- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему к интегрированному уроку по английскому языку и биологии Водные папоротники
Содержание
- 2. Fern - any of numerous flowerless and
- 3. Ferns evolved from moss. Part of scientists
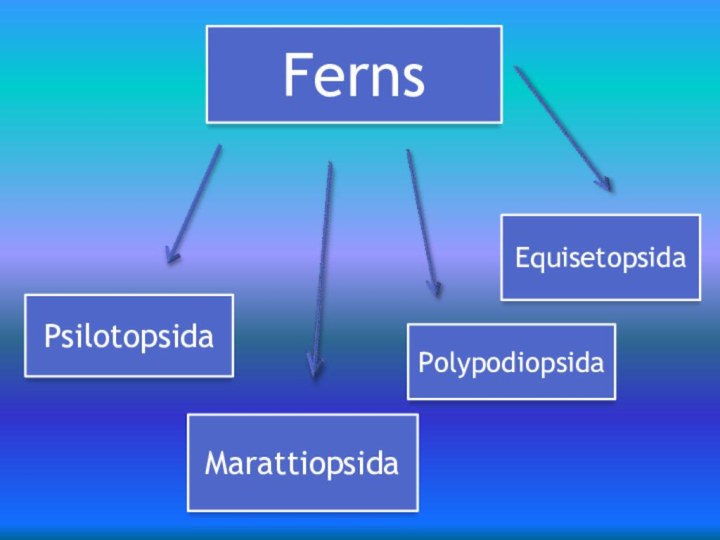
- 4. FernsPsilotopsidaEquisetopsidaMarattiopsidaPolypodiopsida
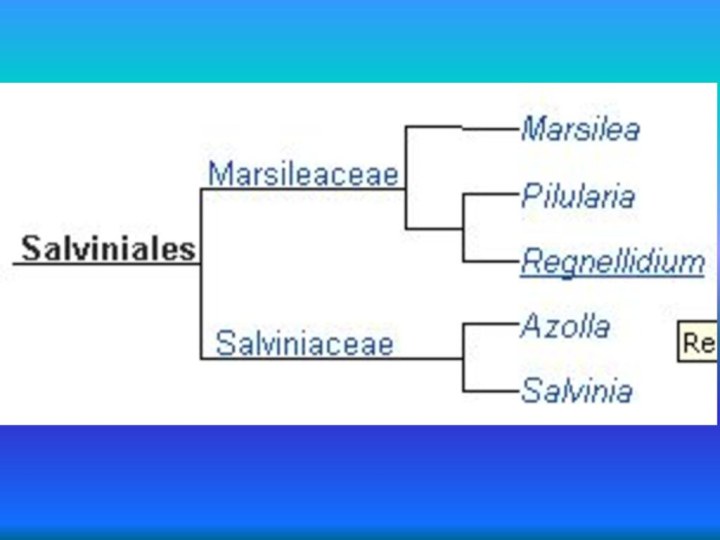
- 5. Salviniales are all aquatic and differ from
- 6. The ferns of this order vary radically
- 8. Marsilea Marsilea is a genus of approximately
- 9. Pilularia Depending on the taxonomic revisor, the
- 10. RegnellidiumRegnellidium is a monotypic genus of ferns
- 11. AzollaAzolla (mosquito fern, duckweed fern, fairy moss,
- 12. In addition to its traditional cultivation as
- 13. Azolla has also been suggested as a
- 14. SalviniaSalvinia, a genus in the family Salviniaceae,
- 15. Скачать презентацию
- 16. Похожие презентации
Fern - any of numerous flowerless and seedless vascular plants having true roots from a rhizome and fronds that uncurl upward; reproduce by spores













Слайд 3
Ferns evolved from moss.
Part of scientists believes
that the horsetails, club mosses, mosses and the department
evolved from psilophytes.Слайд 5 Salviniales are all aquatic and differ from all
other ferns in being heterosporous, meaning that they produce
two different types of spores (megaspores and microspores) that develop into two different types of gametophytes (female and male gametophytes, respectively), and in that their gametophytes are endosporic, meaning that they never grow outside the spore wall and cannot become larger than the spores that produced them.Слайд 6 The ferns of this order vary radically in
form from one another and do not look particularly
fern-like. Species of the family Salviniaceae are natant (floating), while those of the family Marsileaceae are rooted. However, the natant species may temporarily grow on wet mud during times of low water, and the Marsileaceae may grow as emergent species, depending on species and location.
Слайд 8
Marsilea
Marsilea is a genus of approximately 65 species
of aquatic ferns of the family Marsileaceae. The name
honours Italian naturalist Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli (1656–1730)These small plants are of unusual appearance and do not resemble common ferns. Common names include water clover and four-leaf clover because the long-stalked leaves have four clover-like lobes and are either held above water or submerged.
Слайд 9
Pilularia
Depending on the taxonomic revisor, the genus
contains between 3 and 6 species of small plants
with thread-like leaves, and creeping rhizomes. The sporangia are borne in spherical sporocarps ("pills") which form in the axils of leaves. Pilularia minuta from SW Europe is one of the smallest of all ferns.
Слайд 10
Regnellidium
Regnellidium is a monotypic genus of ferns of
family Marsileaceae.
The single living species, Regnellidium diphyllum, Two-leaf Water
Fern, is native to South Eastern Brazil and adjacent regions of Argentina. It resembles its relatives from the genus Marsilea, but has 2-lobed leaves (rather than 4). This fern is sometimes grown in aquaria. It is the only non-flowering plant that produces latex.
Слайд 11
Azolla
Azolla (mosquito fern, duckweed fern, fairy moss, water
fern) is a genus of seven species of aquatic
ferns in the family Salviniaceae. They are extremely reduced in form and specialized, looking nothing like other typical ferns but more resembling duckweed or some mosses.Слайд 12 In addition to its traditional cultivation as a
bio-fertilizer for wetland paddy (due to its ability to
fix nitrogen), azolla is finding increasing use for sustainable production of livestock feed.Azolla is rich in proteins, essential amino acids, vitamins and minerals. describe feeding azolla to, chickens and egg production of layers, as compared to conventional feed. One FAO study describes how azolla integrates into a tropical biomass agricultural system, reducing the need for inputs.Слайд 13 Azolla has also been suggested as a food
stuff for human consumption. However, no long term studies
of the healthiness of eating Azolla have been made on humans and Azolla may contain BMAA, a substance that is a possible cause of neurodegenerative diseases.
Слайд 14
Salvinia
Salvinia, a genus in the family Salviniaceae, is
a floating fern named in honor of Anton Maria
Salvini, a 17th-century Italian scientist.Salvinia, like the other ferns in order Salviniales are heterosporous, producing spores of differing sizes. However, leaf development in Salvinia is unique. The upper side of the floating leaf, which appears to face the stem axis, is morphologically abaxial.