- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The Unique Australian Wildlife
Содержание
- 2. Many countries have their own unique fauna.But Australia is mostly unusual in that
- 3. 320-270 million years ago Permo-Carboniferous Age If
- 4. 270-210 million years ago The end
- 5. 270-210 million years ago The end
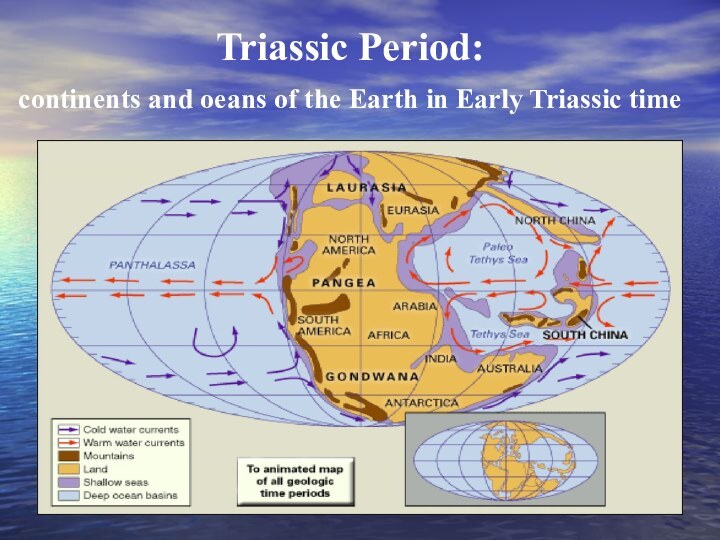
- 6. Triassic Period: continents and oeans of the Earth in Early Triassic time
- 7. MonotremeThe egg-laying mammalians include the amphibious platypusand
- 8. 180 million years ago Middle Jurassic
- 9. 180 million years ago Middle Jurassic
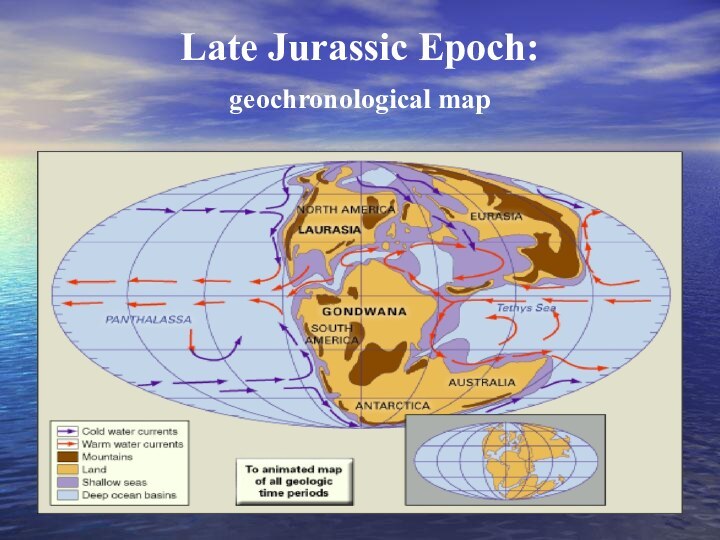
- 10. Late Jurassic Epoch: geochronological map
- 11. 100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period
- 12. Two important groups of modern mammals evolved
- 13. 100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period
- 14. Late Cretaceous Epoch: geochronological map
- 15. 70 million years ago The end of
- 16. Diprotodon characterized by a wombat-like body
- 17. 45 million years ago The beginning of
- 18. Structural and behavioral parallels with placental mammals are in some cases quite striking.
- 19. There are marsupials that look remarkably like moles, shrews, squirrels, mice, dogs, and hyenas.
- 20. The koala and the kangaroo are the most well-known marsupials.
- 21. MarsupialsLong-nosed bandicootSpotted-tailed quoll, or native cat
- 22. MarsupialsVirginia, or opossum
- 23. MarsupialsRed kangaroo –WallabyWestern grey kangaroo
- 24. MarsupialsDunnart, a marsupial mouseKangaroo Rat
- 25. MarsupialsWombatTasmanian Devil
- 26. MarsupialsThe niches that marsupials fill are closely
- 27. The burrowing species have powerful foreclaws with
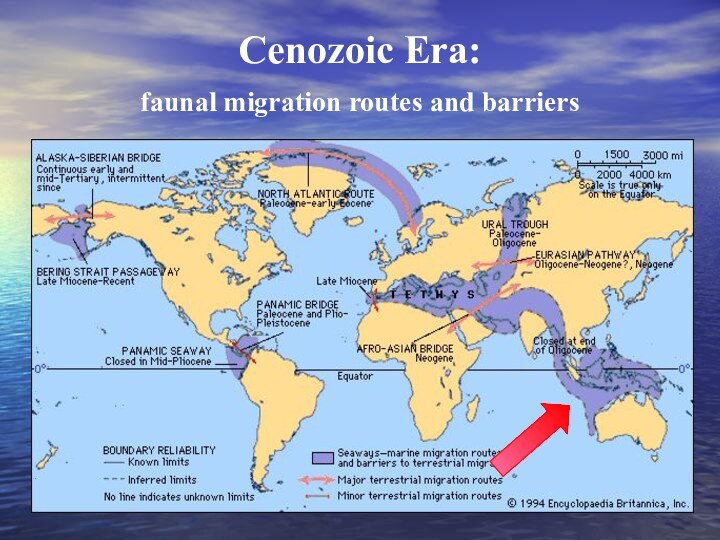
- 28. Cenozoic Era: faunal migration routes and barriers
- 29. The earliest isolation of Australia from all the other continents made its fauna unique
- 30. Скачать презентацию
- 31. Похожие презентации
Many countries have their own unique fauna.But Australia is mostly unusual in that



























Слайд 3
320-270 million years ago
Permo-Carboniferous Age
If we had observed
the
Earth surface
from space at that time,
we would
have seen quite the other picture
Слайд 4 270-210 million years ago The end of Permian
– the beginning of Trias
About 275 million years ago
Euroamerica and Angara
made a huge landmass of
Laurasia
Laurasia
The Tethys Sea
Separated Laurasia
from the protocontinent
of Pangaea
Pangaea
The Tethys Sea
Nowadays it is
the Middeteranian Sea
Слайд 5 270-210 million years ago The end of Permian
– the beginning of Trias
On land the vertebrates are
represented in the Triassic by amphibians and reptiles.The first true mammals, which were very small, are supposed to appear in the Late Triassic.
Слайд 7
Monotreme
The egg-laying
mammalians include
the amphibious platypus
and the
terrestrial echidnas
of Australia, Tasmania,
and New Guinea
short-beaked echidna
amphibious
platipus
Слайд 8
180 million years ago
Middle Jurassic period
The protocontinent
supposedly covered
about half the Earth
and was completely
surrounded
by a world ocean
called Panthalassa.
Слайд 9
180 million years ago
Middle Jurassic period
Dinosaurs and
other reptiles emerged to dominate the land, sea, and
sky.The first birds and new varieties of reefbuilding and other invertebrate faunas, provided Jurassic life with added complexity.
Слайд 11
100 million years ago
Early Cretaceous Period
Later Pangaea began
to break apart.
Its segments Laurasia
and Gondwanaland
gradually
receded, resulting
in the formation
of the Atlantic Ocean.
Слайд 12
Two important groups of modern
mammals evolved
during
the Cretaceous.
100 million years ago
Early Cretaceous Period
Cretaceous placentals, smaller
than those of present-day ones, were poised to take over
the terrestrial environments
as soon as the dinosaurs vanished.
Слайд 13
100 million years ago
Early Cretaceous Period
Another
mammal group,
the marsupials,
evolved during
the Cretaceous
as well.
This
group includes the native species
of Australia,
kangaroos, koalas,
and the North
American
opossum.
Слайд 15
70 million years ago
The end of Cretaceous Period
The
Late Cretaceous
record is much
more complete.
It is
known, for instance, that during the Late
Cretaceous
many dinosaur types
lived in relationships
like the present-day
terrestrial mammals.
Слайд 16
Diprotodon
characterized by
a wombat-like body
the size
of a large
rhinoceros.
massively constructed
skeleton to
support its imposing bulk.
well developed teeth
of gnawing animals.
herbivorous
distantly related
to kangaroos and
wombats.
extinct marsupial mammals
existed 30 - 10,000 years ago
in Australia.
Слайд 17
45 million years ago
The beginning of Cenozoic era
By
that time
Australasia was isolated
from all other
continental
masses, here marsupials evolved
into many diverse forms.
In South America
they survived
alongside placentals,
forming the Neotropical
mammalian fauna.
Слайд 18 Structural and behavioral parallels with placental mammals are
in some cases quite striking.
Слайд 19 There are marsupials that look remarkably like moles,
shrews, squirrels, mice, dogs, and hyenas.
Слайд 26
Marsupials
The niches that marsupials fill
are closely associated
with structure.
The diets of marsupials
are as varied
as the niches they occupy.
Слайд 27 The burrowing species have powerful foreclaws with which
they can tunnel into the ground for food and
for shelterThe gliders
have a membrane
along either flank,
attached to the forelegs
and hind legs,
that enables the animals
to glide down from a high perch





























