- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Introduction to laboratory-treatment of uncertainties
Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Physics LaboratoryErrors / Uncertainties in MeasurementsRandom and Systematic ErrorsEstimating Random Experimental ErrorsCombining Experimental Errors
- 3. Your lab book must be submitted at
- 4.
- 5.
- 6. Accuracy: The degree to which the result
- 8. Random ErrorVaries between successive measurements of the
- 9. A result is said to be accurate
- 10. Digital meter: reading error is usually taken
- 12. When you have several measurements of the
- 14. When two quantities are proportional, you can
- 16. When variables are multiplied or divided, fractional
- 17. When variables are added or subtracted, absolute
- 18. Suppose we want to estimate the acceleration
- 19. Knowing the true value of g at
- 20. Скачать презентацию
- 21. Похожие презентации
Introduction to Physics LaboratoryErrors / Uncertainties in MeasurementsRandom and Systematic ErrorsEstimating Random Experimental ErrorsCombining Experimental Errors

















Слайд 2
Introduction to Physics Laboratory
Errors / Uncertainties in Measurements
Random
and Systematic Errors
Слайд 3 Your lab book must be submitted at the
end of the lab session.
Your report must be structured
Introduction
/ Aim of the experimentApparatus
Experimental results (including tables and graphs)
Answers to the questions in the lab instructions
Uncertainty analysis
Conclusion
Слайд 6 Accuracy: The degree to which the result of
a measurement, calculation conforms to the correct value or
a standard=> accuracy is the measure of exactness
Precision: Refinement in a measurement, calculation, as represented by the number of digits given
=> precision is the measure of reproducibility or consistency
Слайд 8
Random Error
Varies between successive measurements of the same
quantity
Is equally likely to be positive or negative
Can be
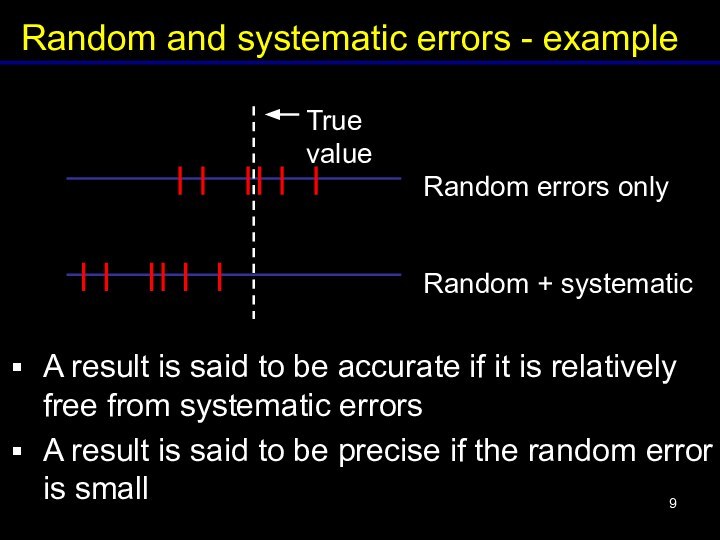
reduced by measuring the same quantity several times and taking the average (or the mean)Слайд 9 A result is said to be accurate if
it is relatively free from systematic errors
A result is
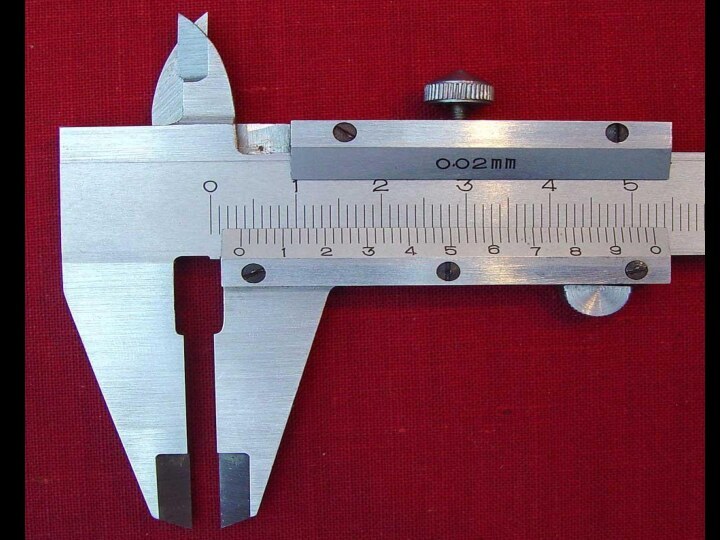
said to be precise if the random error is smallСлайд 10 Digital meter: reading error is usually taken as
V =
(3.36± 0.01) VLinear / Vernier Scale: reading error is usually taken as the smallest scale division
L = (16.7 ± 0.1) cm
Слайд 12 When you have several measurements of the same
quantity, the best estimate is the average (mean)
The random
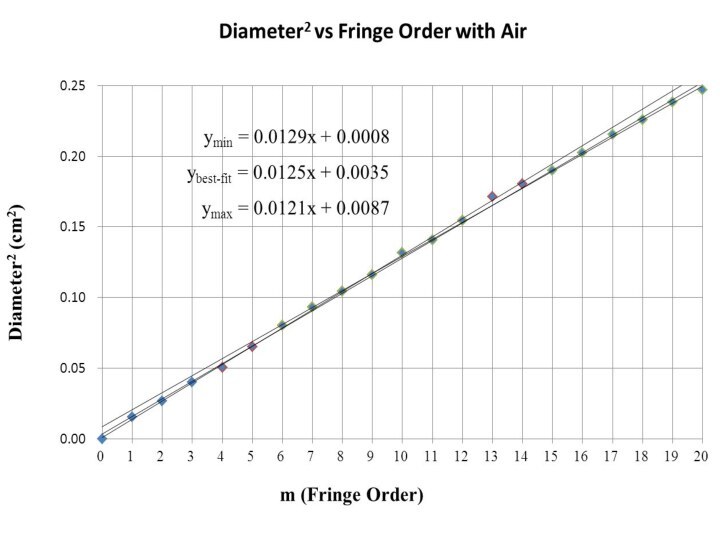
error can be estimated from the minimum and maximum valueСлайд 14 When two quantities are proportional, you can estimate
(visually or using Excel) the random error of the
gradient of the best-fit line as follows:1) Draw a best-fit line and calculate the gradient G
2) Draw two lines of minimum (Gmin) and maximum (Gmax) gradients
3) Estimate the uncertainty in the gradient ΔG as:
Note that gradients usually have a dimension (hence a unit)
Слайд 16 When variables are multiplied or divided, fractional uncertainties
are added
is called the fractional
uncertainty in AIt has no dimension
Слайд 17 When variables are added or subtracted, absolute uncertainties
are added
is called
the absolute uncertainty in AIt has the same dimension as A
Слайд 18 Suppose we want to estimate the acceleration due
to gravity, g, using a simple pendulum and we
estimated:- the period T = (1.848 ± 0.015) s from multiple readings
- the length L = (0.95 ± 0.05) m
Calculate the value of g and its estimated absolute random uncertainty