- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Придаточные предложения в английском языке
Содержание
- 2. Subordinate clausesSubject clauses (придаточные подлежащие)Predicative clauses (придаточные
- 3. Subject clausesПридаточные предложения подлежащие (Subject Clauses) — отвечают
- 4. Predicative clausesПридаточные предложения сказуемые (Predicative Clauses) — вводятся
- 5. Object clausesПридаточные дополнительные предложения (Object Clauses) — отвечают
- 6. Attributive clausesПридаточные определительные предложения (Attributive Clauses) — отвечают
- 7. Adverbial clausesПридаточные обстоятельственные предложения (Adverbial Clauses) — делятся
- 8. Adverbial clausesAdverbial clauses of timeAdverbial clauses of
- 9. Though there were many vacant places she couldn’t
- 10. Add the phrase in brackets to the
- 11. Insert necessary word (who,which…)A hotel is a
- 12. Скачать презентацию
- 13. Похожие презентации
Subordinate clausesSubject clauses (придаточные подлежащие)Predicative clauses (придаточные сказуемые)Object clauses (Придаточные дополнительные предложения)Attributive clauses (Придаточные определительные)Adverbial clauses (Придаточные обстоятельственные)










Слайд 2
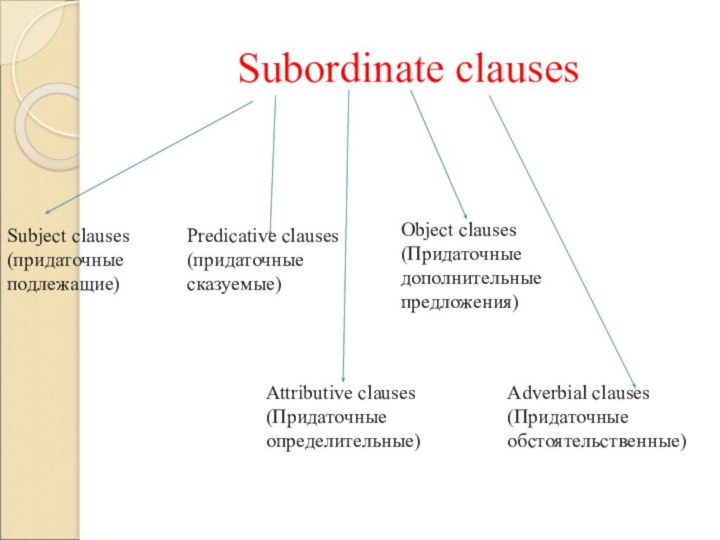
Subordinate clauses
Subject clauses (придаточные подлежащие)
Predicative clauses (придаточные сказуемые)
Object
clauses (Придаточные дополнительные предложения)
обстоятельственные)
Слайд 3
Subject clauses
Придаточные предложения подлежащие (Subject Clauses) — отвечают на
вопрос who? — кто? what? — что? и присоединяются к главному предложению при
помощи союзов that, whether, if или союзных слов who, whose, what, which, when, where, how, why.What he said at the sitting of the Court is very important.
Придаточные предложения подлежащие часто стоят после сказуемого. В этих случаях главное предложение начинается с местоимения it и стоит перед придаточным предложением.
It is strange that he made a mistake.
Слайд 4
Predicative clauses
Придаточные предложения сказуемые (Predicative Clauses) — вводятся теми
же союзами и союзными словами, что и придаточные предложения подлежащие.
This
is what he has done by 6 o’clock.
Слайд 5
Object clauses
Придаточные дополнительные предложения (Object Clauses) — отвечают на
вопрос what? — что?, whom? — кого?, for what? — за что? и
присоединяются к главному предложению теми же союзами и союзными словами, но присоединение может быть и бессоюзное.She said that she had caught a cold.
Слайд 6
Attributive clauses
Придаточные определительные предложения (Attributive Clauses) — отвечают на
вопрос what? — какой?, which? — какой?, который? и вводятся в сложное предложение местоимениями и
союзными словами who, whose, which, that — который, whom — которого или наречиями when — когда, where — где, how — как, why — почему.I know the girl who has won the first prize.
Слайд 7
Adverbial clauses
Придаточные обстоятельственные предложения (Adverbial Clauses) — делятся на
обстоятельственные предложения места, времени, образа действия, причины, цели, следствия,
условия, сравнения и обстоятельственные уступительные предложения.
Слайд 8
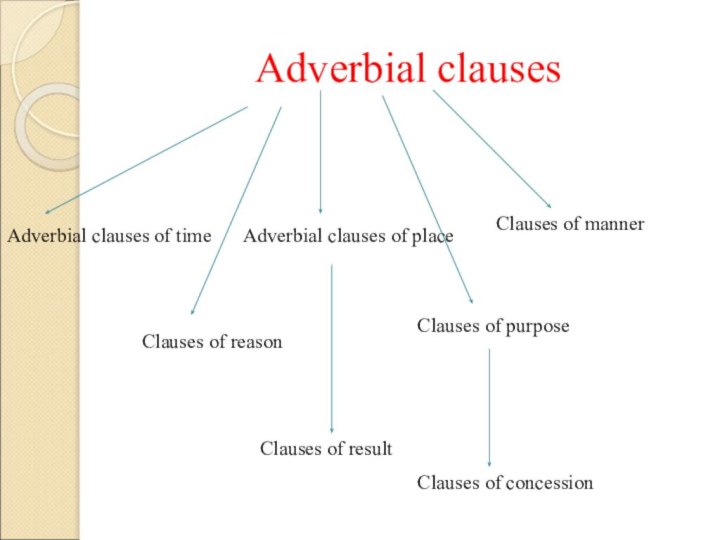
Adverbial clauses
Adverbial clauses of time
Adverbial clauses of place
Clauses
of manner
Clauses of reason
Clauses of purpose
Clauses of result
Clauses of
concessionСлайд 9 Though there were many vacant places she couldn’t get
a job.-Adverbial clause of concession
We camped at noon because we
were too tired.-Adverbial clause of reasonНе looked at me as if he saw me for the first time.-Adverbial clause of manner
Слайд 10 Add the phrase in brackets to the sentence
using 'that' or 'who' and a relative clause
1) She worked
for a man (the man used to be an athlete)2) They called a lawyer (the lawyer lived nearby)
3) I sent an email to my brother (my brother lives in Australia)
4) The customer liked the waitress (the waitress was very friendly)
5) We broke the computer (the computer belonged to my father)
6) I dropped a glass (the glass was new)
7) She loves books (the books have happy endings)
Слайд 11
Insert necessary word (who,which…)
A hotel is a place people
stay when they're on holiday.
What's the name of the
woman lives in that house?What do you call someone writes computer programs?
A waiter is a person job is to serve customers in a restaurant.
Overalls are clothes people wear to protect their clothes when they are working.
Is that the shop you bought your new laptop?
He's the man son plays football for Manchester Utd.
Hal didn't get the job he applied for.