Слайд 2
Agenda
Case Introduction
Background
Project Description
Our Analysis
Recommendation
Questions?
Слайд 3
The Walt Disney Company
Entertainment Conglomerate consisting of Media,
Studio Entertainment, Consumer Products and Theme Parks & Resorts
Theme
Park & Resorts Division
Current Park Locations: Anaheim, Orlando, Tokyo, Paris, Hong Kong (2005)
Also includes: The Disney Cruise Line, Disney Regional Entertainment, The Disney Vacation Club, The Anaheim Angels, and the Mighty Ducks of Anaheim
Revenues of $7 Billion in 2001, or 28% of company-wide revenue
Слайд 4
Disney’s Interest in China
Long-term
Consistently searching for areas
of expansion where there are un-captured markets
Current
Government relations
established through the Hong Kong Disneyland project indicate easier entry into the mainland
Competitive
Universal-Vivendi’s land purchase in Shanghai and proposed expansion into Beijing
Слайд 5
Agenda
Case Introduction
Background
Project Description
Our Analysis
Recommendation
Questions?
Слайд 6
Background: Disney Parks
Disneyland, Anaheim: 1955
Walt Disney World, Orlando:
1971
Tokyo Disneyland:1983
Owned and operated by the Oriental Land Company
Deal
structure indicative of financial turmoil within the company in the early 1980s with a 0% Equity stake
Revenue from royalties and management fees
Disneyland Paris/Euro Disneyland: 1992
Disney retains 39% of Equity Interest and receives management fees as part of reported revenue
Слайд 7
Hong Kong Disneyland
$1.8 Billion USD Project
60% Debt
80% Government
20%
Commercial
40% Equity
43% Disney
57% Government (will eventually sell down ownership
stake)
6 Million Visitors in its first full operating year, and 1.4 Million additional visitors to Hong Kong
$148 Billion value added boost to the Hong Kong economy over the next 40 years
35,800 jobs created in the next 20 years
Слайд 8
Background: China
Largest population in the world with relatively
slow projected population growth
1.26 B (2001) - 1.5 B
(2050F)
63 - 70% Rural
High growth rates in GDP and foreign direct investment (FDI)
Urban income growth of 17.2% in 2002,
Growth in FDI of 14.8% in 2002
2003F: US$58 B
2004F: US$62 B
Accession to the World Trade Organization in December 2001
Increased support for private and foreign investments
Theme parks still fall under Restricted Foreign Investment Industries
Слайд 9
Theme Parks in China
Most parks in China were
American-themed
Few have survived mainly because of transportation issues
Admission Prices:
56 – 100 yuan ($6 – $12)
Park Sizes: 70 – 150 acres
Universal-Vivendi December 2002 agreement to build a park in Shanghai
Projected park opening in 2006, with more than 8 million visitors in the first year
In discussions to build a similar park in Beijing
Слайд 10
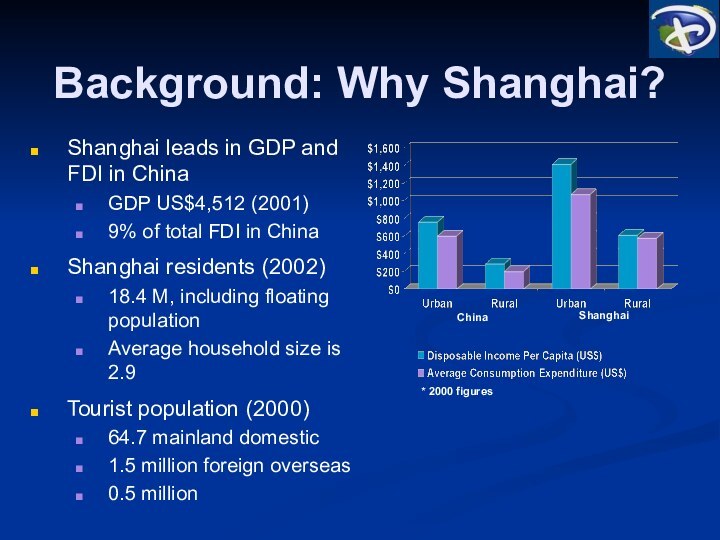
Background: Why Shanghai?
China
Shanghai
Shanghai leads in GDP and FDI
in China
GDP US$4,512 (2001)
9% of total FDI in China
Shanghai
residents (2002)
18.4 M, including floating population
Average household size is 2.9
Tourist population (2000)
64.7 mainland domestic
1.5 million foreign overseas
0.5 million
* 2000 figures
Слайд 11
Agenda
Case Introduction
Background
Project Description
Our Analysis
Recommendation
Questions?
Слайд 12
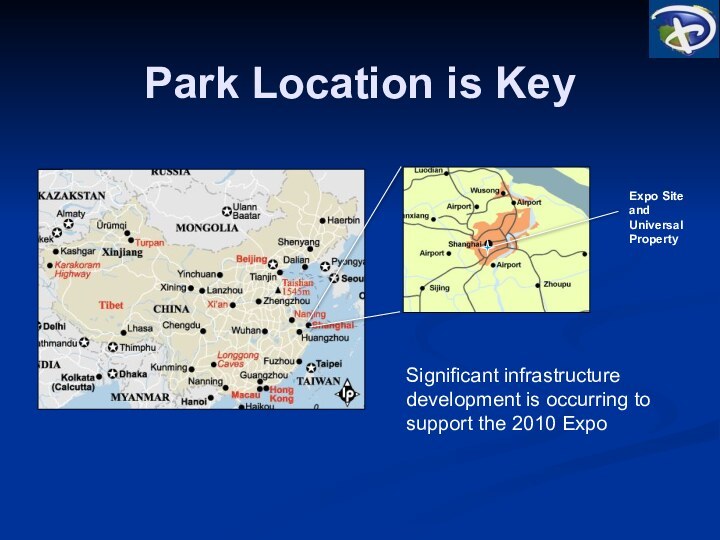
Park Location is Key
Significant infrastructure development is occurring
to support the 2010 Expo
Expo Site and Universal Property
Слайд 13
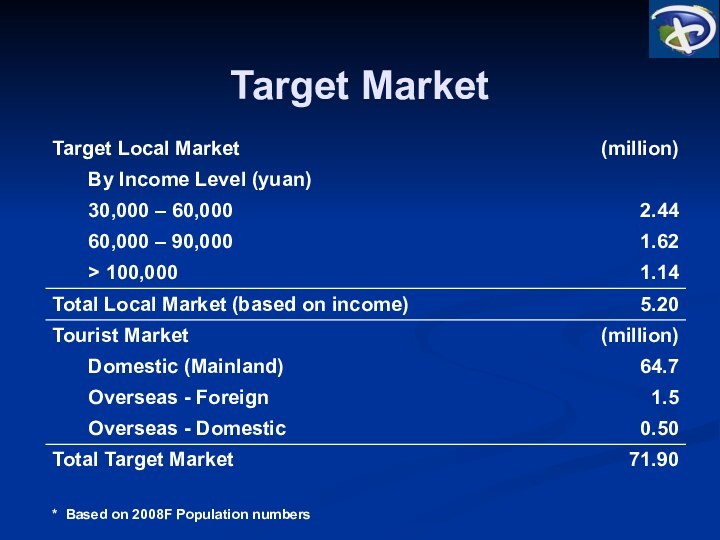
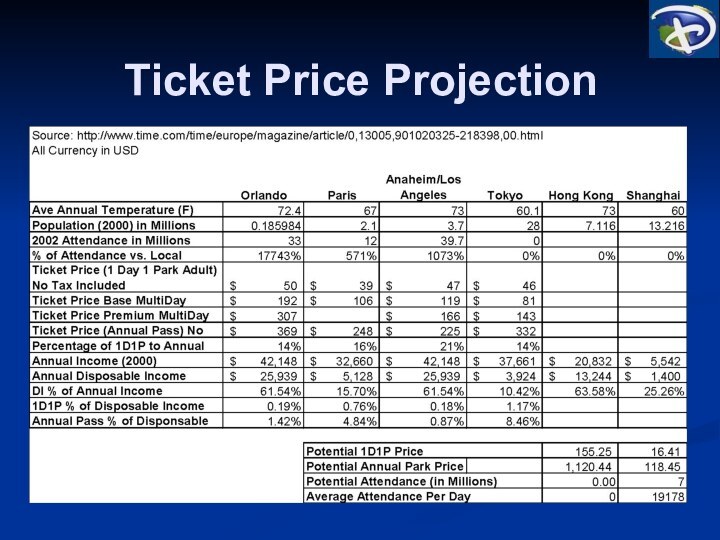
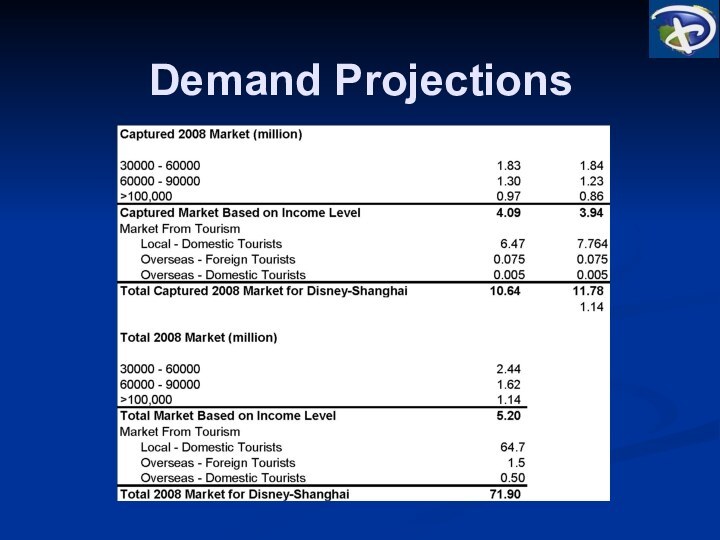
Target Market
* Based on 2008F Population numbers
Слайд 14
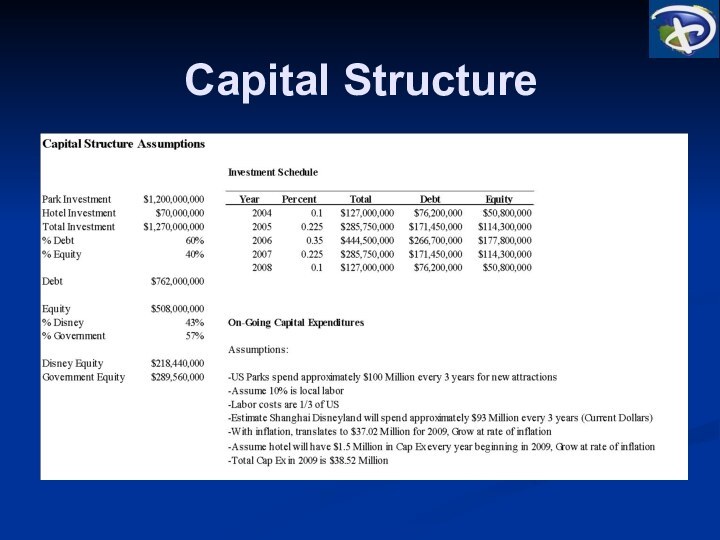
Project Structure
1.27 Billion US$ total capital investment
60% Debt
80%
Government
20% Commercial
40% Equity
43% Disney
57% Government
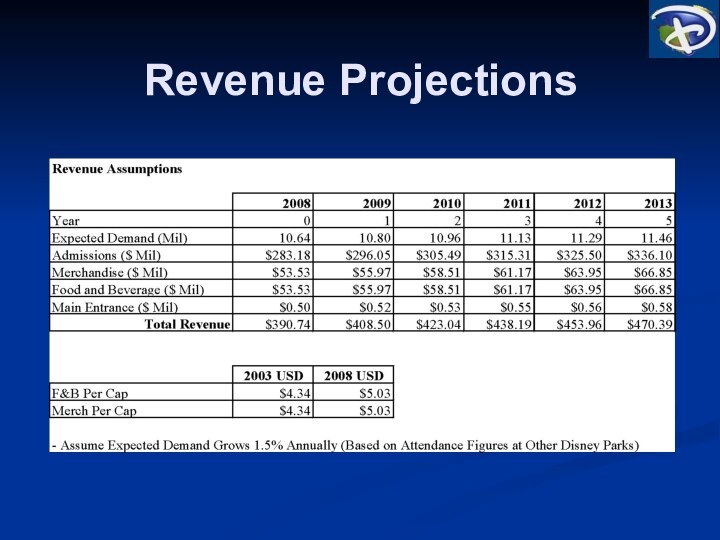
10.6 Million Visitors in its
first full operating year and average annual growth of 1.5%
Corporate tax rate of 30%, with tax loss carry-forwards permitted for five years
Слайд 15
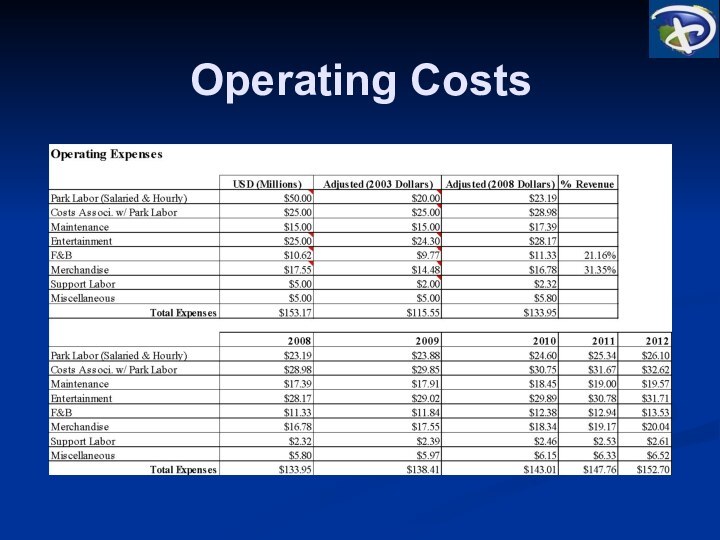
Operating Cash Flows
Admissions (50%)
Food and beverage (24.5%)
Merchandise (24.5%)
Main
entrance (1%)
Park labor and overhead
Maintenance materials
Entertainment (costuming, labor, etc.)
Food
and beverage COGS
Merchandise COGS
Support labor
Miscellaneous
Revenues
Costs
Слайд 17
Agenda
Case Introduction
Background
Project Description
Our Analysis
Recommendation
Questions?
Слайд 18
Risk Analysis - Sovereign
Currency risk is not mitigated
by this project since the majority of cash inflows
and outflows are in local currency
Expropriation risk is mitigated some with the government taking a controlling equity stake
No other commercial or multi-lateral agency partners are involved in the project
Because the project is in the tourism industry and involves an American cultural icon, the susceptibility to strikes or terrorism is slightly higher than average
The project’s location in Shanghai reduces the overall risk of natural disasters when compared to country averages
Слайд 19
Risk Analysis – Operating
and Financial
The technology for this
project will be provided by Disney and is proven
in other locations
Potentially lengthy negotiations with the Chinese government increases start-up risks slightly
Given the project is very service oriented, there is some risk associated with the level of control assumed by the government, but this is difficult to quantify
There are no financial mitigating factors ― rather, this project is closely tied to the government
Real option: A minor amount of cannibalization from the Hong Kong property may be expected
Слайд 20
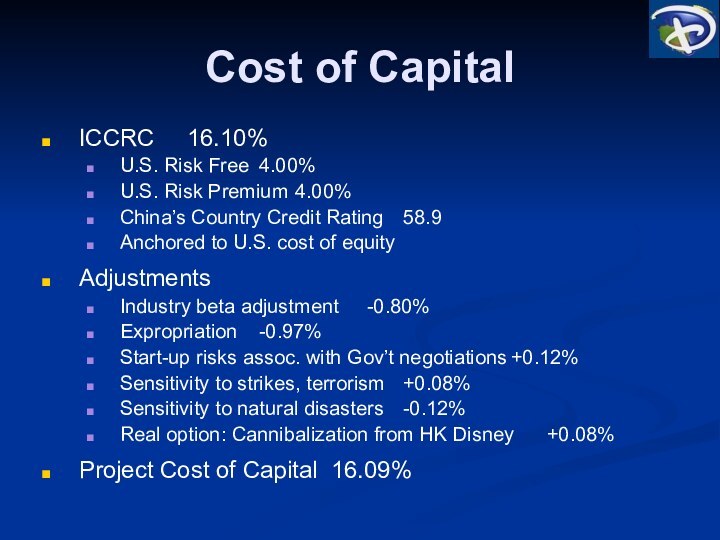
Cost of Capital
ICCRC 16.10%
U.S. Risk Free 4.00%
U.S. Risk Premium 4.00%
China’s Country
Credit Rating 58.9
Anchored to U.S. cost of equity
Adjustments
Industry beta adjustment -0.80%
Expropriation -0.97%
Start-up
risks assoc. with Gov’t negotiations +0.12%
Sensitivity to strikes, terrorism +0.08%
Sensitivity to natural disasters -0.12%
Real option: Cannibalization from HK Disney +0.08%
Project Cost of Capital 16.09%
Слайд 21
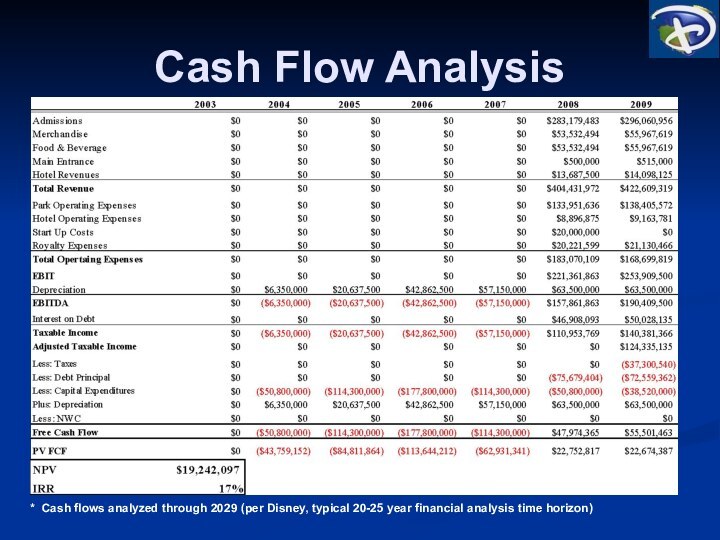
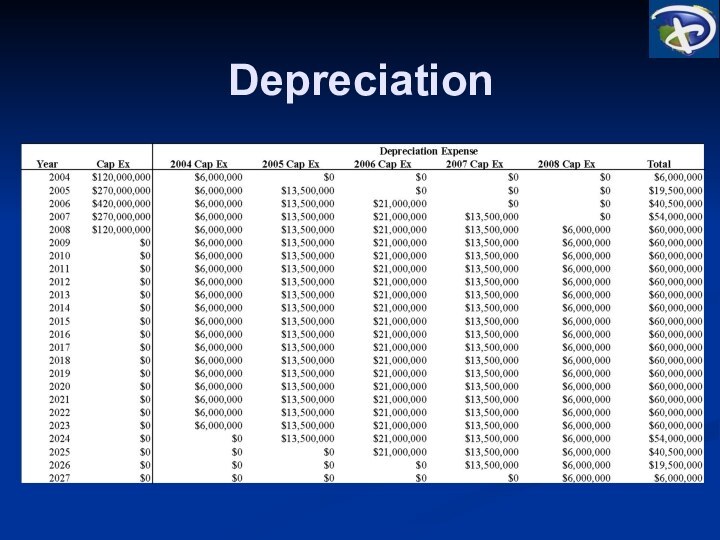
Cash Flow Analysis
* Cash flows analyzed through 2029
(per Disney, typical 20-25 year financial analysis time horizon)
Слайд 22
Real Options
Option to wait until Universal Studios opens
Already
losing any first mover advantage
Universal’s track record at opening
resorts is not on par with Disney’s ― lessons learned from Universal may be minimal
Build a resort hotel in conjunction with the park
Build a “Downtown Disney” entertainment center adjacent to park
Build another gate after several years of operation (double park size)
Слайд 23
Agenda
Case Introduction
Background
Project Description
Our Analysis
Recommendation
Questions?
Слайд 24
Recommendation
Begin negotiations with Chinese government
Government equity stake and
debt provisions
Land and infrastructure provisions
Disney must make the argument
that a Shanghai Park would not substantially damage Hong Kong
Escalating political tensions on the Korean peninsula could change the risk assessment