- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Basic concepts and definitions
Содержание
- 2. Review of modern technologies of software design. Organization of the software development process
- 3. VocabularyWaterfall – сарқырама - водопад gathering –
- 4. The Software ChallengePeople may come and go,
- 5. The Software Specification ChallengeSoftware specification is not
- 6. For the successful implementation of an IT
- 7. A Process of Software Development Process -
- 8. Software DesignDeriving a solution which satisfies software requirements
- 9. Stages of DesignProblem understandingLook at the problem
- 10. The Design ProcessAny design may be modelled
- 11. Phases in the Design Process
- 12. Design of small and large systems
- 13. The Software Life Cycle – The Life
- 14. Waterfall Model Model Falls (waterfall model or
- 15. The Diagram of Waterfall Model
- 16. The classic waterfall model includes the following
- 17. Key considerations for the use of such
- 18. Design Principles in Software Life Cycle ActivitiesTop-down
- 19. Requirements Analysis, Use Cases, and Sequence DiagramsFirst
- 20. Pre- and PostconditionsPrecondition: a statement of any
- 21. An Example: Telephone DirectoryMaintain a collection of
- 22. Dependencies Among Possible Actions
- 23. Things you already know (about) ...Java programs
- 24. The modern technologies of software designRapid application
- 25. Скачать презентацию
- 26. Похожие презентации
Review of modern technologies of software design. Organization of the software development process



















Слайд 2
Review of modern technologies of software design.
Organization
of the software development process
Слайд 3
Vocabulary
Waterfall – сарқырама - водопад
gathering – жинау
- сбор
Conversion – түрлендіру - преобразование
Deployment – орналастыру -
развертывание, размещениеDomain model - домен моделі - модель предметной области
Compliance – сәйкестігі - согласие
Flaws – кемшіліктер - дефекты, недостатки
commercial operation – коммерциялық операциялар - коммерческая эксплуатация
Maintain – қолдау - поддержка
Слайд 4
The Software Challenge
People may come and go, but
software may remain
A software product is often expected to
be used for an extended period of time by someone who did not write the program and who is not intimately familiar with its internal designSoftware may evolve
New features may be added, environments may change, so initial specification may be incomplete
Слайд 5
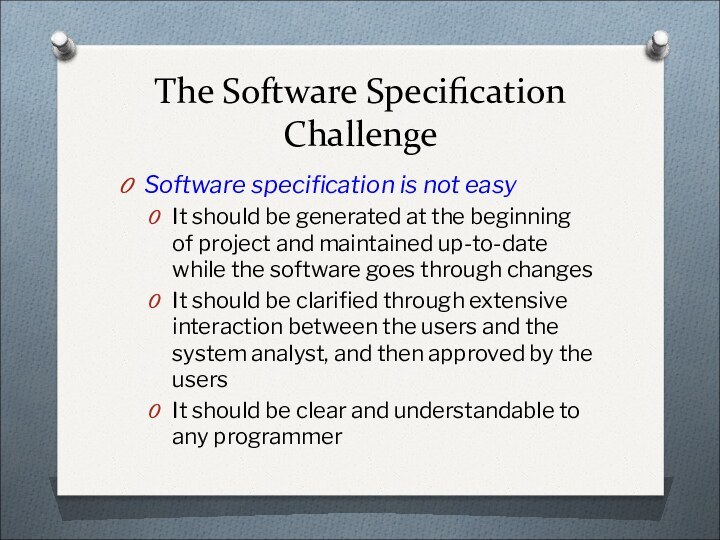
The Software Specification Challenge
Software specification is not easy
It
should be generated at the beginning of project and
maintained up-to-date while the software goes through changesIt should be clarified through extensive interaction between the users and the system analyst, and then approved by the users
It should be clear and understandable to any programmer
Слайд 6 For the successful implementation of an IT project
rather choose effective technology and development tools to provide
the necessary budget, and to find skilled developers.In any organization, there are rules and techniques of project participants (customers, analysts, developers, testers, technical writers) distribute among themselves tasks interact with each other, create project artifacts (specifications, source code, documentation).
These rules may be well organized or chaotic, or be formally documented to exist in the minds of the project team, but in any case it is their combination is called a process of development.
Слайд 7
A Process of Software Development
Process - a
special case of the more general concept of software
development methodologies.Examples of methodologies are structured programming or object-oriented analysis and design.
Слайд 9
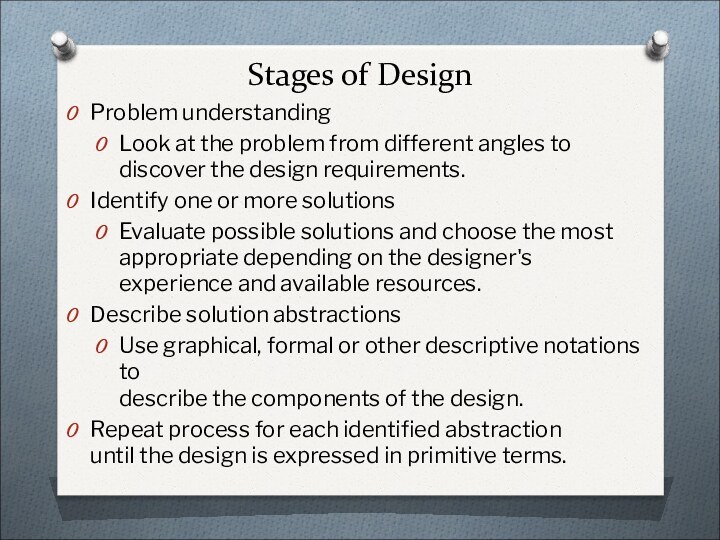
Stages of Design
Problem understanding
Look at the problem from
different angles to discover the design requirements.
Identify one or
more solutionsEvaluate possible solutions and choose the most appropriate depending on the designer's experience and available resources.
Describe solution abstractions
Use graphical, formal or other descriptive notations to describe the components of the design.
Repeat process for each identified abstraction until the design is expressed in primitive terms.
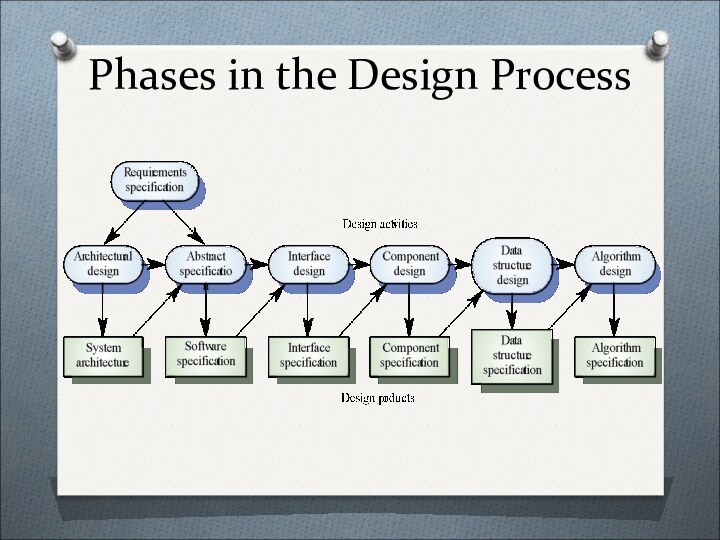
Слайд 10
The Design Process
Any design may be modelled as
a directed graph made up of entities with attributes
which participate in relationships.The system should be described at several different levels of abstraction.
Design takes place in overlapping stages. It is artificial to separate it into distinct phases but some separation is usually necessary.
Слайд 13 The Software Life Cycle – The Life and
Death of Software
Software products go through several stages as
they mature from initial concept to finished productThe sequence of stages is called a life cycle
Слайд 14
Waterfall Model
Model Falls (waterfall model or serial
development) - probably the most famous and historically appeared
one of the first development process.He was described in the article Royce (W.W. Royce) in 1970.
The basic idea is that the development process is divided into well-defined phases, performed strictly sequentially.
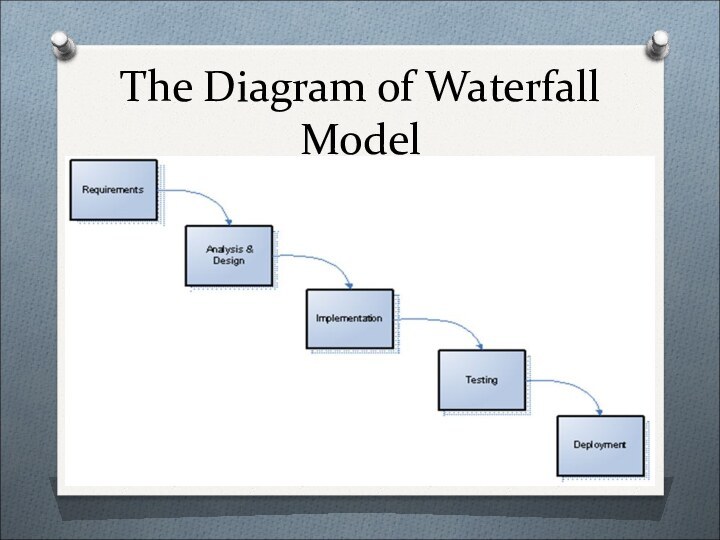
The name "waterfall" appeared due to the appearance of the diagram depicting the process:
Слайд 16
The classic waterfall model includes the following areas
Develop
requirements: gathering business requirements of the customer and their
conversion to the functional requirements of a software product.Analysis and Design: the development of a domain model, the design of the database schema, object model, user interface, etc.
Realization (implementation): creation of a product according to the specifications developed in the previous step.
Testing: includes the verification of compliance with the functionality of the software needs of users (validation), as well as finding flaws in implementation.
Deployment: user training, system installation, transfer into commercial operation.
Слайд 17 Key considerations for the use of such a
model development
As you know, the cost of correcting
mistakes made in the implementation of the project depends on how quickly these errors are detected and corrected. The error in the requirements simply correct requirements at the design stage, but if it becomes aware of after the completion of the deployment, the consequences can be catastrophic.
Waterfall model tends to reduce as far as possible, the number of long-lived errors.
For this design development should not start until the requirements are not identified with sufficient quality, the coding is not started until the complete system design, etc.
Слайд 18
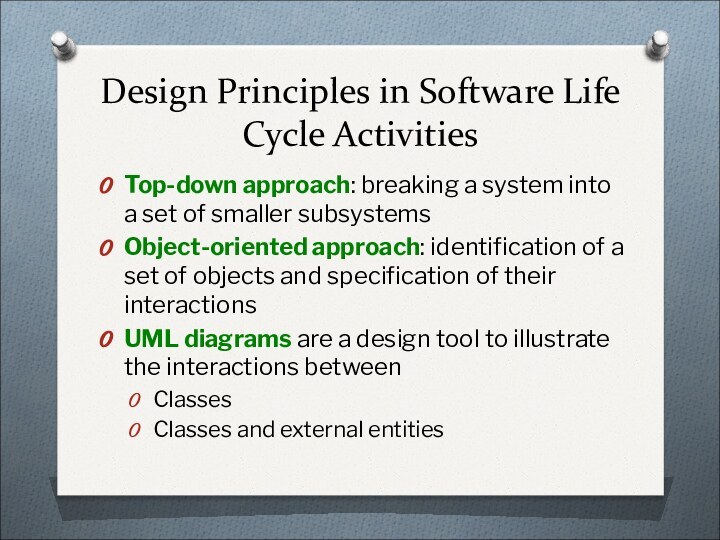
Design Principles in Software Life Cycle Activities
Top-down approach:
breaking a system into a set of smaller subsystems
Object-oriented
approach: identification of a set of objects and specification of their interactionsUML diagrams are a design tool to illustrate the interactions between
Classes
Classes and external entities
Слайд 19
Requirements Analysis, Use Cases, and Sequence Diagrams
First step
in analysis is to study the problem of input
and output requirements carefully to make sure they are understood and make senseUse case: list of the user actions and system responses for a particular sub-problem in the order that they are likely to occur
Sequence diagram: shows all the objects involved in this use case across the horizontal axis, time is shown along the vertical axis
Слайд 20
Pre- and Postconditions
Precondition: a statement of any assumptions
or constraints on the method data before the method
begins executionPostcondition: a statement that describes the result of executing a method
Слайд 21
An Example: Telephone Directory
Maintain a collection of telephone
directory entries, where each entry is referred to by
a unique name.Can read from a file, save to a file, lookup, add, remove, and change phone number
Слайд 23
Things you already know (about) ...
Java programs (you
know and love)
Classes and objects (you can create and
use)Inheritance (you understand and can extend)
Abstract classes (you remember what they are)
Interfaces (your contractual obligations)
Слайд 24
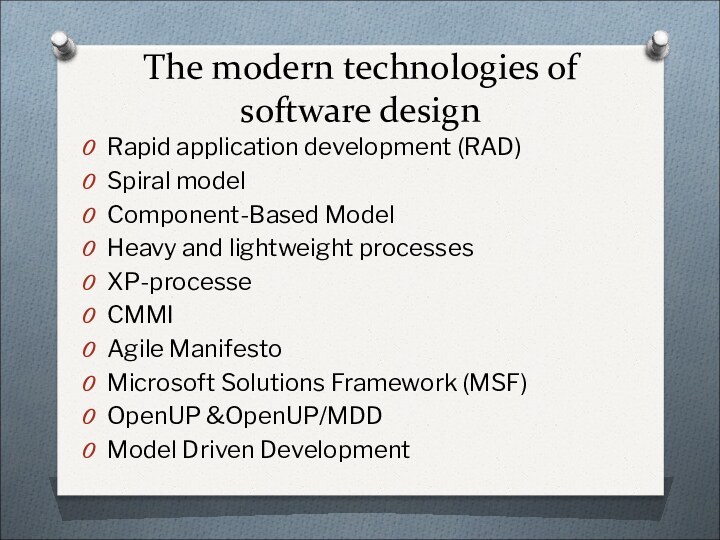
The modern technologies of software design
Rapid application development
(RAD)
Spiral model
Component-Based Model
Heavy and lightweight processes
XP-processe
CMMI
Agile Manifesto
Microsoft Solutions Framework
(MSF)OpenUP &OpenUP/MDD
Model Driven Development