Слайд 2
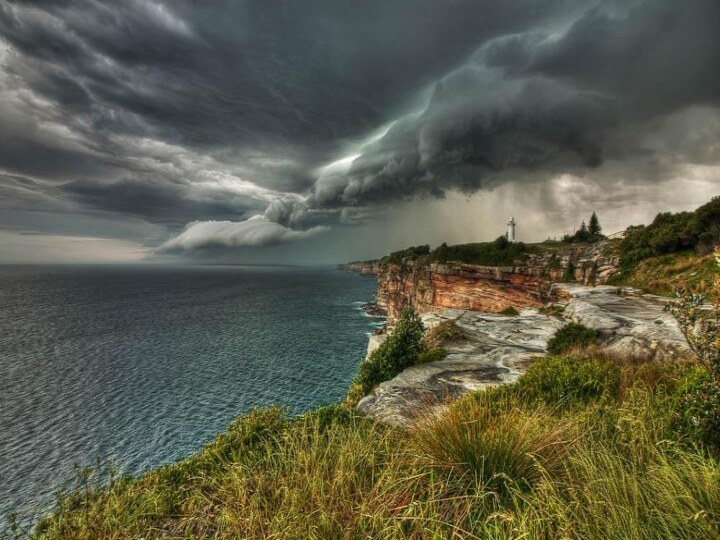
Australia is a country comprising the mainland of
the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous
smaller islands. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area. Neighbouring countries include Indonesia, East Timor and Papua New Guinea to the north; the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and New Caledonia to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east.
Neighbourhood
Слайд 3
On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated,
forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Since Federation, Australia has
maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy. The federation comprises six states and several territories. The population of 23.1 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated in the eastern states.
Слайд 4
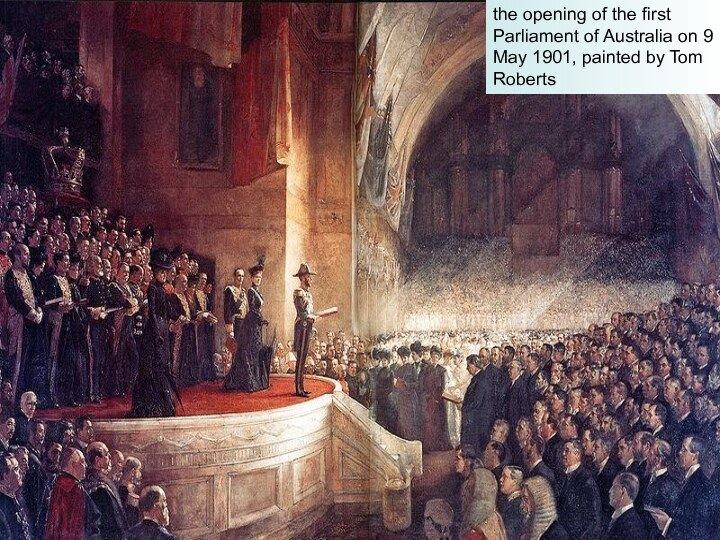
the opening of the first Parliament of Australia
on 9 May 1901, painted by Tom Roberts
Слайд 5
Australia is a developed country and one of
the wealthiest in the world, with the world's 12th-largest
economy. In 2012 Australia had the world's fifth-highest per capita income, Australia's military expenditure is the world's 13th-largest. With the second-highest human development index globally, Australia ranks highly in many international comparisons of national performance, such as quality of life, health, education, economic freedom, and the protection of civil liberties and political rights. Australia is a member of the United Nations, G20, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), World Trade Organization, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, and the Pacific Islands Forum.
Слайд 6
For almost two centuries the majority of settlers,
and later immigrants, came from the British Isles. As
a result the people of Australia are primarily of British and/or Irish ethnic origin. The 2011 Census asked respondents to provide a maximum of two ancestries with which they most closely identify. The most commonly nominated ancestry was English (36.1%), followed by Australian (35.4%), Irish (10.4%), Scottish (8.9%), Italian (4.6%), German (4.5%), Chinese (4.3%), Indian (2.0%), Greek (1.9%), and Dutch (1.7%). Asian Australians make up 12% of the population.
Demographics
Слайд 7
For at least 40,000 years before the first
British settlement in the late 18th century, Australia was
inhabited by indigenous Australians, who spoke languages grouped into roughly 250 language groups. After the discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, Australia's eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades; the continent was explored and an additional five self-governing Crown Colonies were established.
Слайд 8
The biggest cities
Melbourne
Brisbane
Sydney
Perth
Canberra
Слайд 9
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city
in the state of Victoria, and the second most
populous city in Australia.
Слайд 10
Brisbane is the capital and most populous city
in the Australian state of Queensland, and the third
most populous city in Australia.
Слайд 11
Sydney is the state capital of New South
Wales and serves as the most populous city in
Australia and 47th most populous city in the world.
Слайд 12
Perth is the capital and largest city of
the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the
fourth most populous city in Australia.
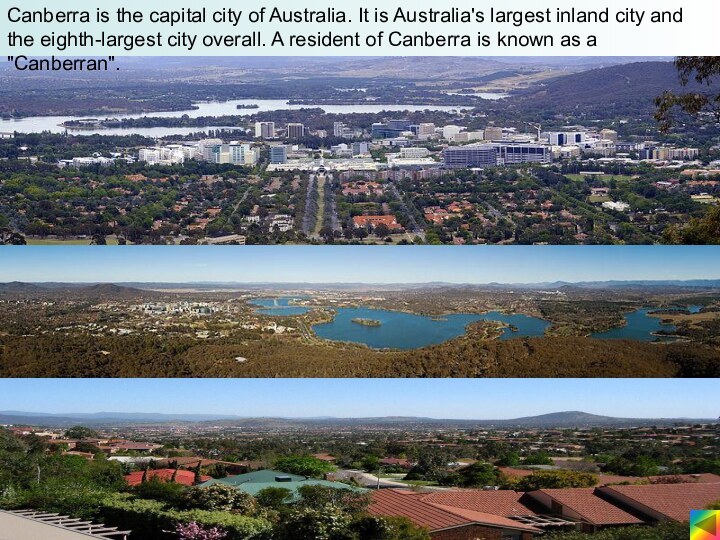
Слайд 13
Canberra is the capital city of Australia. It
is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city
overall. A resident of Canberra is known as a "Canberran".
Слайд 14
Language
Although Australia has no official language, English has
always been entrenched as the de facto national language.
Australian English is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon, and differs slightly from other varieties of English in grammar and spelling. General Australian serves as the standard dialect. According to the 2011 census, English is the only language spoken in the home for close to 81% of the population. The next most common languages spoken at home are Mandarin, Italian Arabic, Cantonese, Greek and Vietnamese.
Слайд 15
Australia has no state religion; Section 116 of
the Australian Constitution prohibits the federal government from making
any law to establish any religion, impose any religious observance, or prohibit the free exercise of any religion. In the 2011 census, 61.1% of Australians were counted as Christian, including 25.3% as Roman Catholic and 17.1% as Anglican; 22.3% of the population reported having "no religion"; 7.2% identify with non-Christian religions, the largest of these being Buddhism (2.5%), followed by Islam (2.2%), Hinduism (1.3%) and Judaism (0.5%). The remaining 9.4% of the population did not provide an adequate answer.
Religion
Слайд 16
Prior to European settlement in Australia, the animist
beliefs of Australia's indigenous people had been practised for
millennia. In the case of mainland Aboriginal Australians, their spirituality is known as the Dreamtime and it places a heavy emphasis on belonging to the land. The collection of stories that it contains shaped Aboriginal law and customs. Aboriginal art, story and dance continue to draw on these spiritual traditions. In the case of the Torres Strait Islanders who inhabit the islands between Australia and New Guinea, spirituality and customs reflected their Melanesian origins and dependence on the sea. The 1996 Australian census counted more than 7000 respondents as followers of a traditional Aboriginal religion.
Слайд 17
Culture
Since 1788, the basis of Australian culture has
been strongly influenced by Anglo-Celtic Western culture. Distinctive cultural
features have also arisen from Australia's natural environment and Indigenous cultures. Since the mid-20th century, American popular culture has strongly influenced Australia, particularly through television and cinema. Other cultural influences come from neighbouring Asian countries, and through large-scale immigration from non-English-speaking nations.
Слайд 18
Cuisine
The food of Indigenous Australians was largely influenced
by the area in which they lived. Most tribal
groups subsisted on a simple hunter-gatherer diet, hunting native game and fish and collecting native plants and fruit. The general term for native Australian flora and fauna used as a source of food is bush tucker. The first settlers introduced British food to the continent, and much of that is now considered typical Australian food; the Sunday roast has become an enduring tradition for many Australians.
Слайд 19
Since the beginning of the 20th century, food
in Australia has increasingly been influenced by immigrants to
the nation, particularly from Southern European and Asian cultures. Australian wine is produced in 60 distinct production areas totalling approximately 160,000 hectares, mainly in the southern, cooler parts of the country.
Слайд 20
The wine regions in each of these states
produce different wine varieties and styles that take advantage
of local climates and soil types. The predominant varieties are Shiraz, Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, Merlot, Sémillon, Pinot noir, Riesling, and Sauvignon blanc. In 1995, an Australian red wine, Penfolds Grange, won the Wine Spectator award for Wine of the Year, the first time a wine from outside France or California achieved this distinction.
Слайд 21
Sport
Approximately 24% of Australians over the age of
15 regularly participate in organised sporting activities. Australia has
strong international teams in cricket, field hockey, netball, rugby league, and rugby union, having been Olympic or world champions at least twice in each sport in the last 25 years for both men and women where applicable. Australia is also powerful in track cycling, rowing, and swimming, having consistently been in the top-five medal-winners at Olympic or World Championship level since 2000. Swimming is the strongest of these sports; Australia is the second-most prolific medal winner in the sport in Olympic history.
Слайд 22
The first Australian cricket team to go on
tour internationally did so in 1868. The Australian side
was an all Aboriginal one and toured England where they played 47 games, where they won 14 games, drew 19 and lost 14. Australia's adoption of sport as a national was pastime was so comprehensive that the Anthony Trollope remarked in his book, Australia, published in 1870, "The English passion for the amusements which are technically called 'sports', is not a national necessity with the Americans, whereas with the Australians it is almost as much so as home."
Слайд 23
Soccer was being played in Australia by the
1870s, with the first team formally being organised in
Sydney in 1880 that was named the Wanderers. Sport was receiving coverage in Australian newspapers by 1876 when a sculling race in England was reported on in the Sydney Morning Herald. In 1877 Australia played in the first Test Cricket match against England. In 1882, The Ashes were started following the victory of the Australia national cricket team over England.
Слайд 24
Field hockey teams for men and women were
established by 1890. The Sheffield Shield cricket competition was
first held in 1891 with New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia participating in the inaugural competition. The remaining states would not participate until much later, with Queeensland first participating in 1926/1927, Western Australia in 1947/1948 and Tasmania in 1982/1983. In 1897 the Victorian Football League, which later became the AFL the Australian Football League, was founded after breaking away from the Victorian Football Association.
Слайд 25
When Messenger and the All Golds returned from
Great Britain in 1908, they helped the new clubs
adapt to the rules of rugby league prior to the inaugural 1908 NSWRFL season. The Queensland Rugby Football League also formed early in 1908 by seven rugby players who were dissatisfied with the administration of the Queensland Rugby Union. The Australia national rugby union team had their first international test against New Zealand in 1903, and first international tour in 1908, earning their nickname of the Wallabies after two British journalist used it to refer to the team. The team won gold at the 1908 London Olympics, however the majority of the squad joined rugby league clubs upon returning to Australia.