Слайд 2
1D.Mendeleev created
2 I. Pavlov discovered
3 S. Freid
(Freud) created
4. A. Einstein worked on the
5.
Pythagoras invented
6. J. Cook explored
7 M. Lomonosov discovered …made
8 I. Newton discovered
9 Aristotel (Aristotle) started
10. R.Amundsen explored
Слайд 3
1D.Mendeleev created (the table of chemical elements).
2 I.
Pavlov discovered (conditional reflexes)
3 S. Freid (Freud) created
(psychoanalysis).
4. A. Einstein worked on the (theory of relativity).
5. Pythagoras invented (the theorem)
6. J. Cook explored (Australia)
7 M. Lomonosov discovered …made (the atmosphere on Venus and … important contributions to literature, education, science).
8 I. Newton discovered ( laws of motion and universal gravitation).
9 Aristotel (Aristotle) started (the study of philosophy and defined metaphysics )
10. R.Amundsen explored (Arctic)
Слайд 4
Discoveries
and
Explorations
Слайд 8
“The scientist is not a person who gives
the right answers, he's one who asks the right
questions.”
― Claude Lévi-Strauss
Слайд 11
Pythagoras
570 - 490 BC
Aristotel
384 – 322 BC
Newton
1643 -
1727
Lomonosov
1711 - 1765
Mendeleev
1834 - 1907
Pavlov
1849 - 1936
Freid
1856 - 1939
Einstein
1879
- 1955
Слайд 12
_____________________He lived in a Greek colony in Italy.

He worked in such fields of science as Philosophy,
Physics and Mathematics. Also he founded his own philosophical school. He was very clever and wise man. He was the author of a famous Pythagorean Theorem.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He lived in Ancient Greece. He was very famous and even popular scientist. Не was the first who made a system of all philosophical studies. He created the term “logic”. Also he defined “politics” as some separate branch of scientific research.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He was English physicist, mathematician and astronomer. He was the author of many and many physical theories and laws. Нe was one of the founders of the classical physics. The most famous of his works are the three laws of Mechanics and the Law of Universal Gravitation.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He was an outstanding Russian scientist-naturalist. He worked in the fields of Physics, Geography, Chemistry, Thermodynamics, History, Literature and many others. He created technology of producing of colored glass. He made a project of Moscow State University.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He was famous Russian scientist who worked in the fields of Chemistry, Economy, Pedagogic, Aerostatics etc. One of his most outstanding research works was devoted to periodical law of chemical elements. He created a table to systematize them. And even left some places for those elements that hadn’t been discovered at that time describing some of their characteristics.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________One of the most competent Russian scientists known all over the world thanks to his research works in Psychology, Physiology. He is a creator of science about higher nervous activity. In 1904 he got Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology for his work “Physiology of Digestion”.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He was born in Austria. He was a psychologist, psychiatrist and neurologist. He was a founder of therapeutic school in Psychology. His most famous works were devoted to dreams, problems of childhood, the conscious and the unconscious.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____________________He lived in Germany. He was one of the founders of modern Theoretical Physics. He was the Doctor of 20 most prestigious universities of the world. He was the author of more than 300 scientific works in Physics and about 150 in History, Philosophy and Political Journalism. In 1921 he got Nobel Prize in Physics. He was the author of Quantum Theory and Theory of Relativity.
Слайд 14
This is the House that Jack built.
This
is the Malt,
That lay in the House that Jack
built.
This is the Rat,
That ate the Malt,
That lay in the House that Jack built.
This is the Cat,
That killed the Rat,
That ate the Malt,
That lay in the House that Jack built.
This is the Dog,
That worried the Cat,
That killed the Rat,
That ate the Malt,
That lay in the House that Jack built.
…………………………………………………………..
Слайд 15
THE ATOM THAT BOHR BUILT
(with apologies to Jack)
Атом,
который построил Бор (простите, Джек)
This is the atom that
Bohr built,
This is the nucleus
That sits in the atom
That Bohr built.
This is the drop that looks like the nucleus
That sits in the atom
That Bohr built.
Вот атом, который построил Бор,
Это - протон,
Который в центр помещен
Атома,
который построил Бор.
А вот электрон,
Который стремглав облетает протон,
Который в центр помещен
Атома,
который построил Бор.
Слайд 16
https://vimeo.com/50639251
Nik Morris:
- Prize-winning animated documentary
Stars
There are billions of
stars in the univers. Stars are massive, energy-filled globes
of fiery gases. The force of gravity holds these gases together. At a star's core, atoms of hydrogen join together to form helium in a process called nuclear fusion. The energy generated by this process produces a star's heat and light. Collections of stars are called galaxies, and each galaxy contains many different types of stars.
Vocabulary
:
call - называть
contain (contained; contained) - содержать
core - ядро, центр
each - каждый
fiery - пламенный, газовый
fill (filled; filled) - заполнять
fusion - сплав
galaxy - галактика
hydrogen - водородный
join (joined; joined) - объединение, соединять
massive - массивный, огромный
nuclear - ядерный
together - вместе
universe - мир, вселенная
Слайд 18
“Everything must be made as simple as possible.
But not simplier.”
― Albert Einstein
Слайд 19
Marie Curie
Polish-born physicist Marie Curie and her French
husband Pierre are famous for their work on radioactivity.
They were inspired by the work of the French physicist Henri Becquerel (1852-1908). Marie Curie was the first to use the term "radioactive" for substances that have considerable electromagnetic activity. She also isolated two new radioactive elements, polonium and radium. After Pierre's death, she took over his job as professor of physics at the University of Paris, the first woman to teach there. She continued her research, looking for medical uses for radioactivity. She was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1903 and for chemistry in 1911.
Слайд 20
Nikola Tesla
The Croatian-born American inventor Nicola
Tesla
patented an electricity-generating and
distribution system that transmitted alternating
current (AC).
He developed and applied many other important ideas
in the fields of electricity and radio. The Tesla coil, an induction coil he invented, is used in radio technology and operates at every high frequencies. Tesla worked briefly for the American inventor Thomas Edison (1847-1931), but they fell out because they disagreed about the best form of electric current to use for large-scale supply. In the end, Tesla's alternating current system was favored over Edison's direct current (DC) system.
Слайд 21
Galileo Galilei
The work of Italian scientist Galileo Galilei
(known as Galileo) revolutionized astronomy. Galileo developed the telescope
and made important discoveries about the planets and the sun. His observations confirmed the work of the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) who believed that the Earth and other planets revolve around the sun. This finding went against the Church's teaching that the Earth is the center of the universe, and the Church punished Galileo. Galileo suggested the use of the pendulum in clocks and also discovered an important principle about gravity that the rate at which an object falls is not related to its weight.
Слайд 22
Hypatia
The first renowned woman of science was an
astronomer and mathematician named Hypatia from Alexandria, Egypt. Her
work was famed in many Mediterranean countries, but it came into conflict with the teaching of powerful Christian leaders, who ordered her to be murdered. For almost 1,000 years after Hypatia's death, the period in history known as the Middle Ages, few scientific advances were made in the Western world. Sadly, Hypatia is better remembered for the violence of her death than for her work in science.
Hypatia
Слайд 23
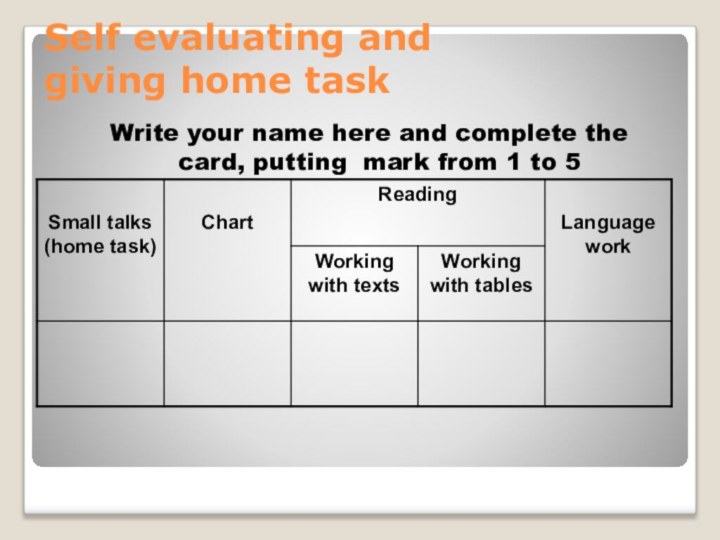
Self evaluating and
giving home task
Write your name
here and complete the card, putting mark from 1
to 5
Слайд 24
Hometask
Create one more entry to WIKIPEDIA about the
scientist you admire and be ready to present it.
Слайд 26
Тема урока Explorations and Discoveries
Оборудование Учебник, компьютер, проектор
,раздаточный материал; компьютерная презентация, материалы сети для создания
визуальной речевой опоры. фотографии ученых разных стран.
Тип урока Обобщения и систематизации знаний
Формы проведения Экскурс в историю, интерактивная беседа
Формы работы Групповая, самостоятельная
Методы обучения
Объяснительно - иллюстративный с элементами проблемного изложения;
Репродуктивный;
Частично – поисковый
Оборудование и наглядность Интерактивная доска, проектор, экран, компьютер.
Методическое обеспечение:
yчебник английского языка для 10 класса для общеобразовательных учреждений авторов Эванс В, Дули Д, Оби Б, Афанасьева О, Михеева И, - Москва, «Экспресс паблишинг», «Просвещение», 2015,глава 8., мультимедийная презентация (Приложение 2), раздаточный материал (Приложение 1,2,3,4)
Доп пособия: Activate B1+ Carolyn Barraclough, Megan Roderick Pearson Longman 2012 Chapter 12; My grammar Lab
Слайд 27
Планируемые результаты:
Предметные
Обучающиеся
-повторят российские и мировые научные достижения и ученых,
их свершивших
- попрактикуются в использовании новой лексики по теме
- попрактикуются в применении относительных придаточных предложений
-попрактикуют навыки письменной речи
- попрактикуют навыки устной речи
Личностные
-научатся осознавать себя членами школьного коллектива, рассмотрят историю и пути научных открытий
Слайд 28
Формируемые УУД
Познавательные Обучающиеся научатся
-
работать с информационным источником.
- выстраивать сложноподчиненные предложения описательного характера
-
извлекать информацию из прослушанного текста и просмотренного сюжета.
- работать с визуальной речевой опорой
- структурировать свои знания
- устанавливать логические связи, анализировать, сравнивать и структурировать свои знания
-определять и выделять основную и второстепенную информацию
Регулятивные
обнаруживать проблему, формулировать тему урока,
находить и исправлять ошибки, оценивать степень успешности
- выдвигать версии
- планировать свои действия
Коммуникативные
- работать в паре и группе, распределять поручения
-излагать свою точку зрения в письменной и устой форме,
-участвовать в презентации…
Слайд 29
Использованные сайты
http://teacherluke.co.uk/2016/01/20/326-catching-up-with-oli-future-predictions/
httphttp://http://teacherlukehttp://teacherluke.http://teacherluke.cohttp://teacherluke.co.http://teacherluke.co.ukhttp://teacherluke.co.uk/?http://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribehttp://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=http://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=successhttp://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=success#http://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=success#bloghttp://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=success#blog_http://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=success#blog_subscriptionhttp://teacherluke.co.uk/?subscribe=success#blog_subscription-2
http://englisholgasav.blogspot.ru/p/blog-page_29.html
http://novyurok.ru/userpanel/blizlistbids.php?robo_success_paid&robo_success_paid_order_id=23278701
http://infourok.ru/material.html?mid=114100
http://www.native-english.ru/topics/category/nauka