- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Hydrosphere. biosphere.
Содержание
- 2. Plan:1. Hydrosphere and its structure.2. The World
- 3. 1. HYDROSPHERE the liquid water component of
- 4. It includesthe oceans, seas, lakes, ponds, rivers and streams.
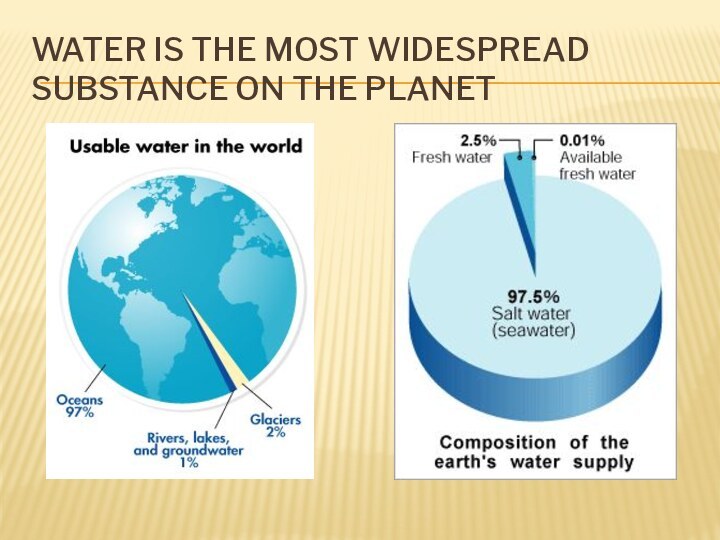
- 5. Water is the most widespread substance on the planet
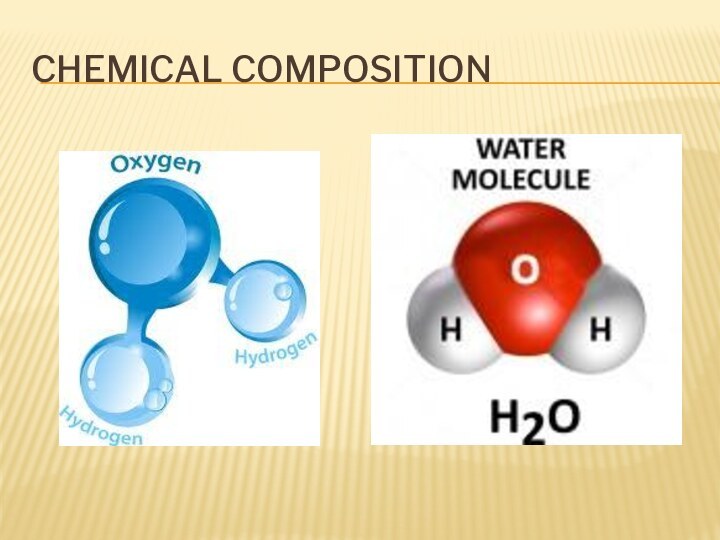
- 6. Chemical composition
- 7. Properties of waterAggregate stateWhen water freezes, it
- 8. Water cycle Continuous cycle water movement in atmosphere,
- 9. 2. World Oceantotal capacity is about 1
- 10. The Pacific Oceanthe largest and the deepest
- 11. The Atlantic OceanThe Atlantic Ocean stretches from
- 12. The Indian OceanThe Indian Ocean is only
- 13. The Arctic OceanThe smallest ocean is the
- 14. SeaSmall and large parts of ocean that
- 15. GulfGulf is a component of oceans, seas,
- 16. Channel Channel is rather narrow space, which
- 17. 3. Land’s watersGround waters, (Water, which leaks
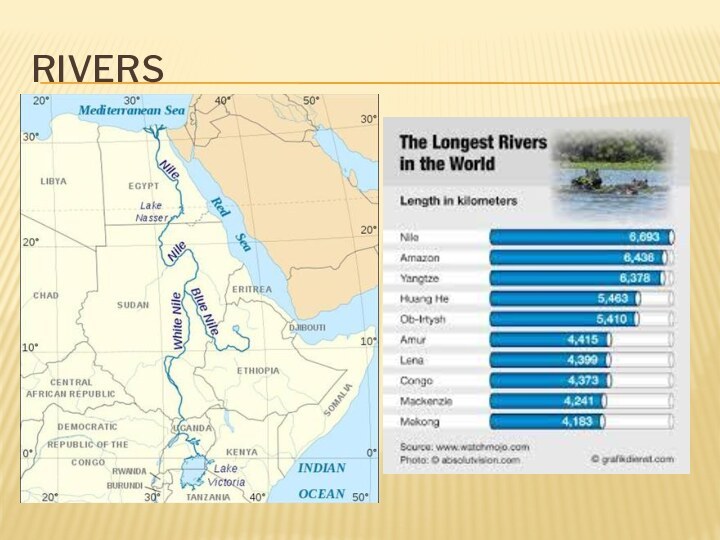
- 18. RiversThe Nile (4160 km)The Amazon (4000 km)The Mississippi (3870km)
- 19. Lakes
- 20. 4. Biospherea special Earth cover, where activity
- 21. Biosphereincludes the bottom of atmosphere, hydrosphere and
- 22. Living organismsFlora (plants)Fauna (animals)
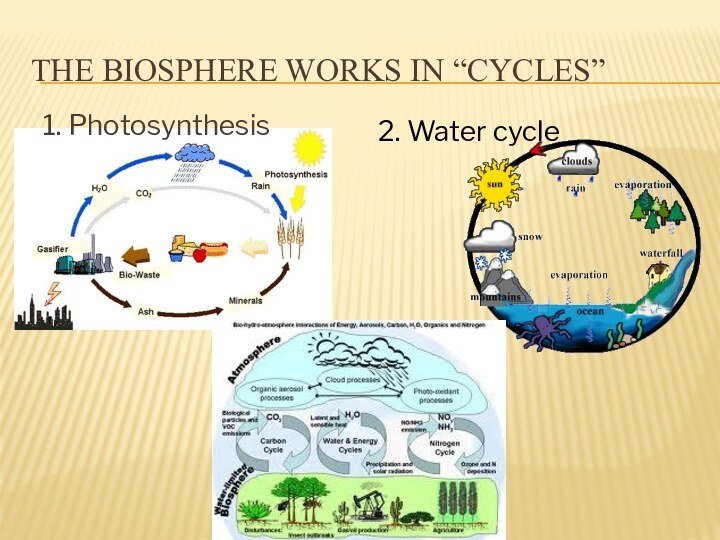
- 23. The biosphere works in “cycles” 1. Photosynthesis 2. Water cycle
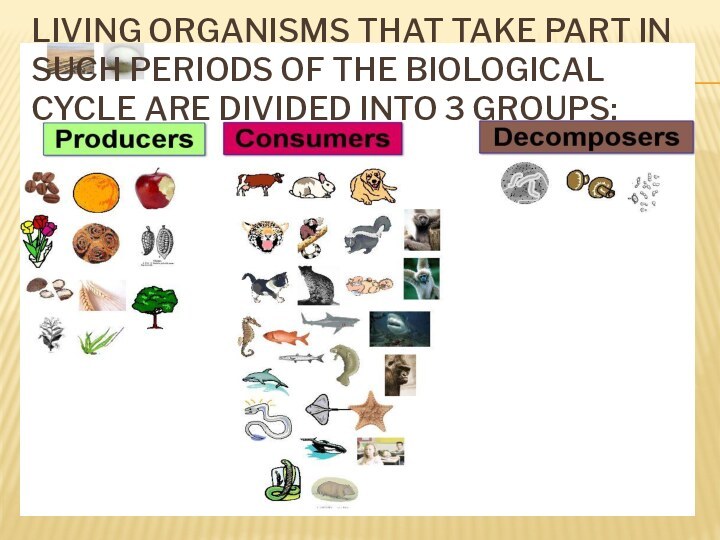
- 24. Living organisms that take part in
- 25. Скачать презентацию
- 26. Похожие презентации
Plan:1. Hydrosphere and its structure.2. The World Ocean and its parts.3. Land’s waters. 4. Structure and texture of biosphere.














Слайд 3
1. HYDROSPHERE
the liquid water component of the
Earth.
covers 70% of the surface of the Earth and
is the home for many plants and animals.Total capacity of hydrosphere is about 1,4 billion km².
Слайд 7
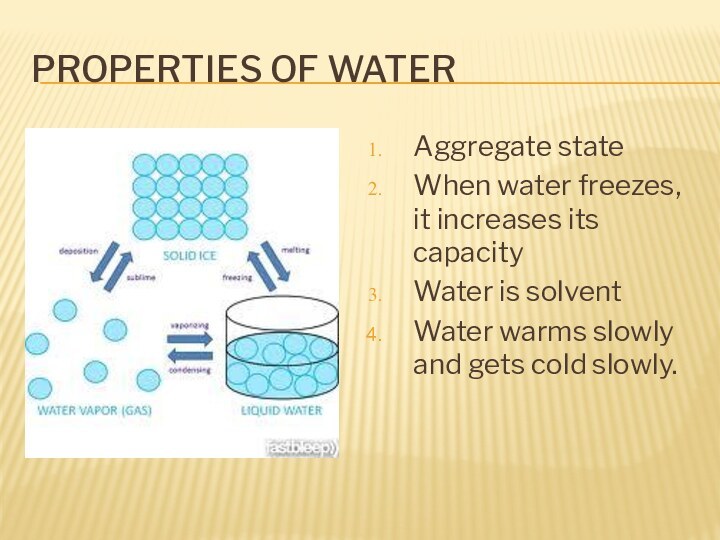
Properties of water
Aggregate state
When water freezes, it increases
its capacity
Water is solvent
Water warms slowly and gets cold
slowly.
Слайд 8
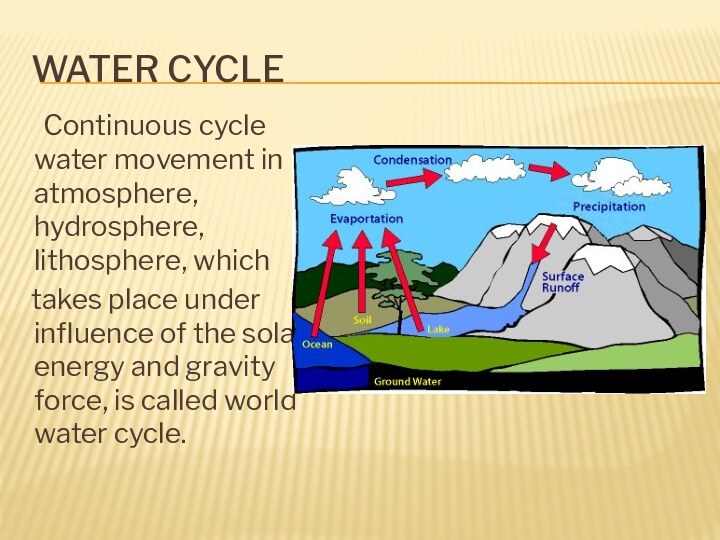
Water cycle
Continuous cycle water movement in atmosphere, hydrosphere,
lithosphere, which
takes place under influence of
the solar energy and gravity force, is called world water cycle.
Слайд 9
2. World Ocean
total capacity is about 1 billion
370 million km
94% of hydrosphere
There are 73 from 110
chemical elements in its waters.includes oceans, seas, gulfs and channels. There are four oceans.
Слайд 10
The Pacific Ocean
the largest and the deepest of
all, its total area is greater than that of
all the dry land.
Слайд 11
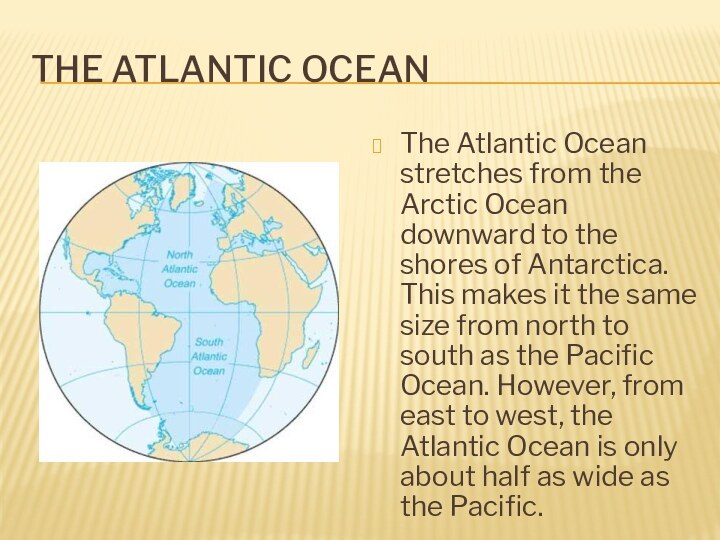
The Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean stretches from the
Arctic Ocean downward to the shores of Antarctica. This
makes it the same size from north to south as the Pacific Ocean. However, from east to west, the Atlantic Ocean is only about half as wide as the Pacific.
Слайд 12
The Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is only slightly
smaller than the Atlantic.
The Indian Ocean lies between
Africa on the west, Australia on the east, Asia on the north, and Antarctica on the south. 90% of this ocean lies to the south of the Equator.
Слайд 13
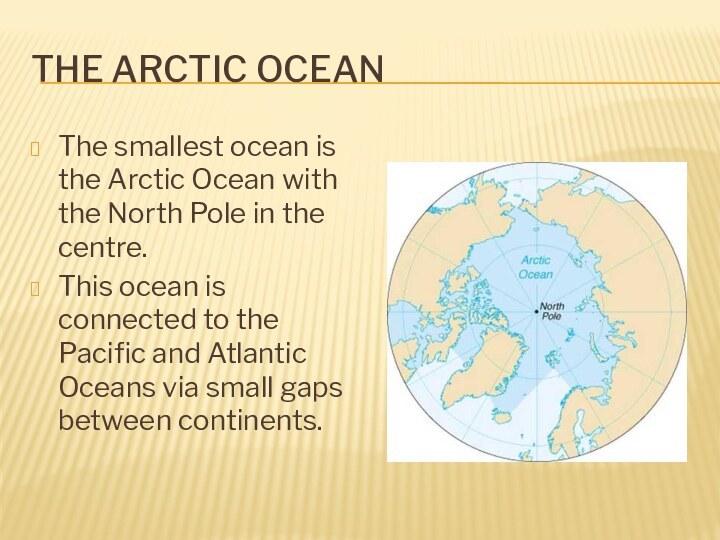
The Arctic Ocean
The smallest ocean is the Arctic
Ocean with the North Pole in the centre.
This
ocean is connected to the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans via small gaps between continents.
Слайд 14
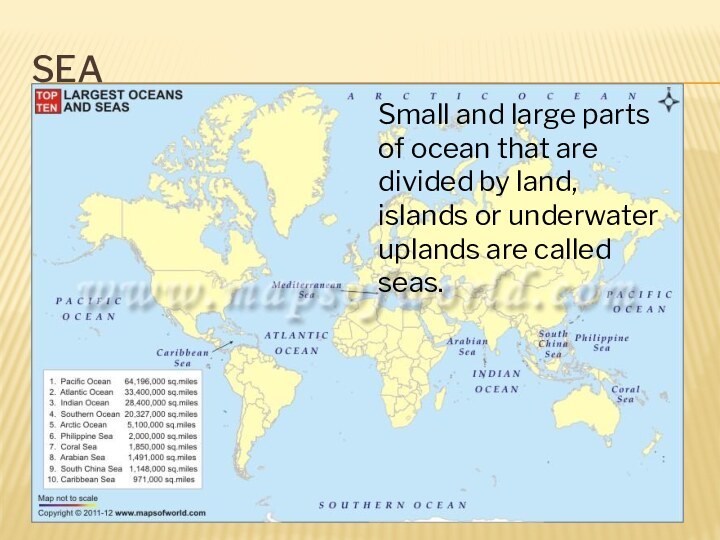
Sea
Small and large parts of ocean that are
divided by land, islands or underwater uplands are called
seas.
Слайд 15
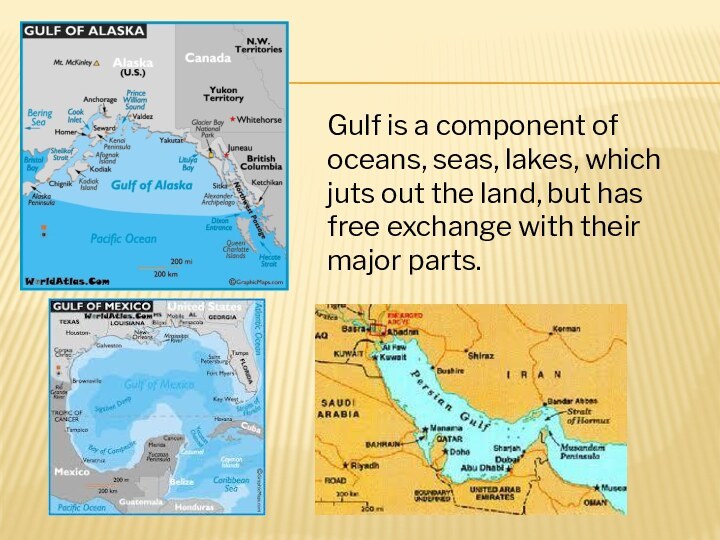
Gulf
Gulf is a component of oceans, seas, lakes,
which juts out the land, but has free exchange
with their major parts.
Слайд 16
Channel
Channel is rather narrow space, which connects
water area with any separate land’s parts. It’s natural
water basin.Canal – man-made basin. (Suez, Panama Canals)
Слайд 17
3. Land’s waters
Ground waters, (Water, which leaks through
the Earth crust upper layer, is forming ground waters.)
rivers,
lakes, (Lake is the natural reservoir, filling up with water, which has not a direct connection with the World Ocean. Lakes occupy about 2% of the land and are situated unevenly)
glaciers, (Glacier is a perennial icy layer, formed on the land at the expense of accumulation and transform of the falling solid precipitations. There are 24 millions km of fresh water in glaciers)
bogs,
artificial reservoirs (canals etc.)
Слайд 20
4. Biosphere
a special Earth cover, where activity of
all living organisms and cycle of matter and energy
between them is realized actively.«vital cover» of the Earth.





























