- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The Diamonds
Содержание
- 2. Contents: Diamond History Identification Formation Where and how to extract diamonds? The well-known diamonds
- 3. Diamond- the firmest substance on
- 4. History:The name diamond is derived from the ancient
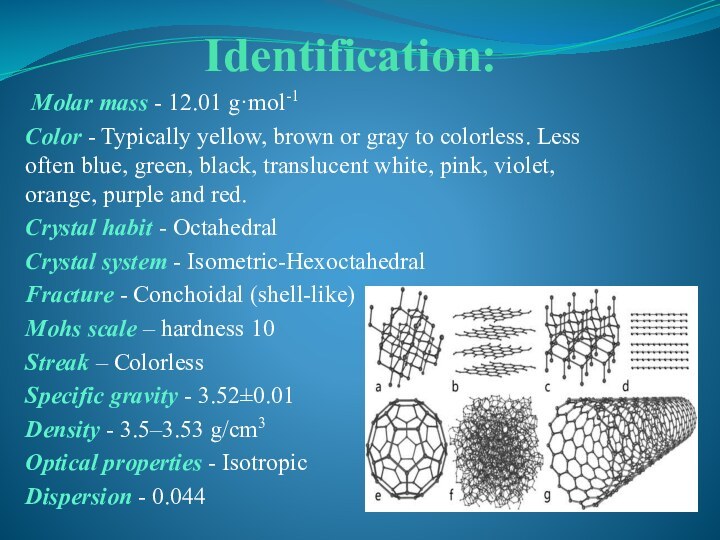
- 5. Identification: Molar mass
- 6. FormationThe conditions for diamond formation to happen
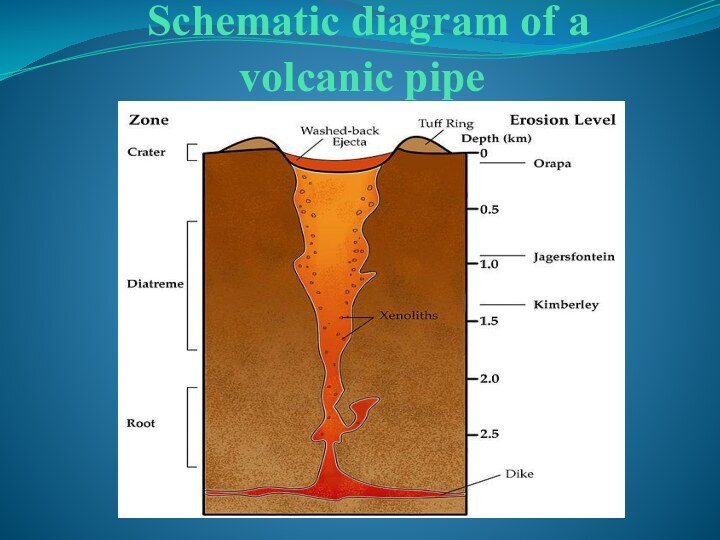
- 7. Schematic diagram of a volcanic pipe
- 8. Where and how to extract diamonds? Ordinary
- 9. Diamantiferous kimberlites pipe:Yakutia
- 10. Diamond in a kimberlite pipe:
- 11. The well-known diamonds:“Yellow diamond of Tiffani”“The princess"“Malt liquor of Rods"“The miner”
- 12. Now you know: About a mineral
- 13. Скачать презентацию
- 14. Похожие презентации
Contents: Diamond History Identification Formation Where and how to extract diamonds? The well-known diamonds











Слайд 4
History:
The name diamond is derived from the ancient Greek αδάμας (adámas),
"proper", "unalterable", "unbreakable, untamed". Diamonds are thought to have been
first recognized and mined in India, where significant alluvial deposits of the stone could be found many centuries ago along the rivers Penner, Krishna, and Godavari.
Слайд 5
Identification:
Molar mass -
12.01 g·mol-1
Color - Typically yellow, brown or gray to colorless.
Less often blue, green, black, translucent white, pink, violet, orange, purple and red.Crystal habit - Octahedral
Crystal system - Isometric-Hexoctahedral
Fracture - Conchoidal (shell-like)
Mohs scale – hardness 10
Streak – Colorless
Specific gravity - 3.52±0.01
Density - 3.5–3.53 g/cm3
Optical properties - Isotropic
Dispersion - 0.044
Слайд 6
Formation
The conditions for diamond formation to happen in
the lithospheric mantle occur at considerable depth corresponding to
the requirements of temperature and pressure. These depths are estimated between 140 and 190 km though occasionally diamonds have crystallized at depths about 300 km as well.Also diamonds formed in diamantiferous kimberlites and volcanic pipe.
Слайд 8
Where and how to extract diamonds?
Ordinary diamonds
are and extracted worldwide in the special volcanic breed,
named a kimberlite.Now diamonds are extract from two types of deposits: radical (kimberlites and lamproite pipes) and secondary – scatterings.
The main center of extraction there were South African countries and minor - Brazil.





























