- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The main types of nutrition in microorganisms
Содержание
- 2. The main types of nutrition in microorganisms
- 3. Learning ObjectiveIdentify the main types of nutrition in microorganisms
- 4. Success criteria 1.Analyse information about microbes and
- 5. Terminology bacteria, yeast, fungus, dose, continuous growth
- 6. Classification of Nutrition in MicrooganismsCarbon sources –
- 7. All bacteria require two things for growth:1)
- 9. Nutrient Required for GrowthCarbon – heterotrophs: glucose,
- 10. Elemental Assay of E. coli (dry weight)50%
- 11. Carbonthe backbone of functional biological molecules: cells
- 12. Hydrogenstructural molecule, participant in process of energy
- 13. Nitrogenin amino acids, nucleic acids. membranes, cell
- 14. Sulfurin certain amino acids, some B-vitamins (biotin
- 15. Phosphorusa constituent of high energy compounds (ATP), phospholipids in membranes, nucleic acids.
- 16. Oxygenequal amounts in aerobes and anaerobes, but
- 17. Trace elements, though not required in large
- 18. Organic Growth FactorsOrganic Growth Factors are essential
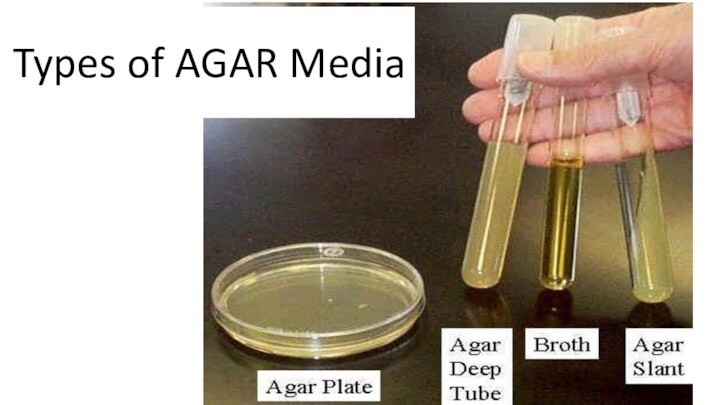
- 19. Types of AGAR Media
- 20. Liquid agar cultures of bacteria at the
- 21. Serial Dilutions are used to reduce the
- 22. Spectrophotomer or a colorimeter measures transmission of
- 23. Turbidity – the cloudiness shows bacterial growthTurbidity
- 24. Serial Dilutions are used to reduce the
- 25. Practical: Plate it on different nutrient agar
- 26. Success criteria 1.Analyse information about microbes and
- 27. Скачать презентацию
- 28. Похожие презентации
The main types of nutrition in microorganisms
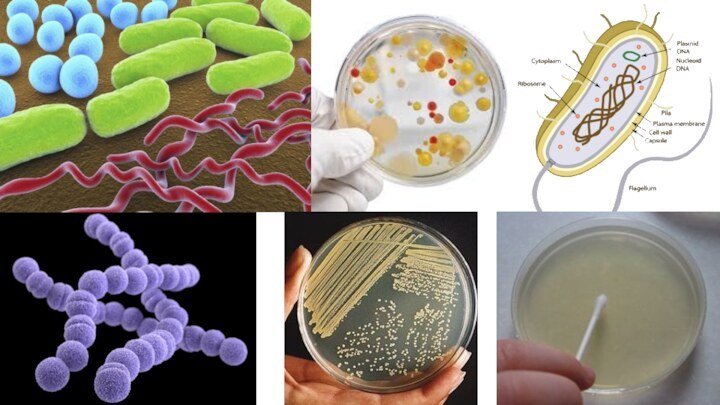


















Слайд 4
Success criteria
1.Analyse information about microbes and name
them.
2.Name and identify correctly at least four types
of nutrition.
Слайд 5
Terminology
bacteria, yeast, fungus, dose, continuous growth curve,
a lag phase, an exponential / lag phase, stationary
phase, a dead phase, monitors, viable cell microorganism, optical density, seedingGrowth factor, Trace elements, Macronutritions, Nitrogen, carbohydrates, Hydrogen, Phosphorus, oxygen, Sulfur, Potassium, Calcium, glucose, carbon dioxide, water, pH, temperature, mineral ions
Nutrient supply, agar medium/growth medium, aeration
Aseptic techniques, sterile, streak pattern
Слайд 6
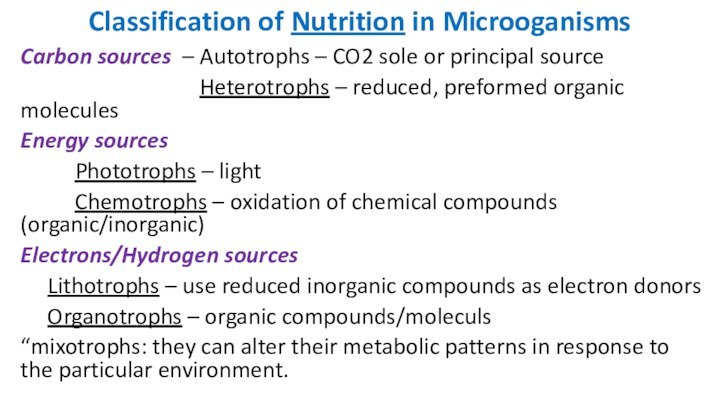
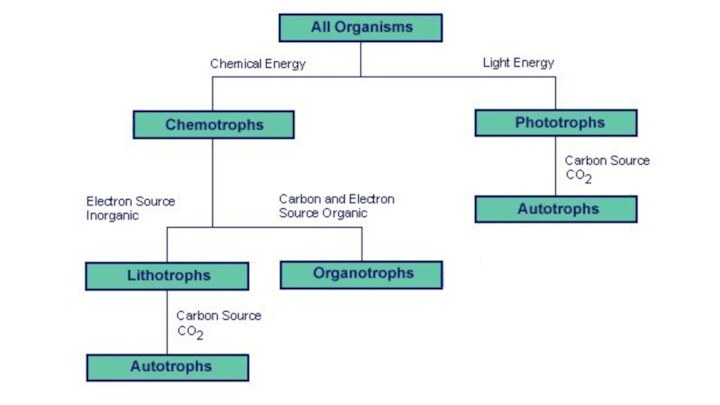
Classification of Nutrition in Microoganisms
Carbon sources – Autotrophs
– CO2 sole or principal source
Heterotrophs – reduced, preformed organic moleculesEnergy sources
Phototrophs – light
Chemotrophs – oxidation of chemical compounds (organic/inorganic)
Electrons/Hydrogen sources
Lithotrophs – use reduced inorganic compounds as electron donors
Organotrophs – organic compounds/moleculs
“mixotrophs: they can alter their metabolic patterns in response to the particular environment.
Слайд 7
All bacteria require two things for growth:
1)
A source of energy
2) A source of matter
for building additional cells: C, O, H, N, S, P, trace minerals.
Слайд 9
Nutrient Required for Growth
Carbon – heterotrophs: glucose, fatty
acids, alcohols, hydrocarbons…
Nitrogen – organic: amino acids, peptides, proteins
inorganic: ammonium salts and nitratesWater – chemical reactions
Growth factors, Vitamins, Mineral salts – positive ions: calcium, potassium, sodium, B vitamins, some in TRACE (small) amounts
Energy – chemical or light
chemotrophs-chemical energy – glucose
phototrophic – light energy: blue green algae bacteria
Слайд 10
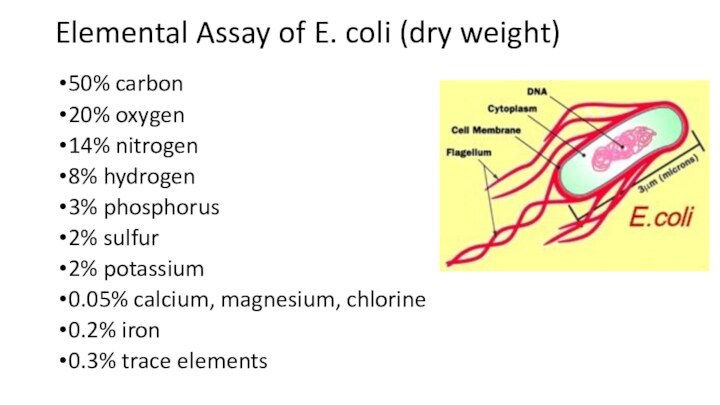
Elemental Assay of E. coli (dry weight)
50% carbon
20%
oxygen
14% nitrogen
8% hydrogen
3% phosphorus
2% sulfur
2% potassium
0.05% calcium, magnesium, chlorine
0.2%
iron0.3% trace elements
Слайд 11
Carbon
the backbone of functional biological molecules: cells vary
in their ability to synthesize all of their carbon
compounds. Range of carbon compounds utilized: CO, CH4, to complex organic compounds.
Слайд 12
Hydrogen
structural molecule, participant in process of energy generation.
Protons (H+) involved in ATP production, CO2 reduction, anaerobic
and aerobic respiration.
Слайд 13
Nitrogen
in amino acids, nucleic acids. membranes, cell walls,
and most macromolecules. Most free-living microbes assimilate ammonia from
their environment or reduce nitrate. An array of microbial types can "fix" atmospheric nitrogen.
Слайд 14
Sulfur
in certain amino acids, some B-vitamins (biotin and
thiamine). Reduced inorganic sulfur (e.g. H2S) used as energy
source for thiobacilli. Sulfur serves as terminal electron acceptor in some Archaea.
Слайд 15
Phosphorus
a constituent of high energy compounds (ATP), phospholipids
in membranes, nucleic acids.
Слайд 16
Oxygen
equal amounts in aerobes and anaerobes, but free
oxygen toxic to anaerobes, so they obtain it in
a combined form from the substrate.Слайд 17 Trace elements, though not required in large amounts,
are essential for cellular growth:
K+ Principle
cellular counterionMg++ DNA polymerase
Ca++ Intracellular signalling, wall structure
Fe++ Cytochromes
Mn++ PsII, photosynthesis
Co++ Vitamin B12 constituent (methylations)
Cu++ Superoxide dimutase
Zn++ Some DNA binding proteins
Слайд 18
Organic Growth Factors
Organic Growth Factors are essential organic
compounds that an organism is unable to synthesize. They
must be obtained directly from the environment.Examples: Vitamins, Amino acids, Purines, pyrimidines
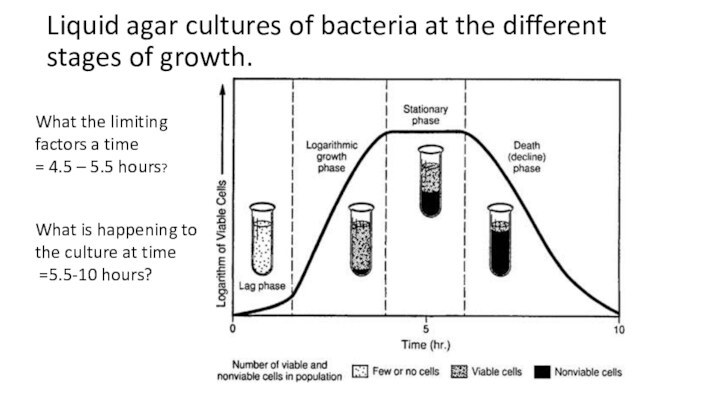
Слайд 20 Liquid agar cultures of bacteria at the different
stages of growth.
What is happening to the culture at
time=5.5-10 hours?
What the limiting factors a time
= 4.5 – 5.5 hours?
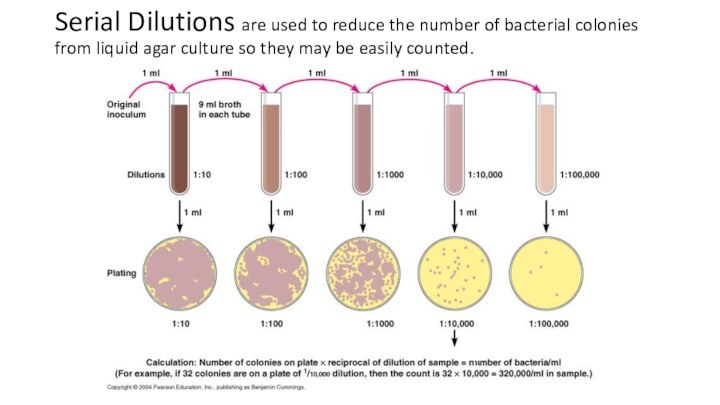
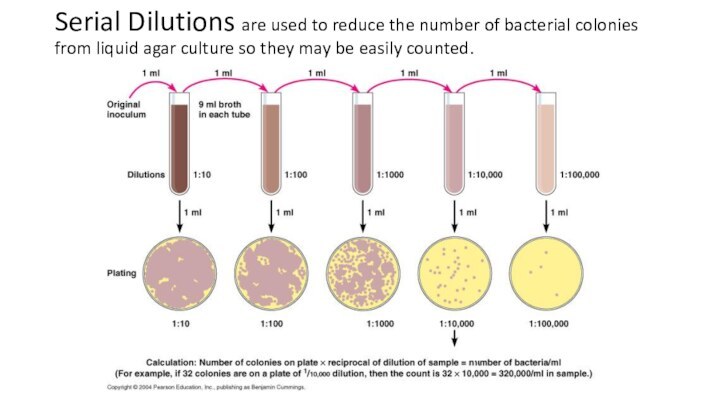
Слайд 21 Serial Dilutions are used to reduce the number
of bacterial colonies from liquid agar culture so they
may be easily counted.
Слайд 22
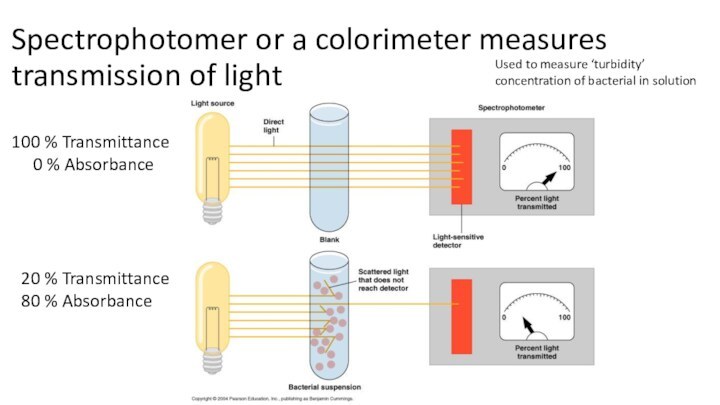
Spectrophotomer or a colorimeter measures transmission of light
100
% Transmittance
0 % Absorbance
20 %
Transmittance80 % Absorbance
Used to measure ‘turbidity’
concentration of bacterial in solution
Слайд 23
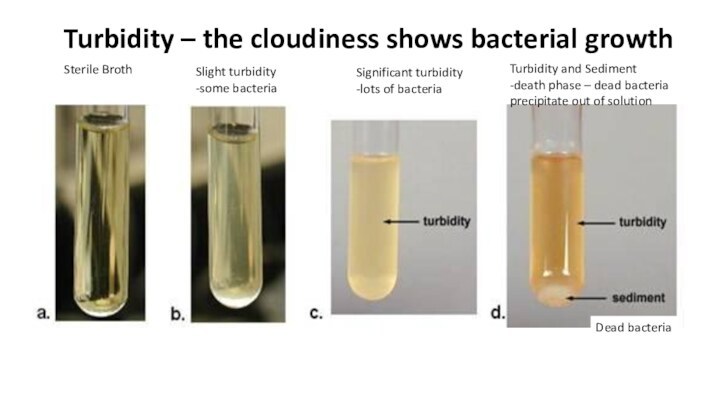
Turbidity – the cloudiness shows bacterial growth
Turbidity and
Sediment
-death phase – dead bacteria
precipitate out of solution
Sterile Broth
Significant
turbidity-lots of bacteria
Slight turbidity
-some bacteria
Dead bacteria
Слайд 24 Serial Dilutions are used to reduce the number
of bacterial colonies from liquid agar culture so they
may be easily counted.
Слайд 25
Practical: Plate it on different nutrient agar dishes
1-
Nutrient closed petri dish
2- No nutrient closed petri dish
3-
Glucose closed petri dish4 – No glucose closed petri dish
5 – Nutrient open petri dish
6 - No nutrient open petri dish
72 hours in incubator or 72 hours covered in warm part of room.