Слайд 2
Mystery Plays
Early theatre in England was religious. Theatre
became a popular form of teaching the Bible and
Christianity to ordinary people. These were called the Mystery Plays.
Small companies moved from town to town performing stories from the bible, performing on pageant wagons in town squares or in the grounds of churches.
Слайд 3
Mystery Plays
Pageant Wagons arriving in Brussels for a
festival of theatre and performance.
Слайд 4
Secular Drama
All religious drama in England was suppressed
as a result of the Reformation. In the 1530s
the court of Henry VIII was opulent and extravagant. Henry saw entertainment as a vital way to impress his courtiers and foreign kings. The Court employed jesters and musicians for entertainment and small companies of actors took on the livery of an aristocratic patron.
Слайд 5
The First Playhouses
By the 1570s purpose-built playhouses started
appearing in London as secular drama began to predominate.
In 1576 Britain’s first playhouse ‘The Theatre’ was built by Leicester’s Men in Finsbury Fields. This was outside the city walls as the City of London was hostile to public performances.
Слайд 6
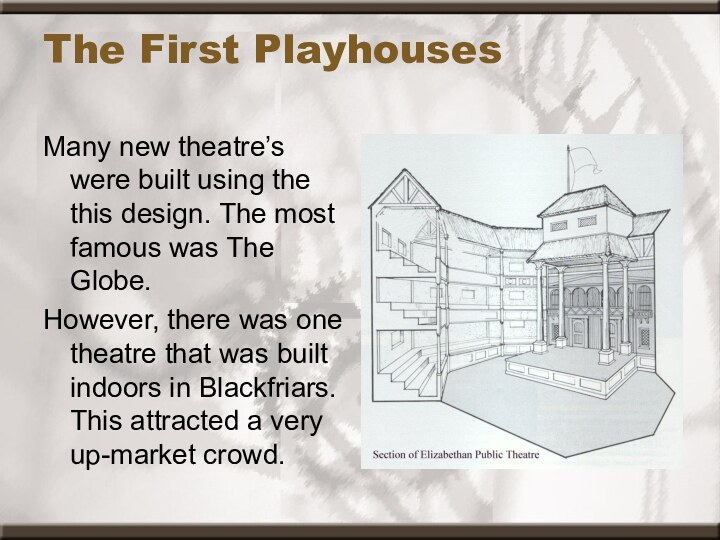
The First Playhouses
Many new theatre’s were built using
the this design. The most famous was The Globe.
However,
there was one theatre that was built indoors in Blackfriars. This attracted a very up-market crowd.
Слайд 7
The First Playhouses
London, 1616.
The South Bank was outside
the control of the city, so a number of
different theatres opened as they were beyond the control of the cities authorities.
Слайд 8
Elizabethan Theatre
In the late 16th century theatres were
popular with everyone and their audiences had a voracious
appetite for new plays. New companies flourished and writers were employed to satisfy the demand for novelty.
Слайд 9
Elizabethan Theatre
Companies were hierarchical - actors who had
a stake in the company were called ‘sharers’ and
divided up the profit between them; ‘hirelings’ were just paid a weekly wage, whilst the boys who played women’s roles were ‘apprentices’ and paid very little. Actors specialised in specific roles which they performed as part of their repertoire.
Слайд 10
Richard Burbage
Richard Burbage has been called the first
great English actor. He was the leading player in
Shakespeare’s company, the Chamberlain’s Men, which later became the King's Men. Burbage created many of the leading roles in Shakespeare's plays. He specialised in tragic roles and was the first Hamlet, King Lear, Othello and, as here, the first Richard III.
Слайд 11
17th Century.
King James I and later his son
Charles I commissioned private performances called ‘masques’ which involved
music, dance, opulent costumes and extraordinary scenery and special effects. They were at and to members of the Royal Court. Such lavish court entertainments was fashionable throughout Europe as an expression of princely power.
Слайд 13
Inigo Jones.
Inigo Jones introduced the proscenium arch and
moveable scenery arranged in perspective into British theatre.
Inigo
Jones’s scenery used a series of shutters that slid in and out using grooves in the floor. He even flew in scenery from above and introduced coloured lighting by placing candles behind tinted glass.
Слайд 14
Civil War.
In 1642 civil war broke out in
England and theatres were closed to prevent public disorder.
The theatres remained closed for 18 years.
Слайд 15
Restoration Drama
The introduction of scenery and elaborate stage
machinery on the English public stage in the 1660s
gave rise to blockbusting semi-opera’s. Many of these were adaptations of other plays - often by Shakespeare. These had episodes of music, singing, dancing and special effects.
Слайд 16
Restoration Drama
The 1674 production of The Tempest had
many spectacular scenes including a storm. The advances in
scene design impacted on the design of theatre buildings, and behind the thrust stage a scenic stage was added, framed by a proscenium arch.
Purcell's song ‘Come to these Yellow Sands’ written for The Tempest, by William Shakespeare.
Слайд 17
Charles II
Charles II had a taste for the
drama and opera he had seen in exile in
France. He encouraged
the introduction of women on stage, thus breaking with the tradition of boy actors taking female roles.
the introduction of moveable perspective scenery which revolutionised staging and the design of theatre buildings.
he also licensed two venues for performance; Lincoln’s Inn Fields and Drury Lane, these became known as the Patent Theatres.
he permitted a wide-ranging repertory: tragedies, comedies, plays, opera, musical theatre and dancing.
Слайд 18
Women in theatre
Other notable actresses included Elizabeth Barry
who was known as the queen of tragedy. She
was trained for the stage by the notorious womaniser the Earl of Rochester, who was also her lover.
The most infamous actress of this period was Nell Gwyn, who was painted nude for Charles II and bore him two children.
Слайд 19
18th Century Theatre
The 18th century saw the flourishing
of theatre as a popular pastime, and many theatres
were enlarged. When built by Christopher Wren in 1674 Drury Lane had held less than 1,000 people. In 1794 it was rebuilt to hold 3000. New playhouses were constructed across London and the first playhouses also opened in the provinces.
Слайд 20
The Beggars Opera
One of the most successful shows
on the London Stage in the early part of
the 18th century was the ballad opera The Beggars Opera John Gay recycled popular songs of the day and wrote new lyrics that were humorous and satirical.
Fill Every Glass
Turtle Dove
Слайд 21
David Garrick
Garrick is one of Britain’s greatest actors
and the first to be called a star.
Garrick
changed the whole style of acting. He rejected the fashion for declamation, where actors would strike a pose and speak their lines formally. Garrick preferred a more easy, natural manner of speech and movement. The effect was a more subtle, less mannered style of acting and a move towards realism.
Garrick as Richard III
Слайд 22
The Licensing Act, 1737.
The Act restricted the production
of plays to the two Patent Theatres and tightened
up the censorship of drama, stating that the Lord Chamberlain with his Examiners of Plays must vet any script before a performance was allowed.
The Act was put in place by Prime Minister Robert Walpole who was concerned that political satire on the stage was undermining him and the authority of the government.
Слайд 23
Censorship
In 1843 the Patent Act was dropped,
enabling other theatres to present drama. However, the Lord
Chamberlain’s censorship of plays remained in place until 1968. One of the last play to be censored was Edward Bond’s production of Saved in 1965.