- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Rh Isoimmunization
Содержание
- 2. Immunologic disorder that occurs in pregnant Rh negative lady carrying Rh positive fetus
- 3. PathophysiologyThe rhesus system which comprises number of
- 4. PathophysiologyInitial response is forming IgM antibodies for
- 5. PathophysiologyMaternal immune system becomes sensitized when there
- 6. Natural History 50% of affected infants have
- 7. The aim of antenatal managementTo predict which
- 8. Recognition of pregnancy at riskFirst ante-natal visit
- 9. Prediction of the severity of fetal hemolysis
- 10. AmniocentesisThere is an excellent correlation between the
- 11. Amniocentesis
- 12. Ultrasound detection of Rh SensitizationSerial U/S examination
- 13. Biophysical surveillance Middle cerebral artery peak velocity
- 14. Biophysical surveillance Middle Cerebral Artery peak systolic
- 15. Fetal Blood Sampling FBSPercutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling
- 16. Fetal Blood Sampling
- 17. Confirmation of fetal bloodVisualizing the needle tip
- 18. Confirmation of fetal blood
- 19. Confirmation of fetal blood
- 20. Intrauterine TransfusionRadiologically guided intraperitoneal transfusion by Liley
- 21. Intravascular transfusion IVT has superseded intraperitoneal transfusion
- 22. Intrauterine blood transfusion
- 23. Donor Blood Washed, filtered or irradiated
- 24. Transfusion volume
- 25. Timing of transfusions Subsequent transfusions are
- 26. Complications of cordocentesis and intravascular transfuaionHemorrhage. Hematomas..Bradycardias. Fetomaternal hemorrhage. Infection. Abruptio placetae. Preterm labor.
- 27. Timing of DeliveryWeighing the risk of fetal
- 28. PreventionThe widespread use of anti D prophylaxis
- 29. PreventionThe usual dose is 300 µg within
- 30. Kleihauer- Betke testThe adult hemoglobin is more
- 31. Скачать презентацию
- 32. Похожие презентации
Immunologic disorder that occurs in pregnant Rh negative lady carrying Rh positive fetus






















Слайд 3
Pathophysiology
The rhesus system which comprises number of antigens
C, D, E, c, e.
A person who lacks D
antigen is called Rh negative.15% of Caucasians, 5% African Americans and 2 % of Asians are Rh negative.
Rh isoimmunisation is due to D antigen in more than 90% of cases.
Occasionally hemolytic disease of the newborn is a result of maternal immunization to Irregular RBC antigens other than Rh group like anti- Kell and anti- Duffy
Слайд 4
Pathophysiology
Initial response is forming IgM antibodies for short
period followed by production of IgG which crosses placenta
IgG
antibodies adhere to the antigen site on the surface of erythrocytes causing hemolysis.The excessive removal of circulatory RBCs leads to severe anemia and hypoxia.
Erythropoiesis results in hepatosplenomegaly.
Tissue hypoxia and hypoproteinemia results in cardiac and circulatory failure, with generalized odema and hydrops
Слайд 5
Pathophysiology
Maternal immune system becomes sensitized when there is
fetal blood leak into the maternal circulation.
Although leaks are
common only 8% are sensitized within 6 months after first del of ABO compatible preg.16% are sensitized after second full term pregnancy of Rh positive ABO compatible pregnancy.
The risk of sensitization after ABO incompatible pregnancy is only 2%
Risk after spontaneous miscarriage is 3.5%
Risk after induce abortion is 5.5%
Risk after ectopic pregnancy is about 1%
Слайд 6
Natural History
50% of affected infants have no
or mild anemia, requiring either phototherapy or no treatment.
25%
have some degree of hepatosplenomegaly and moderate anemia and progressive jundice culminating in kernicterus, neonatal death or severe handicap. 25% are hydropic and usually die in utero or in the neonatal period ( half of these the hydrops develops before 34 weeks gestation ).
Слайд 7
The aim of antenatal management
To predict which pregnancy
is at risk
To predict whether or not the fetus
is severely affected.To correct anemia and reverse hydrops by intrauterine transfusion.
To deliver the baby at the appropriate time, weighing the risks of prematurity against these of intrauterine transfusion.
Слайд 8
Recognition of pregnancy at risk
First ante-natal visit check
blood group, antibody screening.
If indirect coombs test is positive,
the father’s Rh should be tested.Serial maternal Anti D titers should be done every 2- 4 weeks.
If titer is less than 1/16 the fetus is not at risk.
If titer is more than 1/16 then severity of condition should be evaluated.
Слайд 9
Prediction of the severity of fetal hemolysis
History
of previous affected pregnancies
The levels of maternal hemolytic antibodies
Amniocentesis
Biophysical surveillance
Fetal blood sampling
Слайд 10
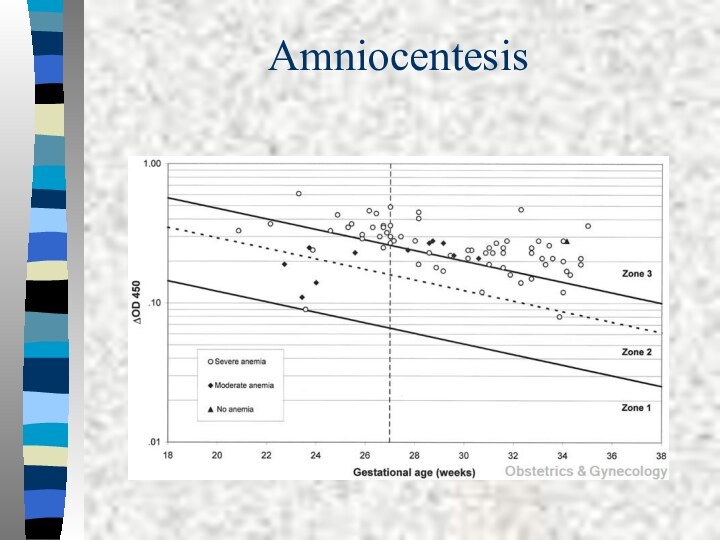
Amniocentesis
There is an excellent correlation between the amount
of bilirubin in amniotic fluid and fetal hematocrit.
The
optical density deviation at 450 nm measures the amniotic fluid unconjugated bilirubin.
Слайд 12
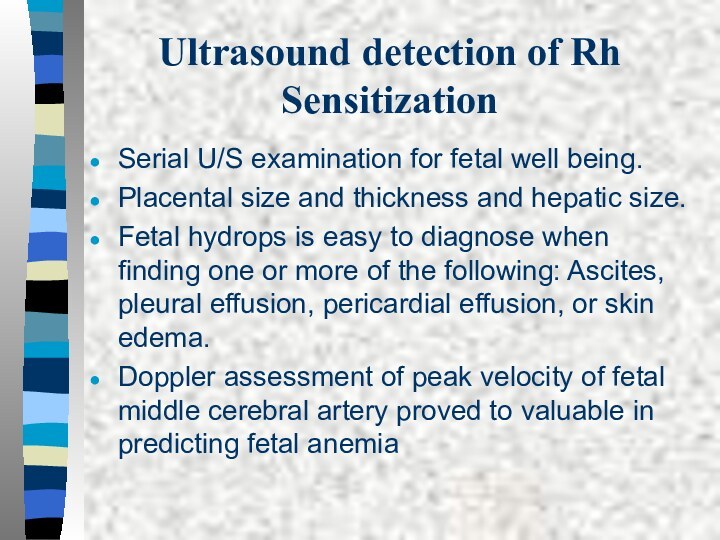
Ultrasound detection of Rh Sensitization
Serial U/S examination for
fetal well being.
Placental size and thickness and hepatic size.
Fetal
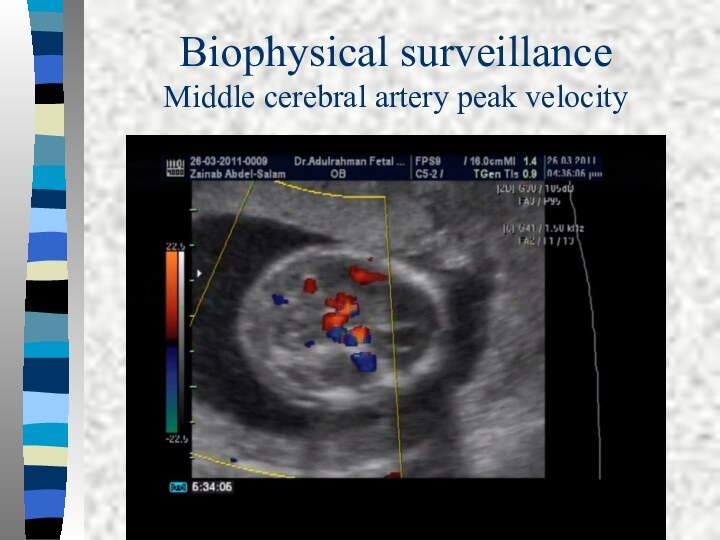
hydrops is easy to diagnose when finding one or more of the following: Ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, or skin edema.Doppler assessment of peak velocity of fetal middle cerebral artery proved to valuable in predicting fetal anemia
Слайд 14
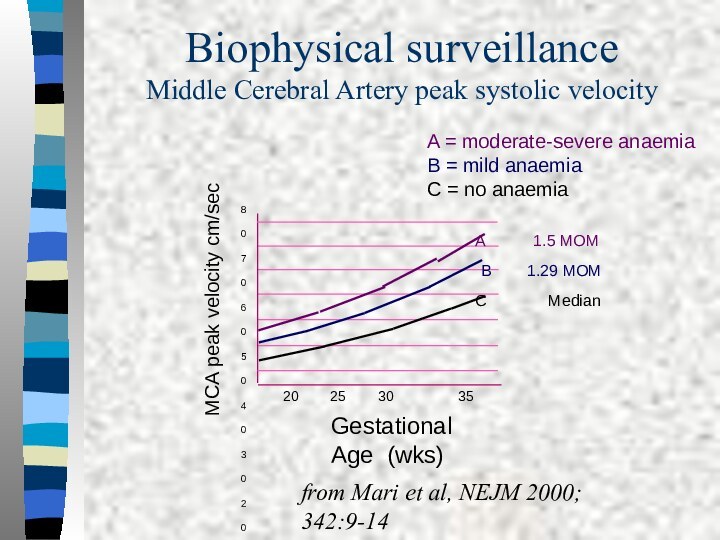
Biophysical surveillance
Middle Cerebral Artery peak systolic velocity
C
Median
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
20 25
30 35A 1.5 MOM
B 1.29 MOM
Gestational Age (wks)
MCA peak velocity cm/sec
from Mari et al, NEJM 2000; 342:9-14
A = moderate-severe anaemia
B = mild anaemia
C = no anaemia
Слайд 15
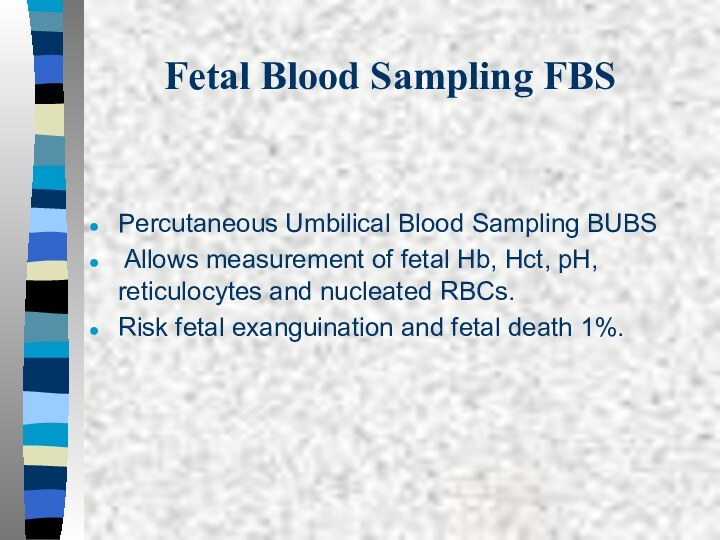
Fetal Blood Sampling FBS
Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling BUBS
Allows measurement of fetal Hb, Hct, pH, reticulocytes and
nucleated RBCs.Risk fetal exanguination and fetal death 1%.
Слайд 17
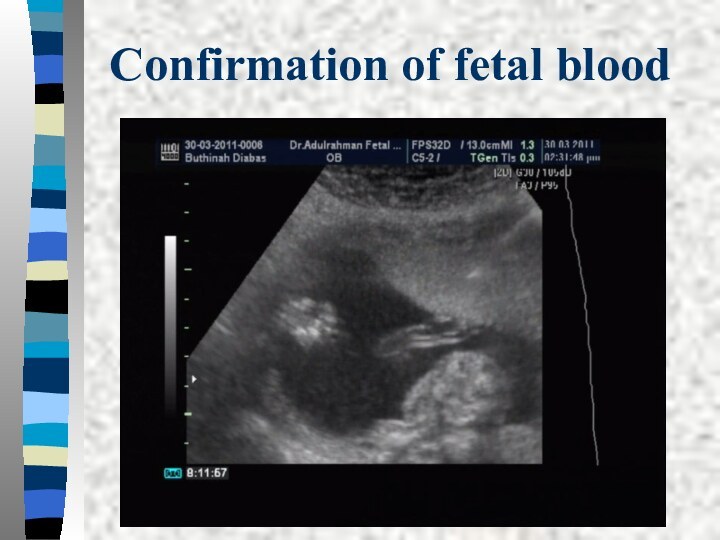
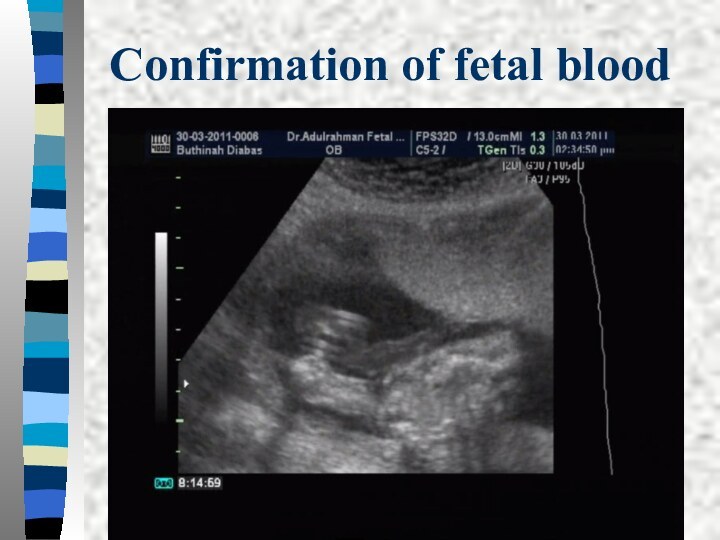
Confirmation of fetal blood
Visualizing the needle tip within
the cord vessel
Turbulance when injecting a small amount of
saline into the vessel.Fetal blood has a higher mean corpuscular volume ( MCV usually >100 fL
An alkali elusion method can be used
Acid elution Betke-Kleihauer test
Слайд 20
Intrauterine Transfusion
Radiologically guided intraperitoneal transfusion by Liley in
1963.
Adoption of ultrasound guided IPT resulted in dramatic
improvement in survival rates. Fetoscopic intravascular route was renewed by Rodeck in 1981.
Percutaneous transfusion into the intrahepatic umbilical vein, Bang 1982.
Cordocentesis, Daffos 1983.
The use of cordocentesis for fetal top up transfusion by Berkowitz.
Слайд 21 Intravascular transfusion IVT has superseded intraperitoneal transfusion in
most centres.
It has superior results, regarding survival rates,
quality of survivors, prolongation of gestation and the higher rate of vaginal delivery. Access to the fetal circulation is extremely essential to avoid the lethal mistake of transfusing the Rh negative fetus or the nonanemic Rh positive fetus.
Decisions regarding transfusion and delivery are made on the basis of fetal blood group, Hb estimation and other hematologic parameters
. IVT results are better in the compromised hydropic fetus.
Слайд 23
Donor Blood
Washed, filtered or irradiated with
2500 rad Gamma ray packed red blood cells with
Hct 75%Group O negative heterologous blood
Maternal blood
Слайд 25
Timing of transfusions
Subsequent transfusions are
timed on the basis of the fetal Hct achieved
at the end of the previous transfusion and the rate of fall in fetal Hct. The latter has been reported to be on average equal to 1% of Hct/day
Слайд 26
Complications of cordocentesis and intravascular transfuaion
Hemorrhage.
Hematomas..
Bradycardias.
Fetomaternal
hemorrhage.
Infection.
Abruptio placetae.
Preterm labor.
Слайд 27
Timing of Delivery
Weighing the risk of fetal loss
including that related to intrauterine transfusion against the risk
of prematurity.
Слайд 28
Prevention
The widespread use of anti D prophylaxis in
the late 1960s has led to a great reduction
in isoimmunisation.Following delivery and caesarean section
Routine anti D administration at 28 weeks.
Following spontaneous and induced abortion.
Vaginal bleeding and threatened miscarriage.
Performing amniocentesis, CVS,
Abdomenal trauma and external cephalic version.
Слайд 29
Prevention
The usual dose is 300 µg within 72
hours following delivery.
This covers 30 ml of fetal blood
leak into maternal circulation. If greater transplacental hemorrhage is suspected the dose should be tailored after Kleihauer- Betke test to determine the volume of hemorrhage.
Слайд 30
Kleihauer- Betke test
The adult hemoglobin is more readily
acid eluted through the cell membrane than fetal hemoglobin.
Maternal blood is fixed on a slide with ethanol 80%, treated with citrate phosphate buffer.
After staining with hematoxylin and eosin the fetal cells will be stained while the adult cells appear like ghost cells.
No. of fetal cells/ No. of adult cells is equal to
fetal blood volume/ maternal blood volume.