- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему General aspects of chemical structure and reactivity of organic compounds
Содержание
- 2. General aspects of chemical structure and reactivity of organic compoundsLecture №1
- 3. Chemical bonding and mutual atoms’ influence in organic molecules
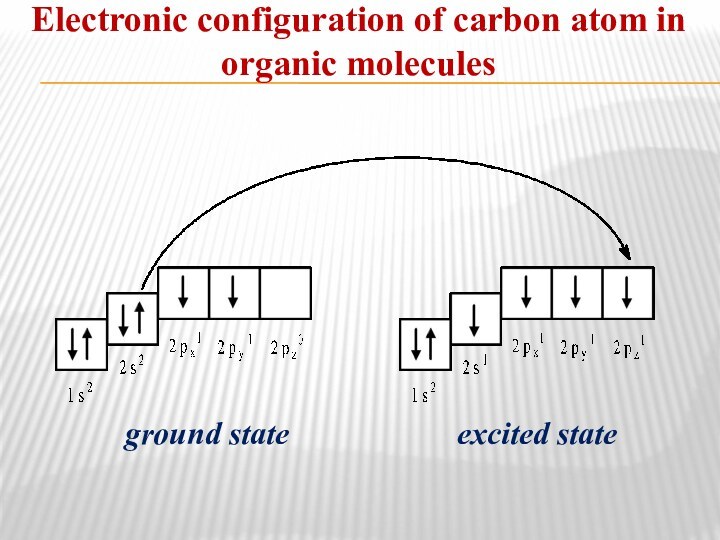
- 4. Electronic configuration of carbon atom in organic moleculesground stateexcited state
- 5. Atomic orbitalsThe orbital is a region of
- 6. Hybridization of orbitalsHybridization is the process of atomic orbitals alignment in form and energy.
- 7. sp3-Hybridizationtetrahedral configuration
- 8. sp2-Hybridizationplanar configuration
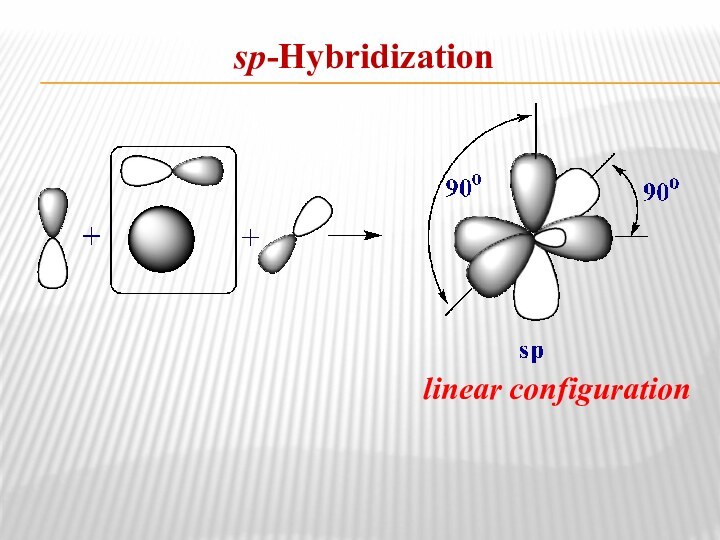
- 9. sp-Hybridizationlinear configuration
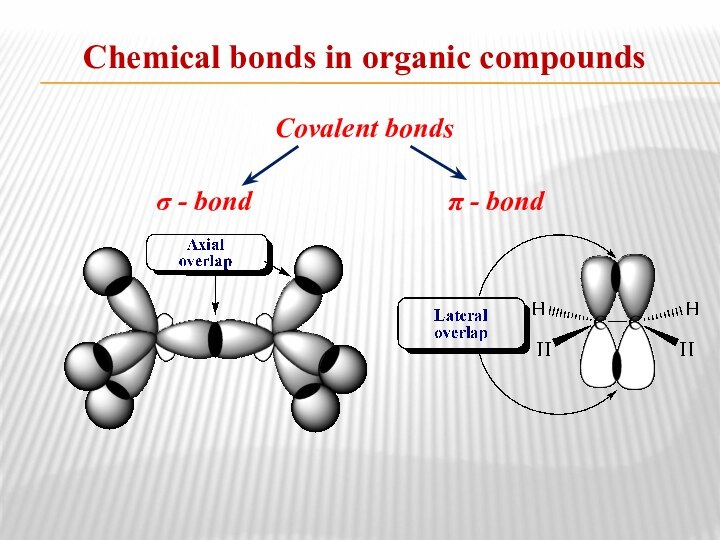
- 10. Chemical bonds in organic compoundsCovalent bonds
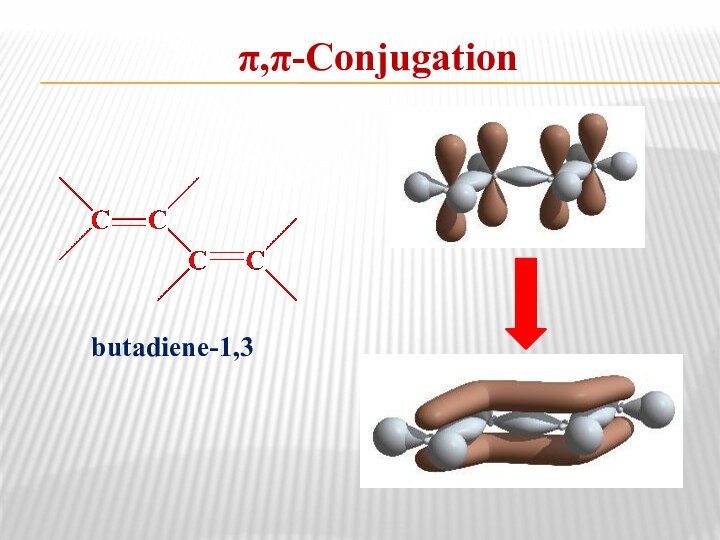
- 11. ConjugationConjugation is the formation of delocalized electronic
- 12. π,π-Conjugationbutadiene-1,3
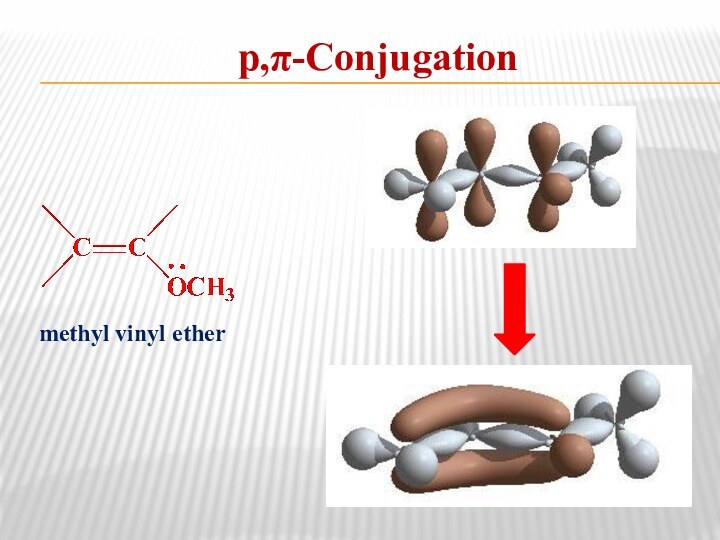
- 13. р,π-Conjugationmethyl vinyl ether
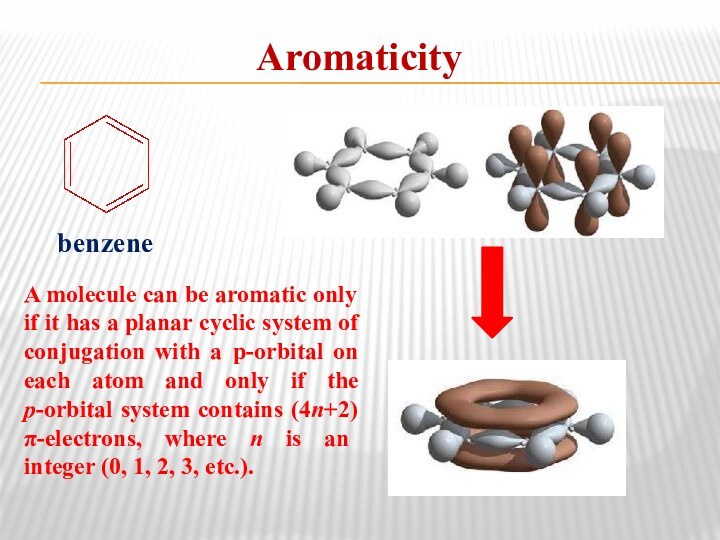
- 14. AromaticitybenzeneA molecule can be aromatic only if
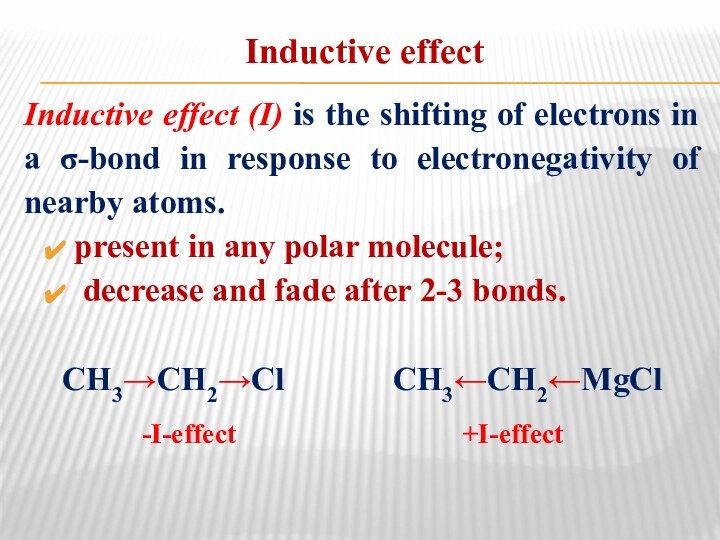
- 15. Inductive effectInductive effect (I) is the shifting
- 16. Mesomeric effectMesomeric effect (М) is the shifting
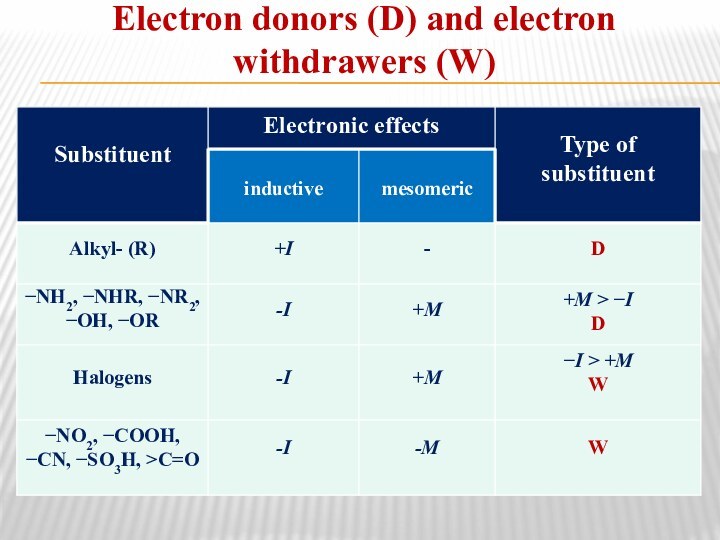
- 17. Electron donors (D) and electron withdrawers (W)
- 18. Spatial structure of organic compounds
- 19. Isomerism of organic compoundsIsomers are the compounds
- 20. StereoisomerismStereoisomers are the compounds that have the
- 21. Configuration is the arrangement of atoms and
- 22. ChiralityChirality is the property of the object
- 23. EnantiomersEnantiomers are the stereoisomers, the molecules of
- 24. Fischer projections
- 25. D,L-Nomenclature Glyceraldehyde is the configurational standard. Fischer
- 26. R,S-Nomenclature The least substituent near the chiral
- 27. DiastereomersDiastereomers are the stereoisomers that are not
- 28. meso CompoundsA meso compound is an optically inactive achiral stereoisomer containing chiral centers.L-tartaricacidD-tartaricacidmeso-tartaricacidplane ofsymmetry
- 29. Acidity and basicity of organic compounds
- 30. Acidity and basicity are the key notions,
- 31. Brønstedt-Lowry conceptJ.-N. BrønstedtТ. М. LowryAn acid is
- 32. Brønstedt acidsAcidic site is a part of
- 33. Brønstedt basesBasic site is a heteroatom with
- 34. Comparison the acidityThe more stable is an
- 35. The influence of atom nature in acidic
- 36. The influence of substituents effects inductive effect mesomeric effectAcidity increaseAcidity increase
- 37. Comparison the basicityThe more stable is an
- 38. The influence of atom nature in the
- 39. Скачать презентацию
- 40. Похожие презентации
















Слайд 5
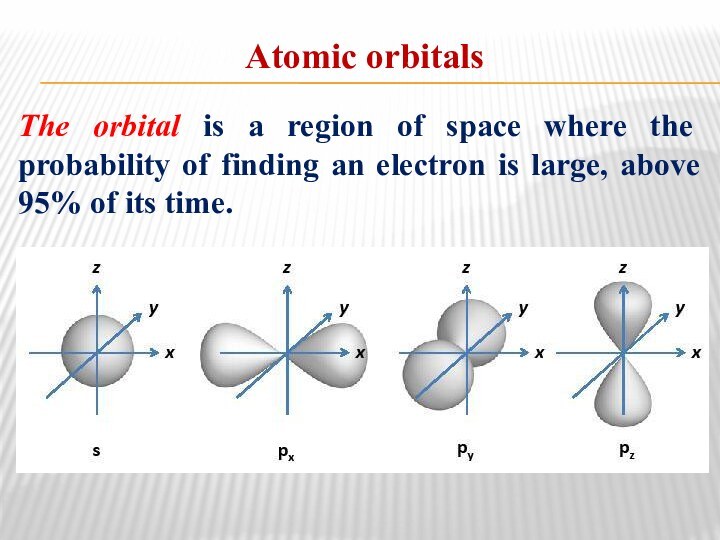
Atomic orbitals
The orbital is a region of space
where the probability of finding an electron is large,
above 95% of its time.
Слайд 6
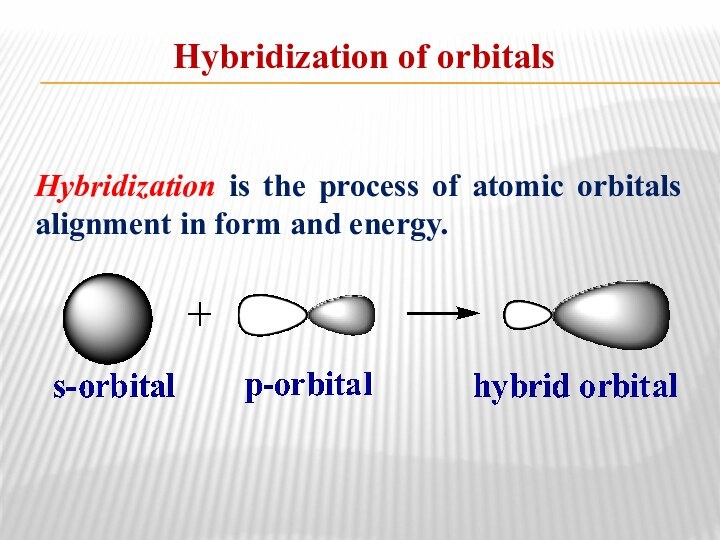
Hybridization of orbitals
Hybridization is the process of atomic
orbitals alignment in form and energy.
Слайд 11
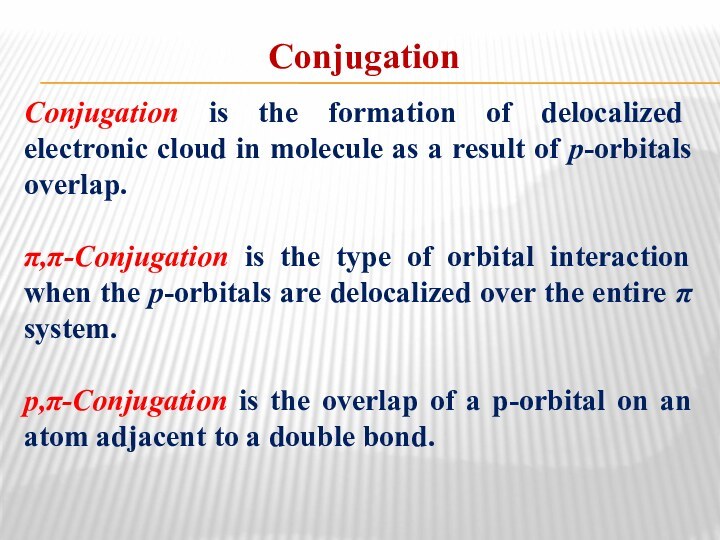
Conjugation
Conjugation is the formation of delocalized electronic cloud
in molecule as a result of p-orbitals overlap.
π,π-Conjugation is
the type of orbital interaction when the p-orbitals are delocalized over the entire π system.p,π-Conjugation is the overlap of a p-orbital on an atom adjacent to a double bond.
Слайд 14
Aromaticity
benzene
A molecule can be aromatic only if it
has a planar cyclic system of conjugation with a
p-orbital on each atom and only if the p-orbital system contains (4n+2) π-electrons, where n is an integer (0, 1, 2, 3, etc.).
Слайд 15
Inductive effect
Inductive effect (I) is the shifting of
electrons in a σ-bond in response to electronegativity of
nearby atoms.present in any polar molecule;
decrease and fade after 2-3 bonds.
СН3→СН2→Сl CH3←CH2←MgCl
-I-effect
+I-effect
Слайд 16
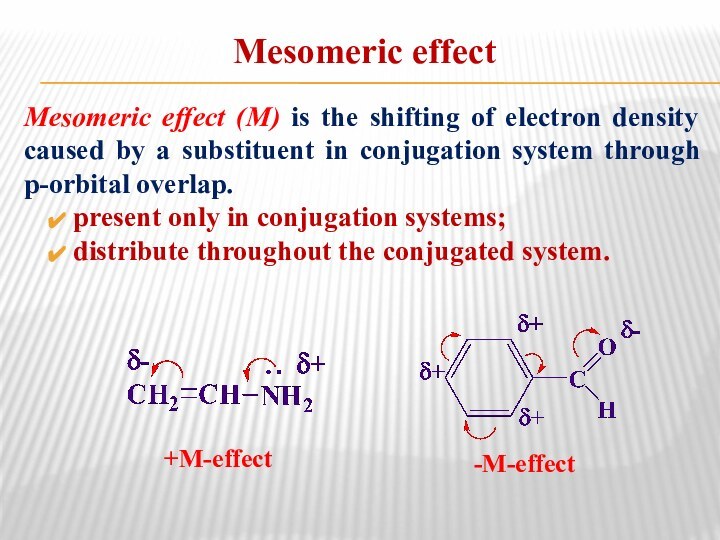
Mesomeric effect
Mesomeric effect (М) is the shifting of
electron density caused by a substituent in conjugation system
through p-orbital overlap.present only in conjugation systems;
distribute throughout the conjugated system.
+М-effect
-М-effect
Слайд 19
Isomerism of organic compounds
Isomers are the compounds which
have the same composition but different sequence of atoms
or their location in space, therefore have different properties.Isomers
Structural
Spatial
Skeleton isomers
Positional isomers
Functional isomers
Geometrical
Optical
Слайд 20
Stereoisomerism
Stereoisomers are the compounds that have the same
order of atoms attachment but differ only in the
arrangement of their atoms or groups in space.Stereoisomers
Configurational
Conformational
Слайд 21 Configuration is the arrangement of atoms and groups
in space without regard to arrangements that differ only
due to rotation about one or more single bonds.Carbon atom configurations
Configuration of molecules
tetrahedral planar linear
Слайд 22
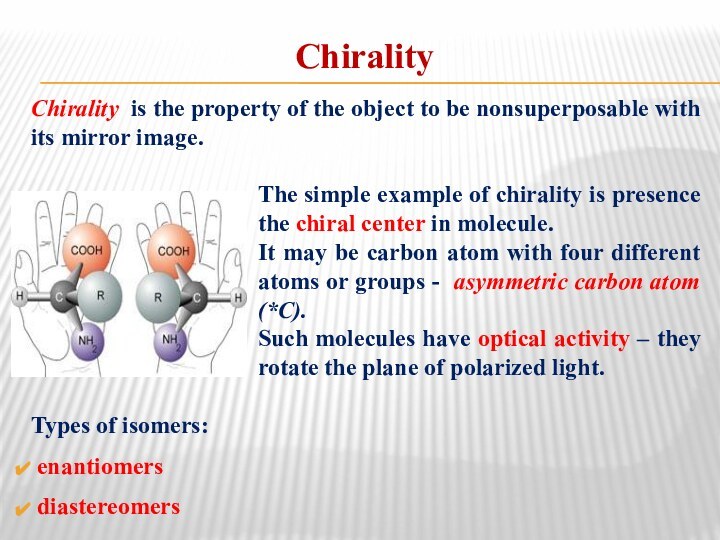
Chirality
Chirality is the property of the object to
be nonsuperposable with its mirror image.
The simple example of
chirality is presence the chiral center in molecule. It may be carbon atom with four different atoms or groups - asymmetric carbon atom (*С).
Such molecules have optical activity – they rotate the plane of polarized light.
Types of isomers:
enantiomers
diastereomers
Слайд 23
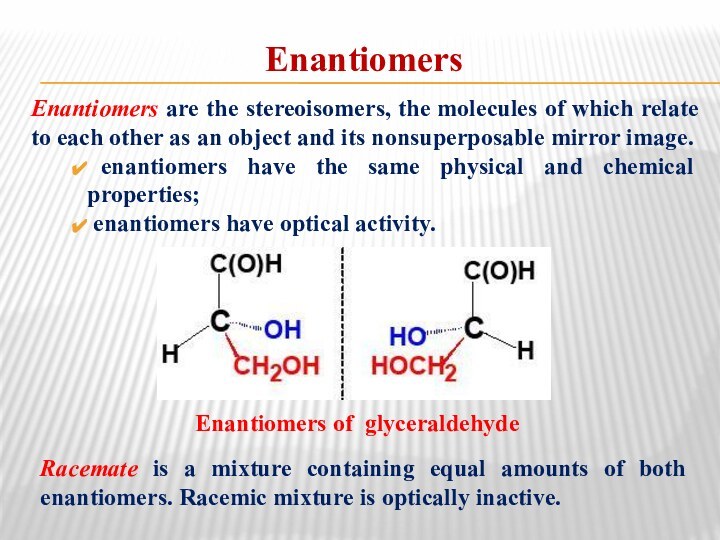
Enantiomers
Enantiomers are the stereoisomers, the molecules of which
relate to each other as an object and its
nonsuperposable mirror image.enantiomers have the same physical and chemical properties;
enantiomers have optical activity.
Enantiomers of glyceraldehyde
Racemate is a mixture containing equal amounts of both enantiomers. Racemic mixture is optically inactive.
Слайд 24
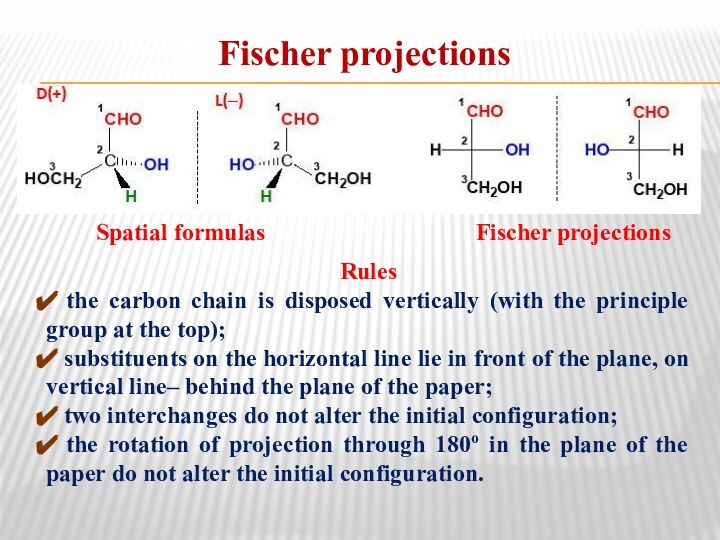
Fischer projections
Spatial
formulas
Fischer projectionsRules
the carbon chain is disposed vertically (with the principle group at the top);
substituents on the horizontal line lie in front of the plane, on vertical line– behind the plane of the paper;
two interchanges do not alter the initial configuration;
the rotation of projection through 180o in the plane of the paper do not alter the initial configuration.
Слайд 25
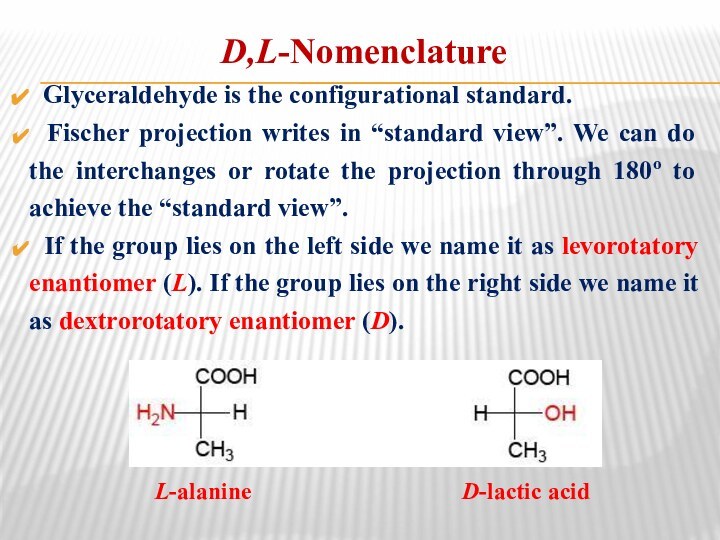
D,L-Nomenclature
Glyceraldehyde is the configurational standard.
Fischer projection
writes in “standard view”. We can do the interchanges
or rotate the projection through 180o to achieve the “standard view”.If the group lies on the left side we name it as levorotatory enantiomer (L). If the group lies on the right side we name it as dextrorotatory enantiomer (D).
L-alanine D-lactic acid
Слайд 26
R,S-Nomenclature
The least substituent near the chiral center
must lie at the bottom of the Fischer projection.
Atoms attached directly to the chiral center are first arranged according to decreased atomic number.
If the remaining three groups are arranged clockwise, the configuration is symbolized by R. If they form a counterclockwise array, the configuration is symbolized by S.
L-lactic acid
(S)-lactic acid
Слайд 27
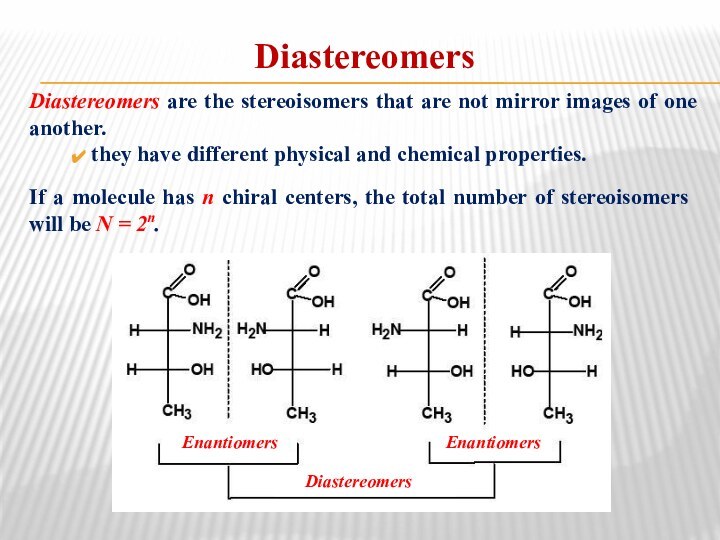
Diastereomers
Diastereomers are the stereoisomers that are not mirror
images of one another.
they have different physical and
chemical properties.If a molecule has n chiral centers, the total number of stereoisomers will be N = 2n.
Diastereomers
Enantiomers
Enantiomers
Слайд 28
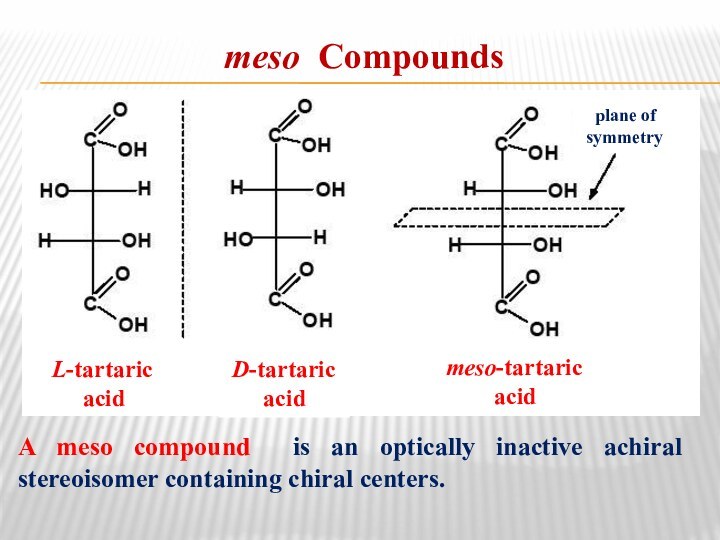
meso Compounds
A meso compound is an optically inactive
achiral stereoisomer containing chiral centers.
L-tartaric
acid
D-tartaric
acid
meso-tartaric
acid
plane of
symmetry
Слайд 30 Acidity and basicity are the key notions, determining
many fundamental physico-chemical and biochemical properties of organic compounds.
Слайд 31
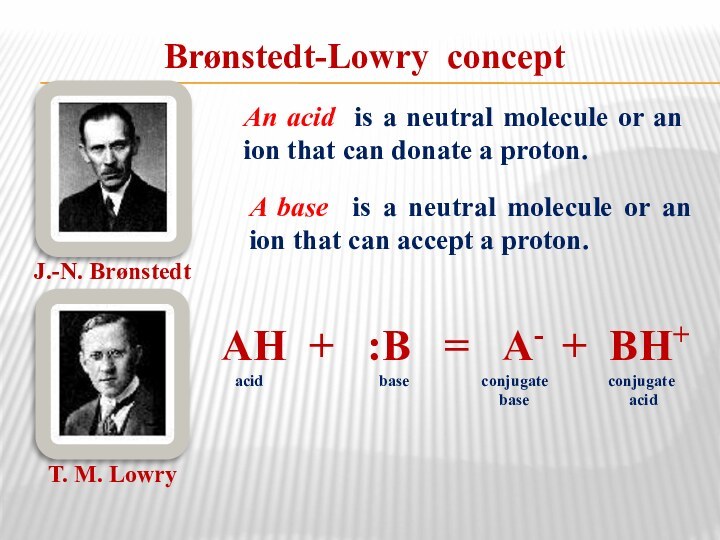
Brønstedt-Lowry concept
J.-N. Brønstedt
Т. М. Lowry
An acid is a
neutral molecule or an ion that can donate a
proton.A base is a neutral molecule or an ion that can accept a proton.
АН + :В = А- + ВН+
acid base conjugate conjugate
base acid
Слайд 32
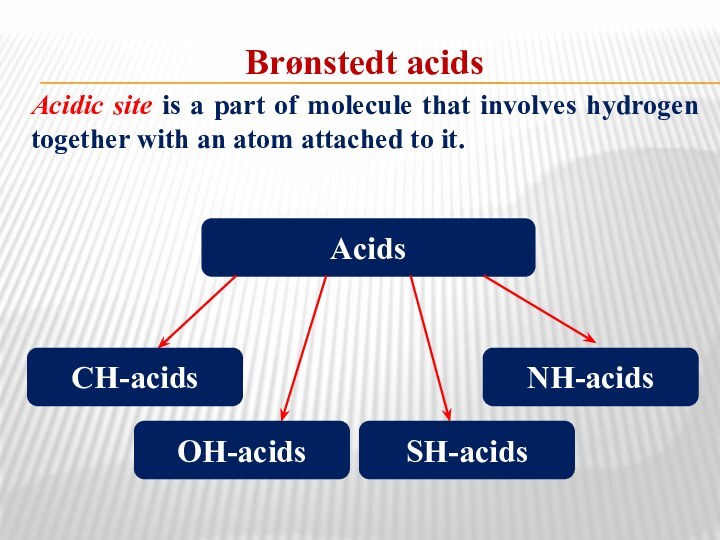
Brønstedt acids
Acidic site is a part of molecule
that involves hydrogen together with an atom attached to
it.Acids
СН-acids
ОН-acids
SН-acids
NН-acids
Слайд 33
Brønstedt bases
Basic site is a heteroatom with a
lone-pair of electrons or a π-bond which are capable
to accept a proton.Bases
n-bases
π-bases
Слайд 34
Comparison the acidity
The more stable is an anion,
the stronger is an acid!
The factors which influence the
stability of conjugate bases:electronegativity and polarizability of the atom in the acidic site;
delocalization of a negative charge due to the effect of substituens in a molecule;
solvation effects.
Слайд 35
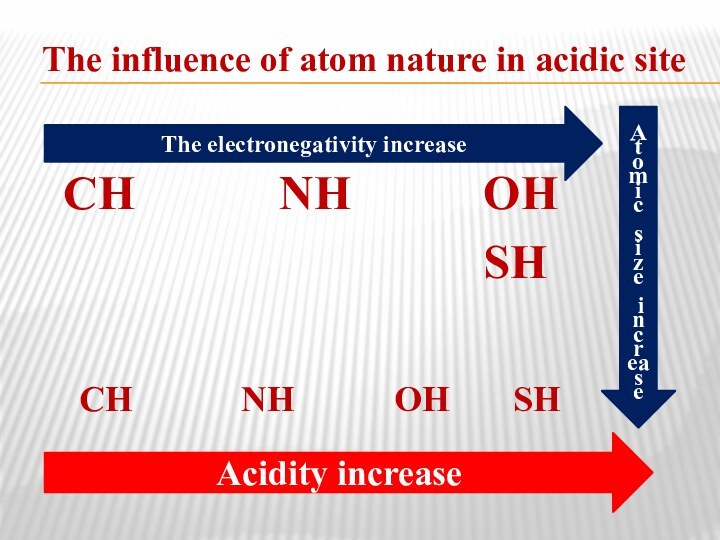
The influence of atom nature in acidic site
СН
NH
ОНSH
СН NH ОН SH
The electronegativity increase
At
omi
c
s
i
z
e
i
nc
r
ea
s
e
Acidity increase
Слайд 36
The influence of substituents effects
inductive effect
mesomeric effect
Acidity increase
Acidity increase
Слайд 37
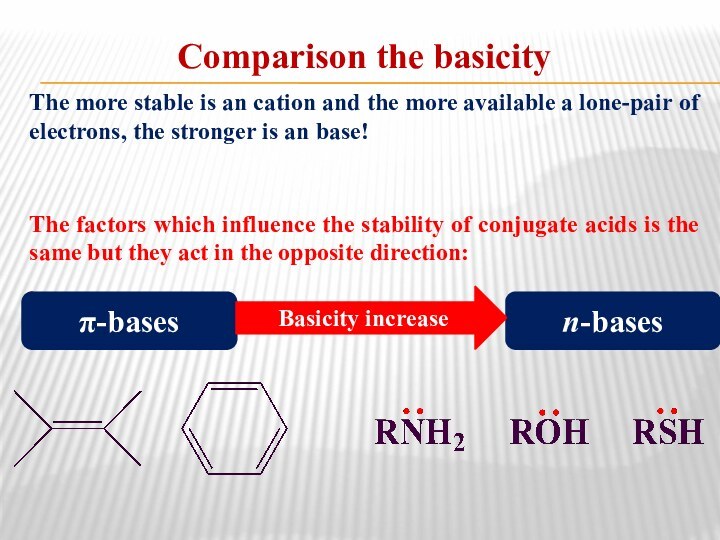
Comparison the basicity
The more stable is an cation
and the more available a lone-pair of electrons, the
stronger is an base!The factors which influence the stability of conjugate acids is the same but they act in the opposite direction:
.
n-bases
π-bases
Basicity increase
Слайд 38 The influence of atom nature in the basic
site
S
О NThe influence of substituents effects
Basicity increase