- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Carbohydrates. starch.
Содержание
- 2. A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms.
- 3. The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes
- 4. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups
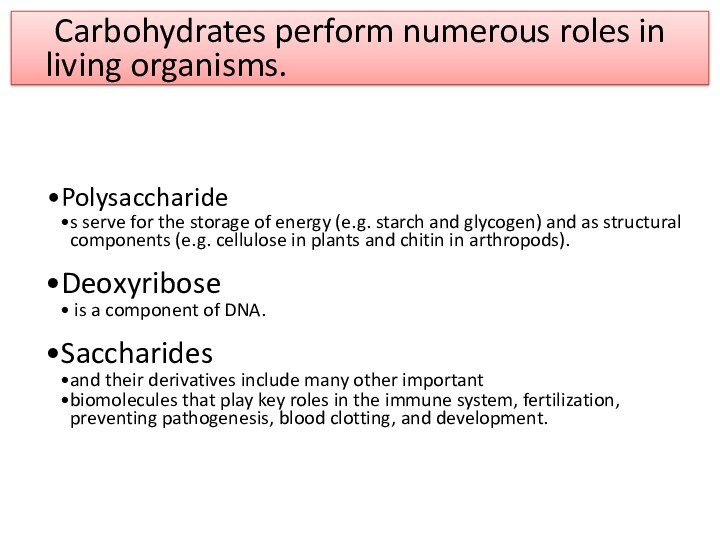
- 5. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms.
- 6. Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units
- 7. Pure starch is a white, tasteless and
- 8. History Starch grains from the rhizomes of Typha (cattails, bullrushes)
- 9. Скачать презентацию
- 10. Похожие презентации
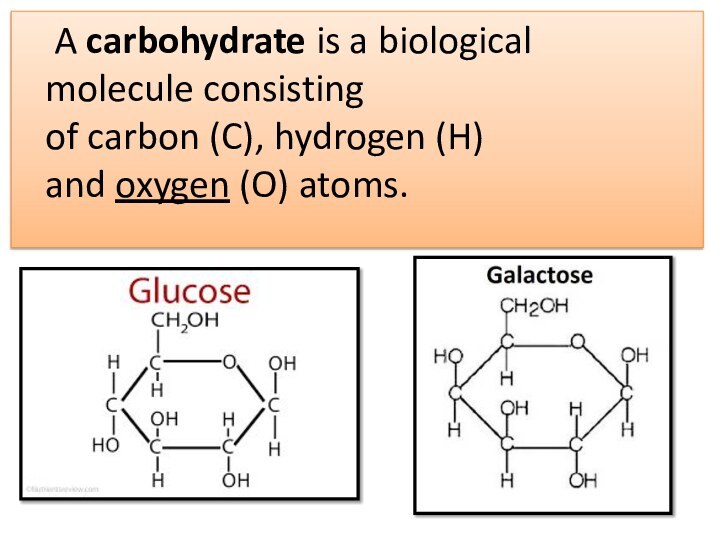
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms.






Слайд 2
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms.
Слайд 3 The term is most common in biochemistry, where it
is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes
Слайд 6 Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined
by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants as an energy
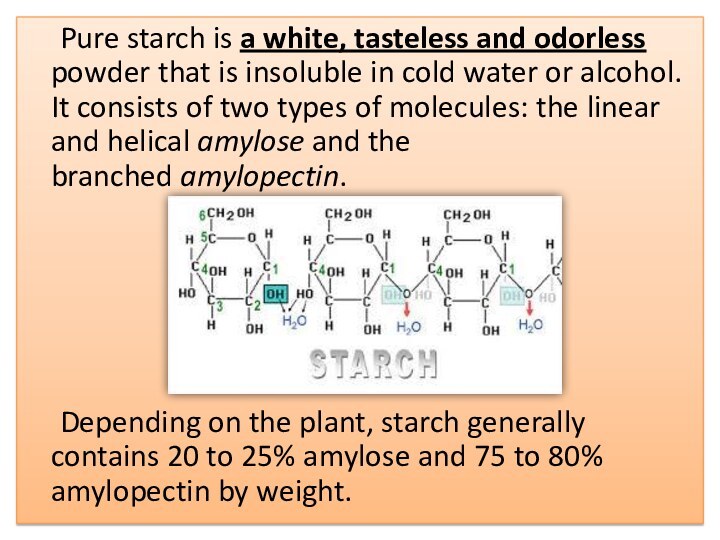
store. It is the most common carbohydrate in human diets and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as potatoes, wheat, maize (corn), rice, and cassava.Слайд 7 Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless
powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol.
It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical amylose and the branched amylopectin.Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight.
Слайд 8
History
Starch grains from the rhizomes of Typha (cattails, bullrushes) as flour have been identified
from grinding stones in Europe dating back to 30,000 years ago.
Pure
extracted wheat starch paste was used in Ancient Egypt possibly to glue papyrus. Romans used it also in cosmetic creams, to powder the hair and to thicken sauces.
Persians and Indians used it to make dishes similar to gothumai wheat halva.
Rice starch as surface treatment of paper has been used in paper production in China, from 700 AD onwards.





























