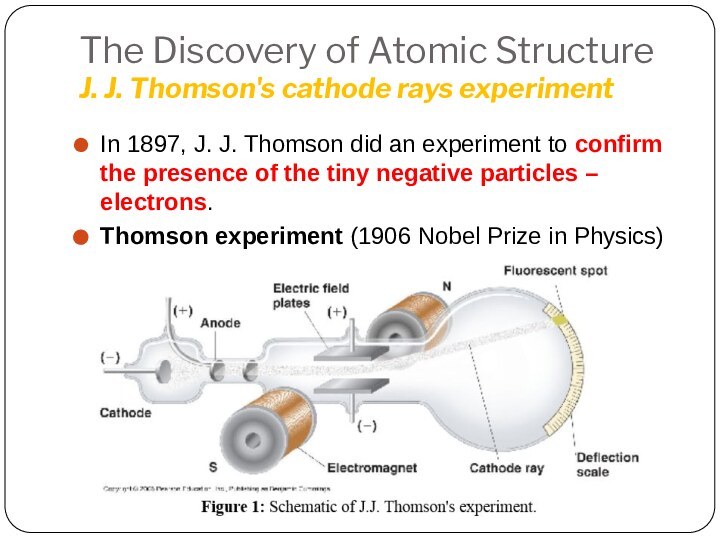
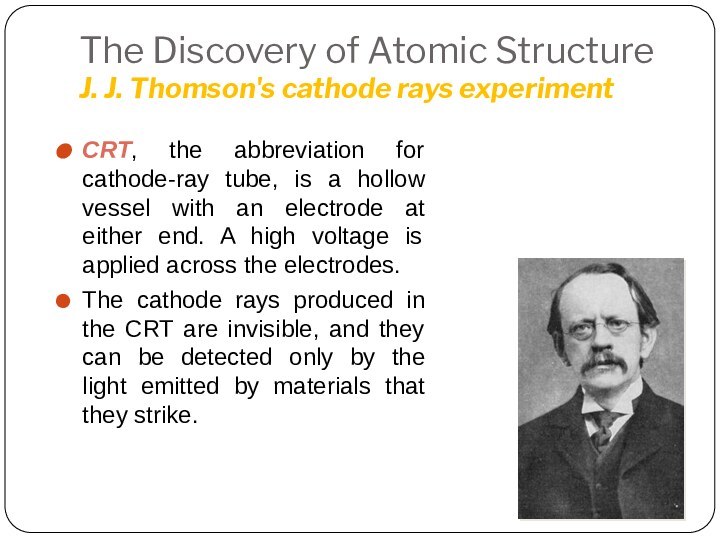
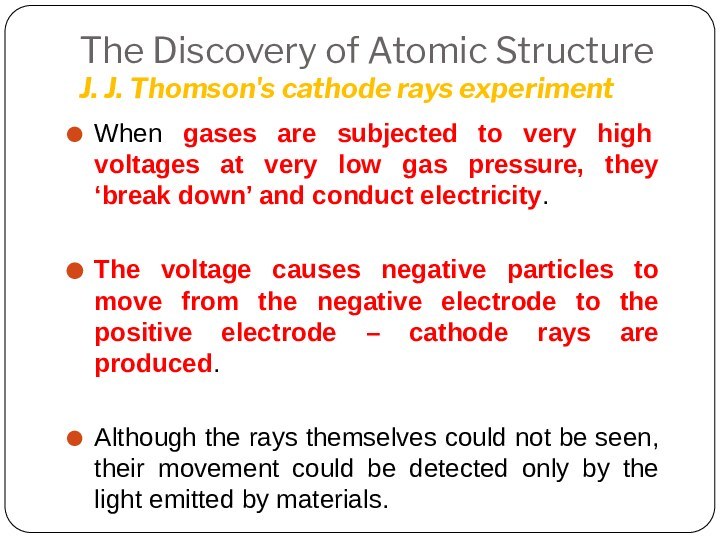
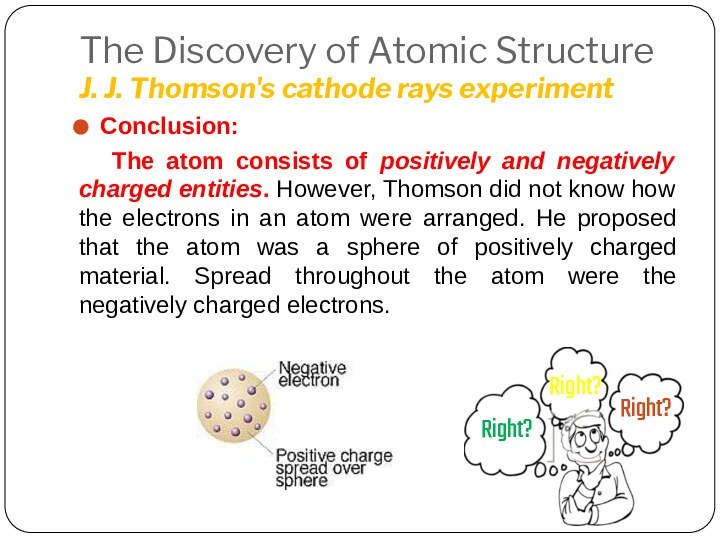
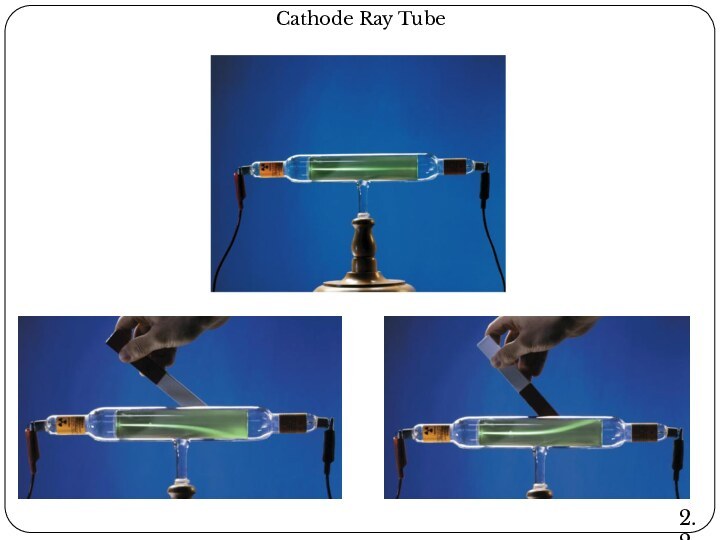
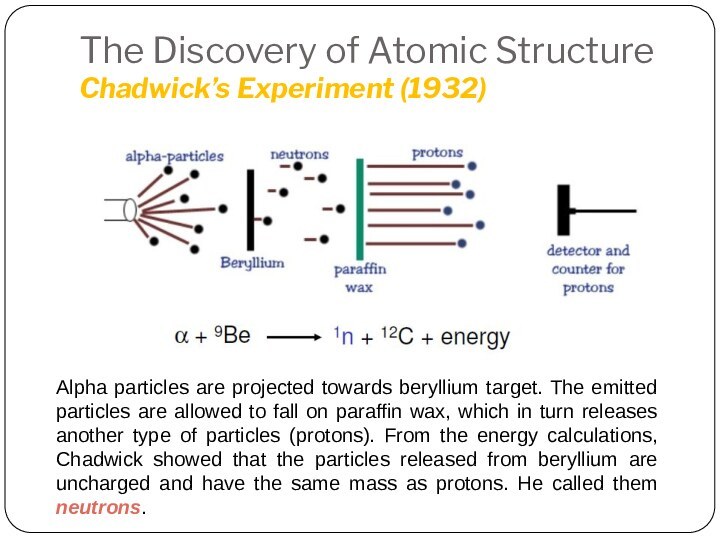
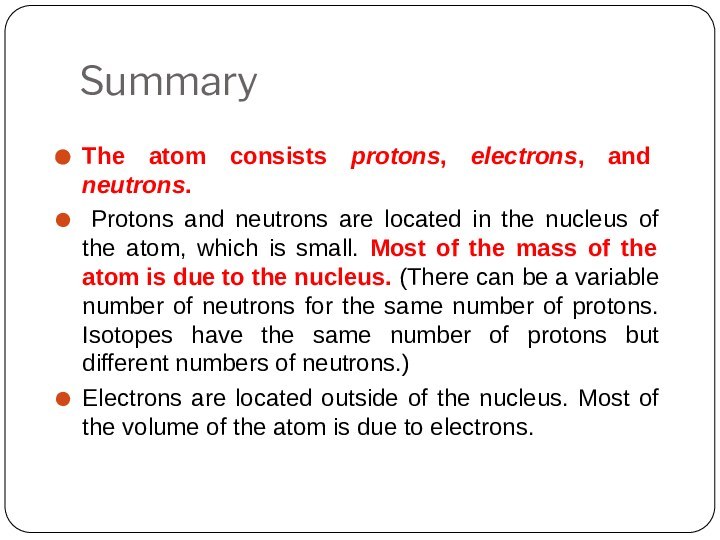
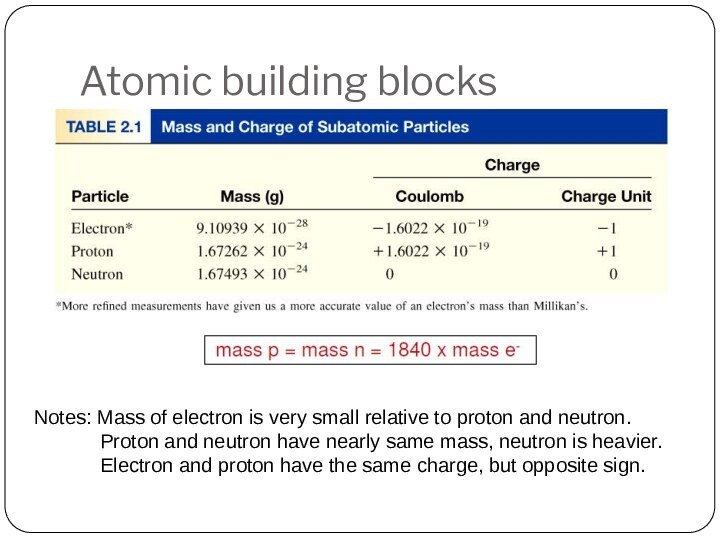
Leucippus originated the atom concept.
One of his students, Democritus
(460BC-371BC) extended it. There are five major points in their atomic concept:
All matter is composed of atoms, which are too small to be seen. These atoms CANNOT be further split into smaller portions.
There is empty space between atoms.
Atoms are completely solid.
Atoms are homogeneous同質, with no internal
structure.
Atoms can differ in size, shape, and weight.