Слайд 2
The Russian victory in the Battle of Poltava
in 1709 freed Tsar Peter I from any further
restraint in his policy aimed at absorbing Ukraine into the Russian Empire:
Left-Bank Ukraine became a military colony.
The Cossack army was put under Russian command
Hetman became subject to constant supervision by Russian residents of the tsar
Слайд 3
In 1775 the Zaporozhian Sich was destroyed.
By
1782 all
the traditional Cossack regiments of the Hetman
state were abolished.
Слайд 4
Ukrainian people participated together with Russians in the
Patriotic War 1812 against the French invaders of Napoleon
Слайд 5
West Ukrainian territories was under the rule of
Austro-Hungarian monarchy.
During the 1st half of the XIX
ct. there was growing wave of popular struggle against national oppression
Слайд 6
The Revolution of 1848-1849 in the Habsburg monarchy
played a decisive role in the process of the
emergence of Ukrainian political organizations and the shaping of the modern Ukrainian identity in Western Ukraine. With the outbreak of the revolution the Ukrainian question became a political question.
Слайд 7
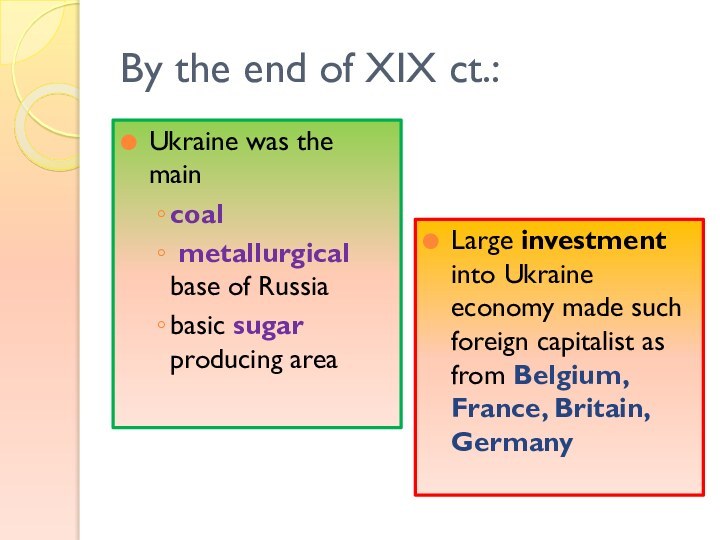
By the end of XIX ct.:
Ukraine was the
main
coal
metallurgical base of Russia
basic sugar producing
area
Large investment into Ukraine economy made such foreign capitalist as from Belgium, France, Britain, Germany
Слайд 8
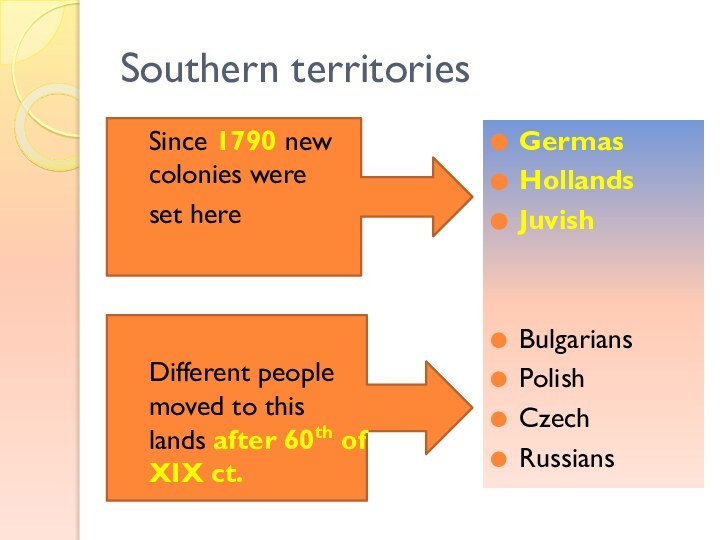
Southern territories
Since 1790 new colonies were
set here
Different
people moved to this lands after 60th of XIX
ct.
Germas
Hollands
Juvish
Bulgarians
Polish
Czech
Russians
Слайд 9
First Russian Revolution
1905 - 1907
Reasons:
Necessity of reformation industry
and agricultural complex
Results:
Reforming monarchy into Parliament monarchy
Guarantee the main
public liberties (personal immunity, freedom of speech, freedom of conscience)
Reforming agricultural sphere
Слайд 10
Beginning of XX ct. – arising of different
problems between European states
World War I
(Great War)
28
July 1914
–
11 November 1918
Слайд 11
Background of the war:
Antagonisms between great states
Economical imperialism
Militarism
Слайд 12
February revolution 1917
results
Abdication of Tsar Nicolas II
results
The
collapse of Russian Empire
results
Tsarism was replaced by Russian Provisional
Government (alliance of liberals and socialists)
Слайд 13
October Revolution 1917
Bolsheviks took the power
The end of
Monarchy
Changes in all spheres of life
Слайд 14
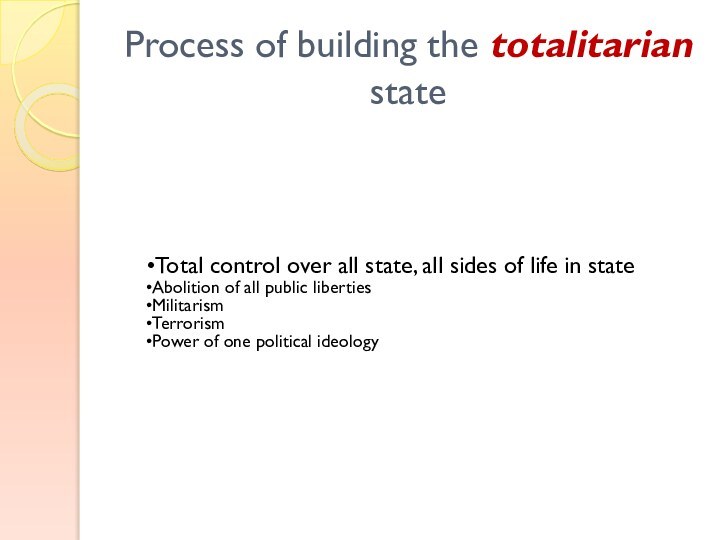
Process of building the totalitarian state
Total control over
all state, all sides of life in state
Abolition of
all public liberties
Militarism
Terrorism
Power of one political ideology
Слайд 15
As Bolsheviks came to power a new period
of Ukrainian history began.
On 17 March 1917 the Central
Rada was created in Kyiv
Слайд 16
Central Rada (Tsentralna Rada).
At first, an all-Ukrainian
center that united political, community, cultural, and professional organizations;
later, after the All-Ukrainian National Congress (17–21 April 1917), the revolutionary parliament of Ukraine that directed the Ukrainian national movement and by the four Universals of the Central Rada led Ukraine from autonomy to independence.
Слайд 17
Universals of the Central Rada
First Universal
(23 June
1917) the CR proclaimed Ukraine's autonomy
‘from this day on
we alone will create our life’
Слайд 18
Second Universal
(16 July 1917) reflected the results
of the negotiations between the General Secretariat and Provisional
Government
A new General Secretariat would be appointed and would be ‘subject to confirmation by the Provisional Government as the repository of the highest regional authority of the Provisional Government in Ukraine.’ The CR would ‘prepare drafts of legislation for Ukraine's autonomous structure,’ would submit them for confirmation to the All-Russian Constituent Assembly, and would not take any steps to establish Ukrainian autonomy until the assembly was convoked.
Слайд 19
Third Universal
20 November 1917
it proclaimed the creation
of the Ukrainian National Republic within a federated Russia
of equal and free peoples. The Ukrainian National Republic would be governed by the Central Rada and General Secretariat of the Central Rada until the convocation of the Constituent Assembly of Ukraine.
Слайд 20
Fourth Universal
22 January 1918 was issued after the
Ukrainian-Soviet War, 1917–21 began
it proclaimed the Ukrainian National Republic
an ‘independent, subject to no one, free, sovereign state of the Ukrainian people.