- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Lesson planning
Содержание
- 2. Lesson plan componentsBrainstorm within the class what
- 5. What are they?Work in small groups and
- 7. Why plan?Look at these comments from teachers.
- 8. I don’t have time to planI think
- 9. Benefits of planning Brainstorm in your groups
- 10. Provides the framework for organizing ideas, methodology,
- 11. Practice exercise Look at the extract of
- 15. What are lesson aims?Statements which describe what
- 16. Main aims – the overarching aim of
- 17. Subsidiary aims – second in importance of
- 18. Personal aims – these focus on an
- 19. Why are learning aims important?They provide a
- 20. Writing effective aimsLook at these two aims.
- 21. Not effective aim:- doesn’t say what learners
- 22. Practical exercise Identifying different learning aimsTo
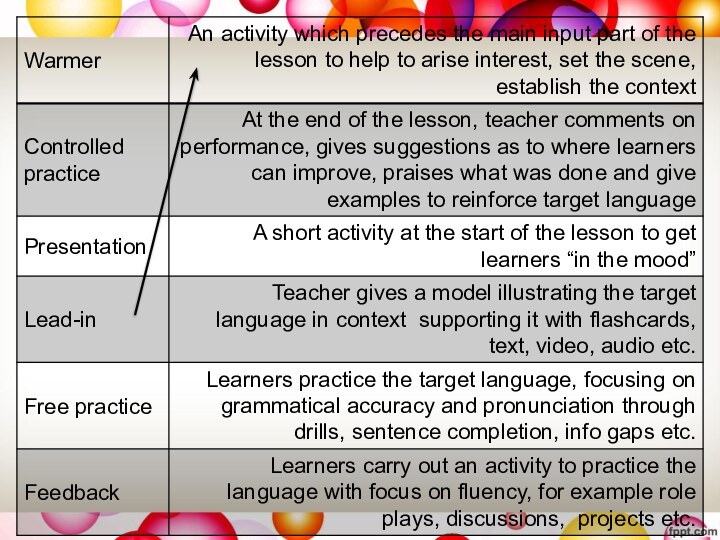
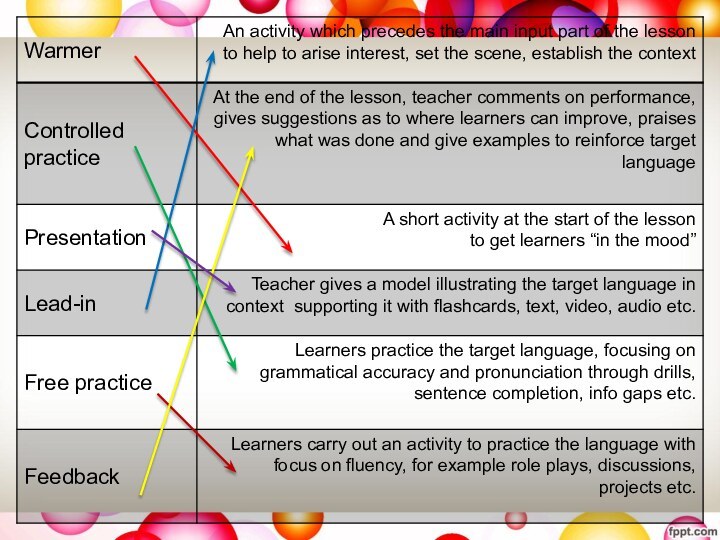
- 23. Lesson stagesMatch the lesson stage to the description, discuss with a partner.
- 26. Put the components of the lesson in
- 27. Warmer (games, brainstorming, chatting, interview, opinion sharing,
- 28. Home taskRead lecture “Lesson planing”Read article “Creating
- 29. Скачать презентацию
- 30. Похожие презентации
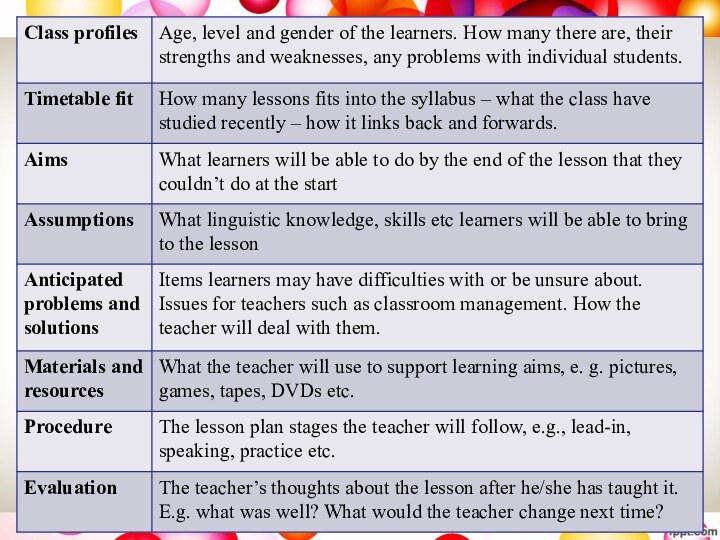
Lesson plan componentsBrainstorm within the class what are the components of a lesson plan and fill the following scheme


























Слайд 5
What are they?
Work in small groups and match
the lesson plan components with the definitions. Check your
answers with next slide
Слайд 7
Why plan?
Look at these comments from teachers. Which
ones reflects how you feel about planning? Discuss in
pairs.
Слайд 8
I don’t have time to plan
I think it’s
important to have aims
I never stick to plans
The textbook
is my planPlanning helps me to teach more efficiently
I don’t do detailed plan, but make rough notes
Слайд 9
Benefits of planning
Brainstorm in your groups and
add your ideas to the list, for example:
Helps to
think what learners will achieve in the lessonHelps teachers to know where they are going and how they are getting there
Слайд 10 Provides the framework for organizing ideas, methodology, materials
etc.
Helps make the lesson coherent.
Avoids over – domination of
coursbooks.Demonstrates to learners that teacher knows what he/she’s doing
Being prepared boosts teacher confidence
Helps to identify any problems or difficulties which may arise during the lesson
Helps teacher to adapt to different classes
Developmental – a learning document for teachers to reflect on after the lesson.
Helps to identify the kinds of activities and materials to include to achieve aims
A plan can link the lesson explicitly to syllabus objectives
Слайд 11
Practice exercise
Look at the extract of the
training session you are following today. Try to complete
the components
Слайд 15
What are lesson aims?
Statements which describe what learners
will be able to do by the end of
the lessonA focus on what learners will learn rather than what teacher will teach
There are 3 types of aims:
Main aims
Subsidiary aims
Personal aims
Слайд 16 Main aims – the overarching aim of the
lesson. These tend to be worded very specifically. The
language learners will understand or be able to use, and the context they will understand or be able to use - this language are usually stated. E.g., learners will be able to discuss leisure plans for the coming week, using the present continuous form.Слайд 17 Subsidiary aims – second in importance of main
aims (usually called objectives). These tend to be worded
less specifically than main aims, and are liked to the main aims of the lessons. E.g.: to enable learners to review / activate previously learnt lexis relating to leisure interestsСлайд 18 Personal aims – these focus on an aspect
of teaching the teacher him or herself would like
to practice / experiment with / improve on e. g.: to provide learners with more efficient feedback.
Слайд 19
Why are learning aims important?
They provide a purpose
and direction for teaching and learning
They enable teachers to
focus on what their learners need to achieveThey help teachers to adapt textbooks to their learners’ needs
They provide a framework for the lesson
They help to the teachers to select appropriate materials and activities
They help teacher to anticipate possible problems an build in solutions
They can serve as a reference point for teachers to measure learners achievements
Слайд 20
Writing effective aims
Look at these two aims. Whish
one do you think more efficient? Which one is
less efficient?Learners will be able to use the present perfect simple to describe situations in their live which began in the past and are still true now.
To teach the present perfect simple with time adverbials
Now think of an effective aim. What makes it less effective? How do you check aims are effective? Brainstorm the ideas and criteria for effective aims.
Слайд 21
Not effective aim:
- doesn’t say what learners will
be able to do
It doesn’t give a context
It is
vague and lacking in detailsIt would be difficult to measure if learners had achieved the aim
Criteria for effective aims
Learner centered, focused on what student will be able to do
Say which situation, context etc the language will be used in
State exactly which sub skills will be developed
Ensure the aims are measurable, i.e., how will teacher know that learners can understand and perform the target language/ situation described in the aims
Слайд 22
Practical exercise
Identifying different learning aims
To use strategies
for dealing with unknown words in reading comprehension passages:
deducing meaning from the context, using knowledge of the world, using word structure.To improve handwriting on the board
To revise language for describing people
To use narrative tenses simple past and past continuous to create stories on the theme of Halloween
To develop learners’ ability to express opinions
To give learners’ a chance to speak without correcting them every time they make a mistake
To give instructions to learners in English
To use imperatives to write instructions for making drinks
To expand vocabulary on the topic of the environment
Слайд 26 Put the components of the lesson in the
logical order
Warmer
Controlled practice
Presentation
Lead in
Free practice
Feedback
Слайд 27 Warmer (games, brainstorming, chatting, interview, opinion sharing, writing
questions and interviewing etc.)
Lead in (mingling, survey, quiz, questionary,
associations, mind maps, discussions etc.)Presentation (vocabulary, text, song, chant, grammar etc.)
Controlled practice (exercises: matching, info gaps completing, true / false, questions, multiple choice etc.)
Free practice (interview, role-play, jigsaw, project, paragraph writing)
Feedback (individually / for a small group/ for the whole class, orally / written, teacher only / together with the class / nominated person – evaluator / traditional assessment / score ore points etc.)