Слайд 2
PLAN FOR THE DAY
Part 1: Discuss the different
types of resources and the nature of firm capabilities
Relate
resources and capabilities to the value chain
Part 2: Barney’s VRIO framework for analyzing resources and capabilities’ potential for improving firm performance
Part 3: Domestic vs International capabilities
To offshore or not offshore
Слайд 3
PART 1:
RESOURCES AND CAPABILITIES AND
THE VALUE CHAIN
Слайд 4
Resource-based View (RBV) of the Firm
Tangible and intangible
resources/ assets
Tangibility implies we can observe or quantify (measure/
count)
Intangibility implies that the resource/ asset is not observable and difficult if not impossible to quantify
Capabilities
These are the things the firm is able to do as a result of combining resources (and capabilities) together to perform a specific task
How useful is it to try and separate resources and capabilities from one another, when they interact to such a great degree?
Слайд 5
Resources, Capabilities and the Value Chain
Value chain =
the vertical activities that create value
Upstream (sourcing/ manufacturing) to
down stream (selling)
Primary and secondary areas of activity in the value chain
Слайд 6
The Airbus A380 Value Chain?
Source: http://www.flightglobal.com/airspace/media/cutawayposters/airbus-a380-microcutaway-14474.aspx
Слайд 7
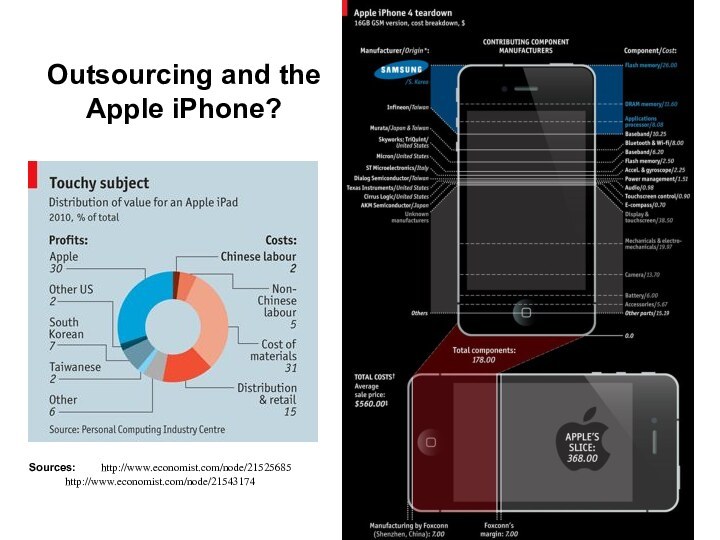
Outsourcing and the Apple iPhone?
Sources: http://www.economist.com/node/21525685
http://www.economist.com/node/21543174
Слайд 8
What does Apple Keep In-House?
Apple Campus 2 Project
Amsterdam
Apple Store
Слайд 9
Example of a Value Chain with Outsourcing
From the
example companies that are included, which could be described
as onshore and which offshore?
Слайд 10
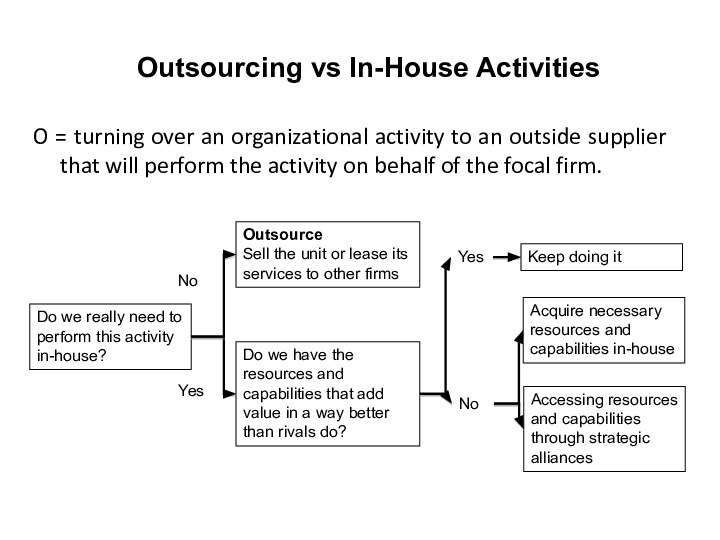
Outsourcing vs In-House Activities
O = turning over an
organizational activity to an outside supplier that will perform
the activity on behalf of the focal firm.
Слайд 11
In-house, Onshoring and Offshoring
Слайд 12
PART 2:
Jay Barney’s VRIO Framework
Слайд 13
VRIO and (Sustained) Competitive Advantage
Source: Barney J.B. (1995)
Looking Inside for Competitive Advantage. Academy of Management Executive,
9(4): 49-61.
Barney, Jay. 1991. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. Journal of Management 17(1): 99-120.
Слайд 14
Core Assumptions of the VRIO Framework
These are the
two foundation assumptions for the resource-based view of the
firm and strategic management
Firm Resource Heterogeneity
Firm Resource Immobility
Слайд 15
Resource Attributes for Achieving Sustained Competitive Advantage
Not all
resources will give a firm a SCA
A resource must
have four attributes to provide a SCA
It must be valuable
It must be rare
It must be imperfectly imitable
The firm needs to be organized to exploit the resource
Слайд 16
When is a Resource Valuable?
A resource is valuable
only when it enables strategies that improve firm efficiency
and effectiveness.
“The traditional ‘strengths-weaknesses-opportunities-threats’ model of firm performance suggests that firms are able to improve their performance only when their strategies exploit opportunities or neutralize threats” (Barney, 1991; p.106).
Слайд 17
When is a Resource Rare?
A resource (or bundle
of resources) is rare when it is not possessed
by many competing firms
Can you think how conditions that would prevent many firms gaining access to a particular resource or resource bundle?
Слайд 18
When is a Resource Imperfectly Imitable?
For a resource
to give a firm a SCA it must however
not only be valuable and rare, it must also be difficult to imitate or obtain
Three sources of resource imperfect imitability are:
Historical dependence
Causally ambiguity
Social complexity
Слайд 19
When is a Firm Organized to Exploit a
Resource?
Organization of the firm is concerned with (amongst other
things):
The development of new resource(s) / capabilities
The exploitation of current resource(s) / capabilities
Exploration vs exploitation and the multinational enterprise?
Слайд 20
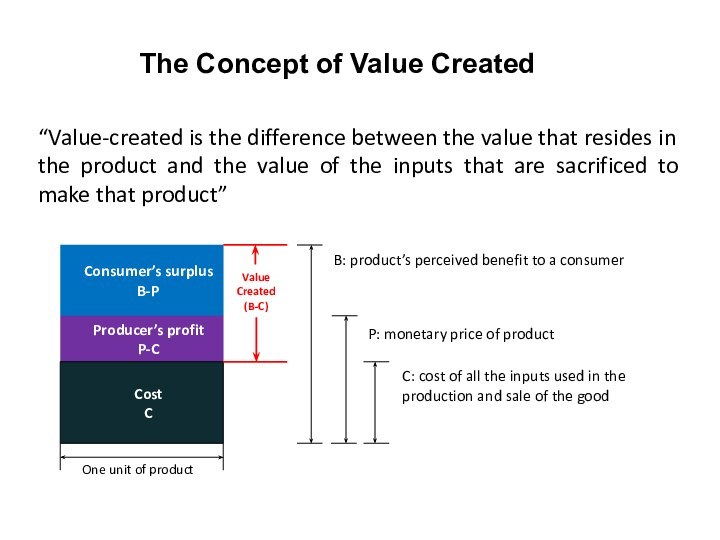
“Value-created is the difference between the value that
resides in the product and the value of the
inputs that are sacrificed to make that product”
The Concept of Value Created
Слайд 21
Describing Performance Outcomes
Comparison of value created (VC) with
a given resource bundle to the expected value (EV)
to be obtained (by the owners of these resources):
Below-Normal Performance: VC < EV
Normal Performance: VC = EV
Above-Normal Performance: VC > EV
This provides a relative conceptualization of how well a firm has performed with a given set of resources.
Слайд 22
PART 3:
DEBATE 1: DOMESTIC VS INTERNATIONAL CAPABILITIES
Слайд 23
RBV of Multinational Management
International diversification (Dess et al.,
1995)
Subsidiary capability development (Birkinshaw & Hood, 1998; Luo &
Peng, 1999)
International strategic human resource management (ISHRM) (Schuler, Dowling & Decieri, 1993; Beechlor and Napier, 1996)
Exploitation vs Exploration?
Слайд 25
RBV of Strategic Alliances
Since the 1980s, both the
corporate world and the academic fields of IB and
strategy have experienced an “alliance revolution” (Dunning, 1995).
While strategic alliances is a multi-faceted phenomenon, the RBV focuses on organizational learning.
RBV advances a core proposition that capabilities to learn from partners may be a tacit resource underlying a firm’s competitive advantage (Hamel, 1991).
For MNCs, the intensity and diversity of learning from local partners facilitate local knowledge acquisition and strengthen firm performance in host countries (Luo & Peng, 1999; Makino & Delios, 1996).
For local firms, learning from MNC parents is likely to enhance survivability and performance (Fahy et al., 2000; Lyles & Salk, 1996).
Слайд 26
RBV of International Entrepreneurship
Historically, IB research focuses on
large MNCs, and entrepreneurship studies concentrate on small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within a domestic context.
How can some SMEs succeed abroad rapidly without going through different stages suggested by the “stage” model?
The answer typically boils down to the superb tacit knowledge about global opportunities (Peng, Hill & Wang, 2000)
Слайд 27
RBV of Emerging Market Strategies
Emerging markets represent a
unique institutional environment
Emerging market MNEs (EM-MNEs)
Developing capabilities constitutes “one
of the most important SOE strategies during the transitions” (Peng, 2000, p. 100)
Privatized firms
Entrepreneurial start-ups
Conglomerates
Слайд 28
PART 3:
DEBATE 2: TO OFFSHORE OR NOT TO
OFFSHORE
Слайд 29
Survey by Offshoring Research Network (ORN)
Study tracking the
adoption of offshoring administrative and technical functions every six
months and over several years
Source: Lewin, A.Y. & Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239
Слайд 30
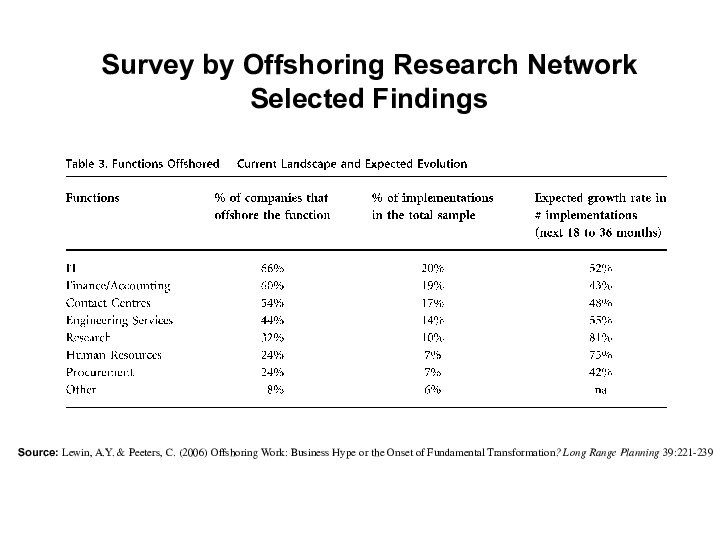
Survey by Offshoring Research Network
Selected Findings
Source: Lewin, A.Y.
& Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or
the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239
Слайд 31
Survey by Offshoring Research Network
Selected Findings
Source: Lewin, A.Y.
& Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or
the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239
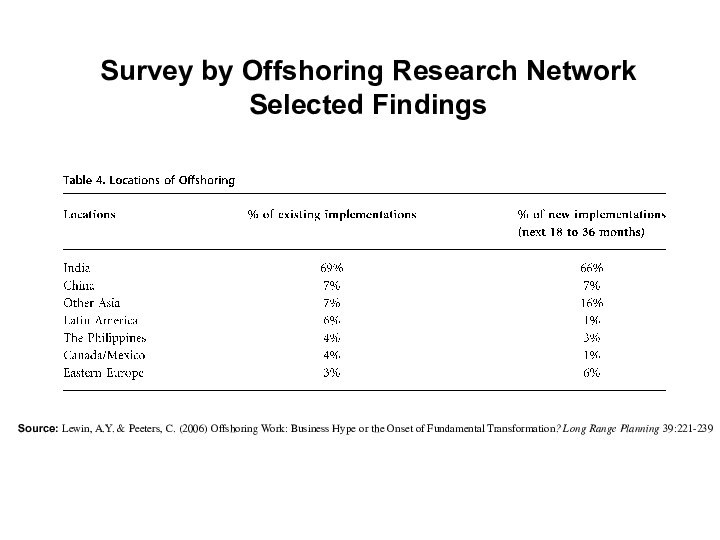
Слайд 32
Survey by Offshoring Research Network
Selected Findings
Source: Lewin, A.Y.
& Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or
the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239
Слайд 33
Survey by Offshoring Research Network
Selected Findings
Source: Lewin, A.Y.
& Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or
the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239
Слайд 34
Survey by Offshoring Research Network
Selected Findings
Source: Lewin, A.Y.
& Peeters, C. (2006) Offshoring Work: Business Hype or
the Onset of Fundamental Transformation? Long Range Planning 39:221-239