- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Ренессанс. На английском языке.
Содержание
- 2. A distinctive feature of the Renaissance -
- 3. Renaissance is divided into 4 stages:Protorenessans(2nd half
- 4. ProtorenessansProtorenessans closely associated with the Middle Ages,
- 5. First of all art protorenessansa manifested in
- 6. The period of so-called "Early Renaissance"
- 7. High Renaissance The third period of
- 8. Late Renaissance Later Renaissance in Italy
- 9. Philosophers of the Renaissance• Nicholas of
- 10. LiteratureThe true ancestor of the Renaissance
- 11. artFor the painting of the Renaissance is
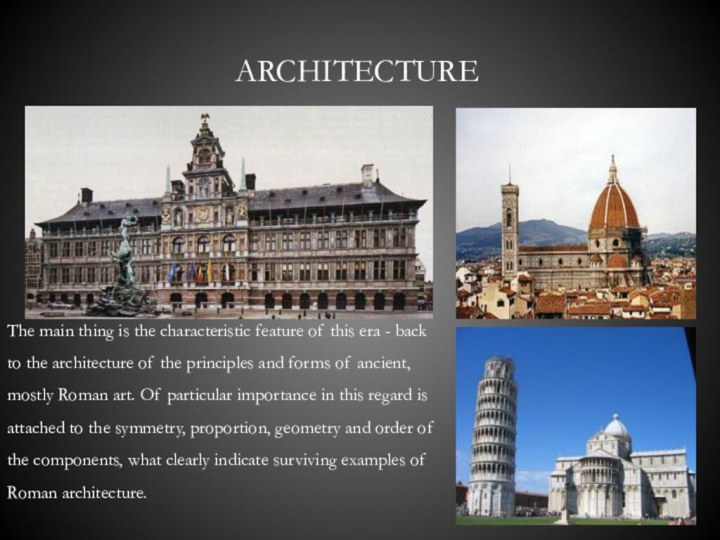
- 12. ArchitectureThe main thing is the characteristic
- 13. Filippo Brunelleschi (1377-1446) - the founder
- 14. His job
- 15. Скачать презентацию
- 16. Похожие презентации
A distinctive feature of the Renaissance - the secular nature of the culture, its humanism and anthropocentrism. Blooming interest in ancient culture, it is as if the "rebirth" - and there was a term.














Слайд 3
Renaissance is divided into 4 stages:
Protorenessans(2nd half of
the XIII century-XIV century)
2. Early Renaissance (beginning of XV
- the end of the XV century) 3. High Renaissance (end XV - the first 20 years of the XVI century)
4. Late Renaissance (mid XVI - 90 years of the XVI century)
Слайд 4
Protorenessans
Protorenessans closely associated with the Middle Ages, the
Byzantine, Romanesque and Gothic traditions of this period was
the forerunner of the Renaissance. It is divided into two sub-periods: before the death of Giotto di Bondone and after (1337). The most important discovery, the brightest masters live and work in the first period. The second part is related to the epidemic of plague that struck Italy.Слайд 5 First of all art protorenessansa manifested in sculpture
(Nicolo and Giovanni Pisano, Arnolfo di Cambio, Andrea Pisano).
Painting is represented by two artistic schools: Florence (Cimabue, Giotto) and Siena (Duccio, Simone Martini). The central figure of the painting became Giotto.Слайд 6 The period of so-called "Early Renaissance" covers a
time in Italy from 1420 to 1500. During these
eighty years the art has not completely renounces the traditions of the recent past, but try to mix them elements borrowed from classical antiquity.Early Renaissance
Слайд 7
High Renaissance
The third period of the Renaissance -
the time of the magnificent development of his style
- called "High Renaissance". It extends approximately in Italy from 1500 to 1527. At this time, the center of the influence of Italian art from Florence moved to Rome, thanks to the accession to the papal throne Julius II - human ambitious, daring, adventurous, privlёkshego to his court the best Italian artists, who held their numerous and important works and give a different example of love to art .
Слайд 8
Late Renaissance
Later Renaissance in Italy covers the period
from the 1530s on the 1590-1620-ies. this time, the
Arts and Culture in its diverse manifestations. In Southern Europe triumphed Counter-Reformation, which cautiously looking at any free, including the human body, and the chanting of the resurrection of the ideals of antiquity as the cornerstones of the Renaissance ideology.
Слайд 9
Philosophers of the Renaissance
• Nicholas of Cusa
•
Leonardo Bruni
• Marsilio Ficino
•Galileo Galilei
• Nicolaus
Copernicus• Giordano Bruno
• Giovanni Pico della Mirandola
• Lorenzo Valla
• Giannozzo Manetti
• Pietro Pomponazzi