Слайд 2
PLAN FOR THE DAY
Part 1: What is ‘International
Business’ (IB) and what types of management issues arise?
Part
2: The state of globalization
Part 3: Explaining risks and opportunities: CAGE and the institutional view
Part 4: Intro to national variations in business-government relations (how “institutions” are built)
Part 5: Practical aspects related to the course: assignments, exam etc.
Part 6: Introduction to next class
Слайд 3
PART 1:
WHAT IS ‘INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS’ AND WHAT DOES
IT MEAN FOR MANAGEMENT?
Слайд 4
WHAT IS INTERNATIONAL MANAGEMENT?
Managing an international business: a
company that engages in international (cross-border) economic activities, sometimes
an “MNE”
A Multinational Enterprise (MNE) is a firm that uses foreign direct investment (FDI) to establish or purchase income-generating assets abroad
IM is about managing complexity and uncertainty:
cross-border activity brings new challenges...
...requiring awareness and strategic thinking
Слайд 6
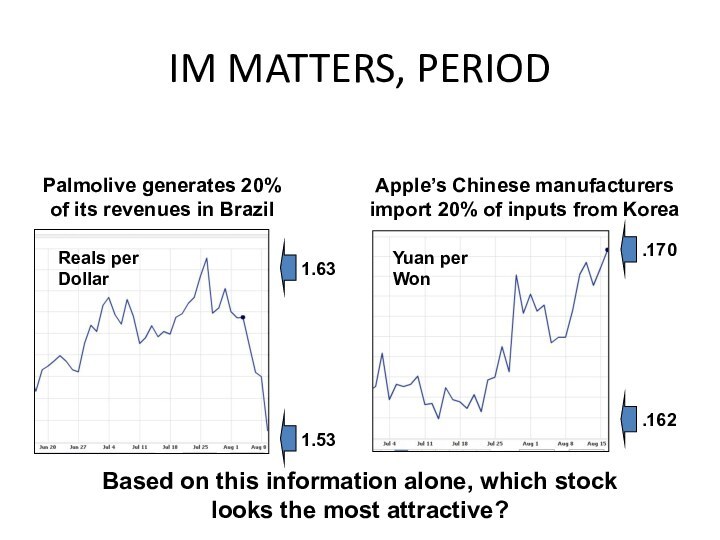
IM MATTERS, PERIOD
Palmolive generates 20% of its revenues
in Brazil
Apple’s Chinese manufacturers import 20% of inputs from
Korea
Based on this information alone, which stock looks the most attractive?
1.63
1.53
Reals per Dollar
Yuan per Won
.170
.162
Слайд 7
How can differences in political systems affect international
competition?
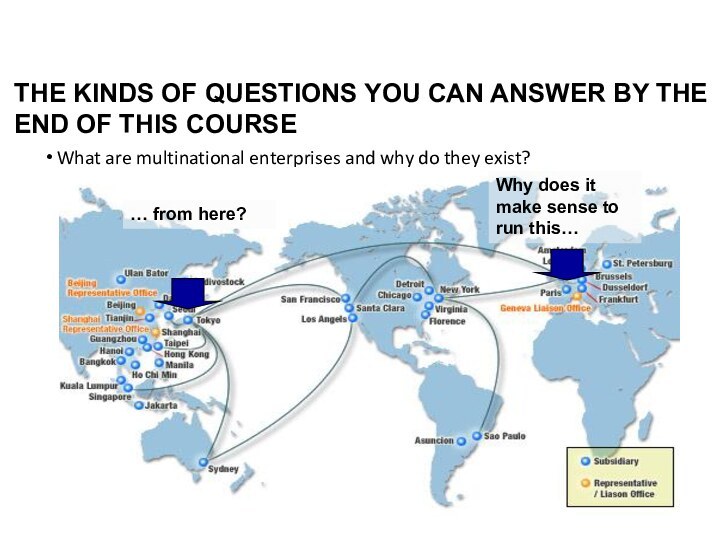
THE KINDS OF QUESTIONS YOU CAN ANSWER BY
THE END OF THIS COURSE
Слайд 8
What are multinational enterprises and why do they
exist?
THE KINDS OF QUESTIONS YOU CAN ANSWER BY THE
END OF THIS COURSE
Why does it make sense to run this…
… from here?
Слайд 9
THE KINDS OF QUESTIONS YOU CAN ANSWER BY
THE END OF THIS COURSE
Why does Starbucks conduct its
international roll-out primarily through joint ventures, when it is famous for maintaining strict control over its intellectual property at home?
ABROAD?
AT HOME?
Слайд 10
THEORETICAL UNDERPINNINGS OF IM
Institutional theory
Resource Based view (RBV)
Organizational
learning
Classical & modern trade theories
Transaction cost / internalization theory
…What
is “theory” anyway?
Слайд 11
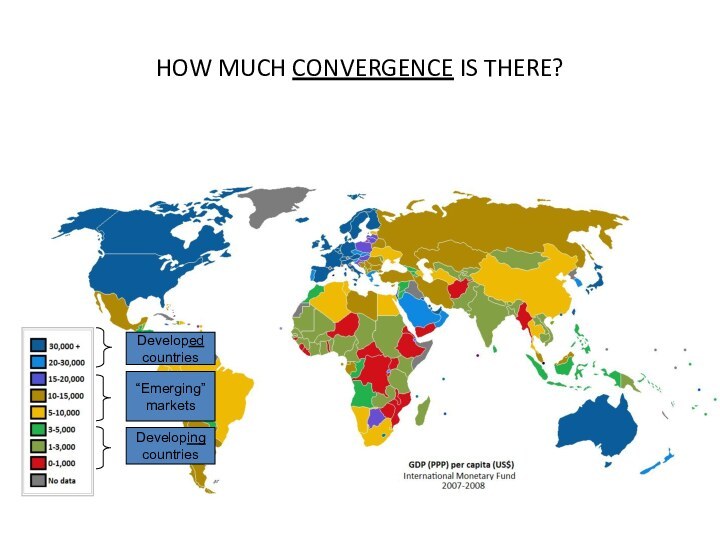
SO: HOW AND WHY IS UNDERSTANDING THE GLOBAL
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT IMPORTANT?
Слайд 12
IM: ABOUT AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING
Ray Vernon, director of
the MNE project at Harvard Business School, once wrote:
“[more
and more of us] …have come to recognize that the world of business offers infinite variety. [Yet] most of us continue to see these phenomena as aberrations, traps on the fairway that have no right to be there. Why can't the others, we plaintively ask, play like us? We must stop addressing that as a rhetorical question and begin looking earnestly for the answer.”
Vernon, R. 1994. Contributing to an International Business Curriculum: An Approach from the Flank. Journal of International Business Studies, 25(2): 215-227.
Слайд 14
PART 2:
THE STATE OF “GLOBALIZATION”
Слайд 15
WHAT IS GLOBALIZATION?
Globalization is…
Слайд 16
HOW GLOBALIZED ARE WE?
Views differ widely... on opportunities
versus risks
Skeptics
Globalists
?
Слайд 17
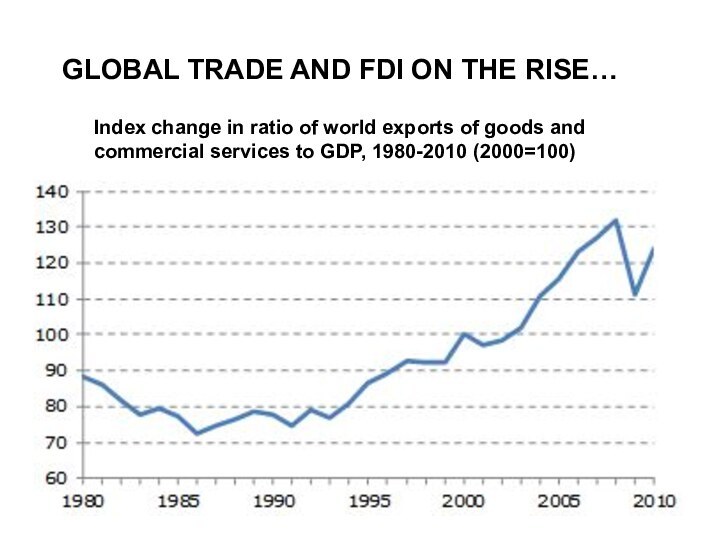
GLOBAL TRADE AND FDI ON THE RISE…
Index change
in ratio of world exports of goods and commercial
services to GDP, 1980-2010 (2000=100)
Слайд 19
… AND HOW MUCH INTEGRATION?
gross domestic product (GDP)
- total market value of all final goods and
services produced within a country in a given period of time, usually a calendar year
gross national income (GNI) - the term used by the World Bank and other international organizations to supersede the GNP term. Like GNP, it means GDP plus (net) income from nonresident, domestically-owned assets
Слайд 20
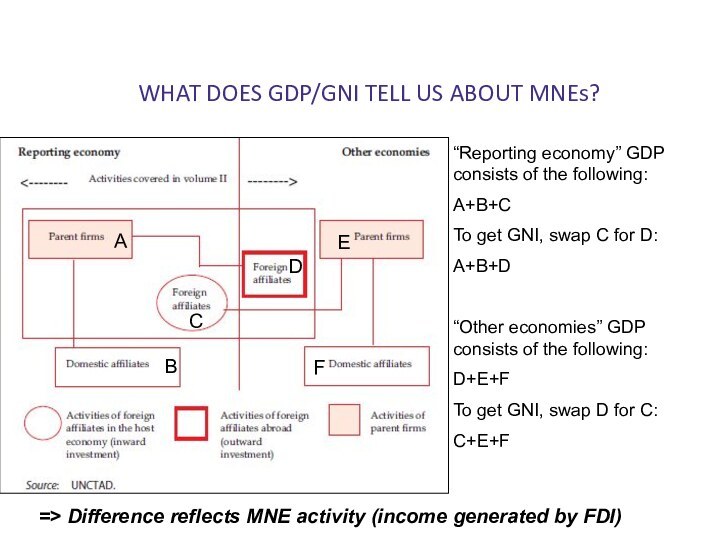
WHAT DOES GDP/GNI TELL US ABOUT MNEs?
“Reporting economy”
GDP consists of the following:
A+B+C
To get GNI, swap C
for D:
A+B+D
“Other economies” GDP consists of the following:
D+E+F
To get GNI, swap D for C:
C+E+F
A
C
B
D
E
F
=> Difference reflects MNE activity (income generated by FDI)
Слайд 21
GDP vs GNI
Q: “Can you see the difference
when looking at ‘tax havens’?”
For example:
NL: GDP =
$52,699; GNI = $52,254
BUT:
Cayman Islands: GDP = $50,716; GNI = $45,941
Bermuda: GDP = $99,383; GNI = $83,659
Слайд 22
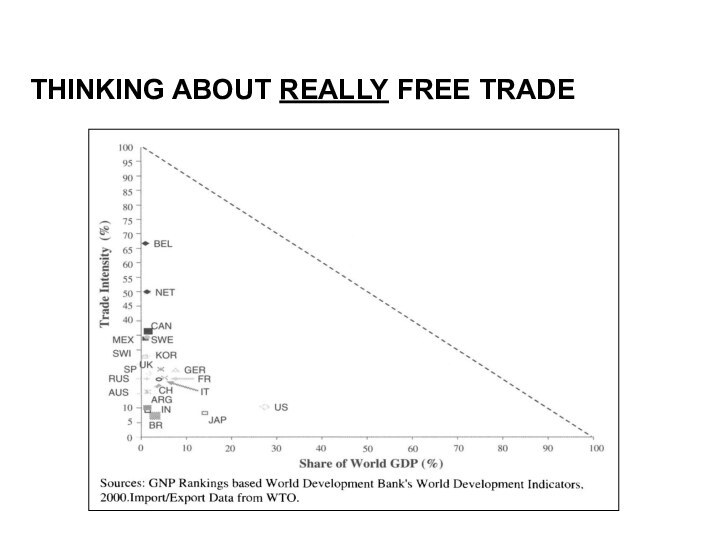
THINKING ABOUT REALLY FREE TRADE
Слайд 23
PART 3:
EXPLAINING RISKS AND OPPORTUNITIES IN THE BUSINESS
ENVIRONMENT
Слайд 24
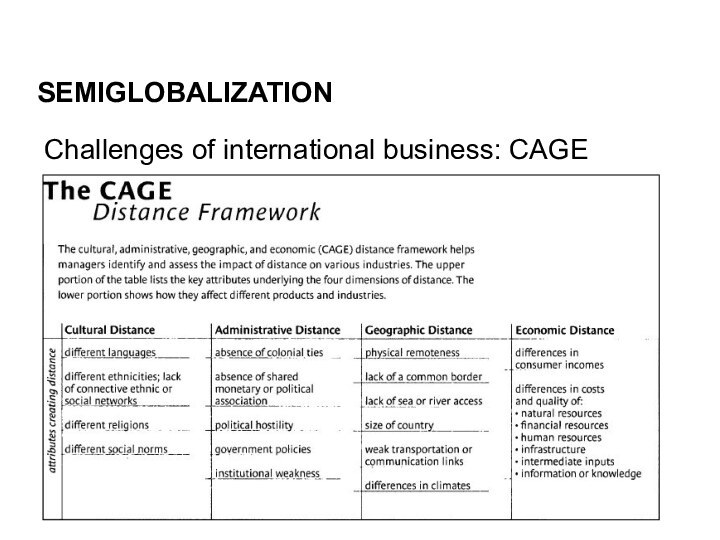
SEMIGLOBALIZATION:
After all, it seems that distance still matters:
Culturally
(norms, customs)
Administratively (laws, bureaucracy)
Geographically (the planet is large)
Economically (different
standards of living)
Слайд 25
Challenges of international business: CAGE
SEMIGLOBALIZATION
Слайд 26
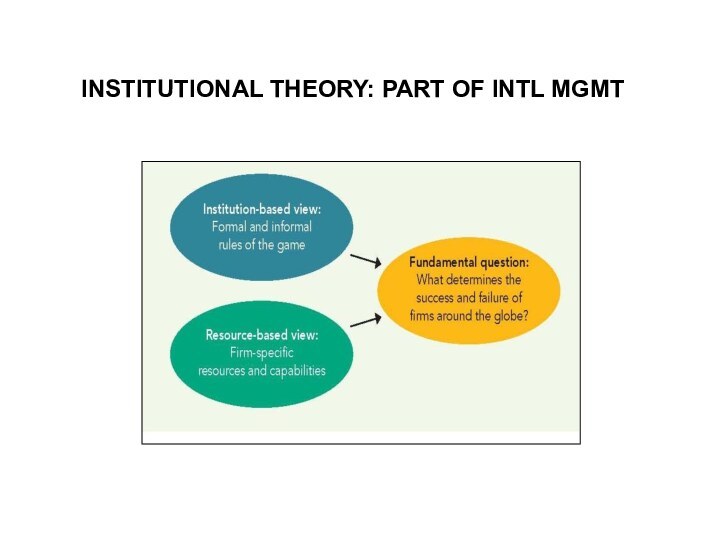
INSTITUTIONAL THEORY: PART OF INTL MGMT
Слайд 27
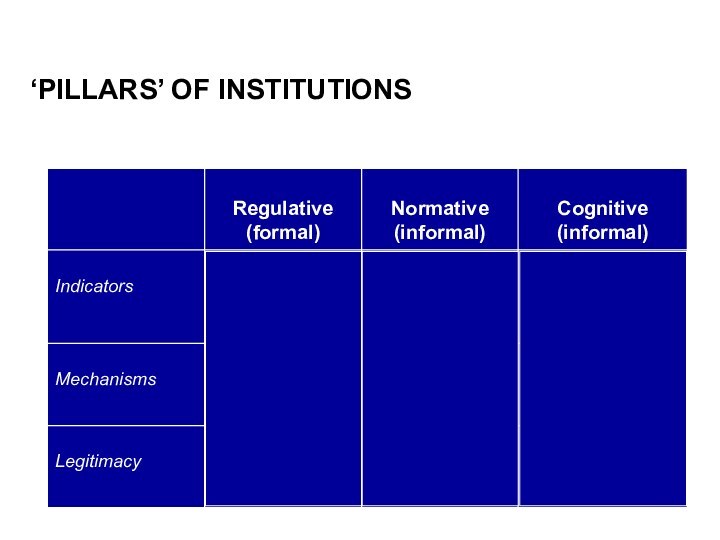
AN INSTITUTION-BASED VIEW
Institutions mean RULES, both formal (regulatory
environment) and informal (norms & culture)
Institutions provide incentive structures
for behavior (rewards for compliance as well as sanctions for violations)
Institutions thus reduce uncertainty and opportunism, keeping transaction costs low
Assumes that actors will behave predictably and in a self-interested fashion (=‘rationally’): seek rewards while trying to avoid sanctions
Слайд 28
AN INSTITUTION-BASED VIEW
How does this relate to Intl
Mgmt?
When you enter a new environment—either as a manager
or as an MNE—you face the disadvantage that comes from not knowing THE RULES
This is known as the “Liability of foreignness”
This disadvantage means higher transaction costs & greater risk of experiencing opportunistic behavior
Слайд 29
WHICH OF THESE ARE “INSTITUTIONS”?
The World Bank?
An auction?
Respect
for your parents?
Posted speed limits?
Слайд 30
1) What are the rules?
2) What are sanctions
& rewards with respect to compliance?
IF THESE ARE “INSTITUTIONS”…
The
World Bank
An auction
Respect for your parents
Posted speed limits
Слайд 32
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN NORMATIVE AND COGNITIVE
Normative is related to
peer pressure / social expectations
“You should wash your hands
after using the restroom”
“You should take off your shoes when entering a home”
“You should pass the ball when playing team sports”
Cognitive is related to deep-seated assumptions and often hard to explain
“Winning is the most important thing”
“Government intervention is bad”
“Polygamy is wrong”
Слайд 33
INSTITUTIONS EFFECTIVE WHEN SUPPORTED BOTH FORMALLY & INFORMALLY
Norms
can lead to regulation
the Kyoto Protocol => environmental regulation
Codes
of Conduct => Sarbanes-Oxley
Cultural values lead to laws
Women banned from driving in Saudi Arabia
Store closures on Sunday in many countries
When a rule rests on only one pillar, it is ineffective.
Jaywalking: law says not ok, norms say ok
Gun possession: law says ok, norms say not ok
Слайд 34
PART 4:
INTRO TO FORMAL INSTITUTIONS:
NATIONAL BUSINESS SYSTEMS
AND POLITICAL ADVANTAGE
Слайд 35
BUSINESS-GOVERNMENT RELATIONS
Policy outcomes (formal institutions) reflect political/ economic
interests – those of firms, industries, sectors
National differences in
how (economic) interests are represented: associational (pluralist) vs corporatist (Spencer et al., 2005)
Q: How much latitude do (different) governments have to grant long-term political favors?
Слайд 36
PART 5:
LEARNING GOALS AND COURSE DESIGN
Слайд 37
LEARNING GOALS
To be able to think systematically about
ways in which countries and regions differ
To be able
to discuss some of the key ways in which those differences affect businesses operating internationally
To establish a link between understanding of practical international management issues and theoretical foundations
Слайд 38
IN THE CLASSROOM
Lecture to elucidate and expand on
concepts from the readings
Open, two-way discussion between you and
me on some of the ‘big picture’ topics of IM
Short cases and other in-class exercises requiring your thought & input (pair work)
Attendance is required
Слайд 39
INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENTS
You have 2 assignments that are spread
out over the semester
Their purpose is to help you
link IM concepts to practice
These assignments are INDIVIDUAL
Слайд 40
READING ARTICLES
Articles are selected based on topic and
broad theoretical relevance
Most articles review important theoretical perspectives that
have been used to understand a particular phenomenon
Make notes in which you capture the essence of these arguments: what does the theory say about X and why?
Слайд 41
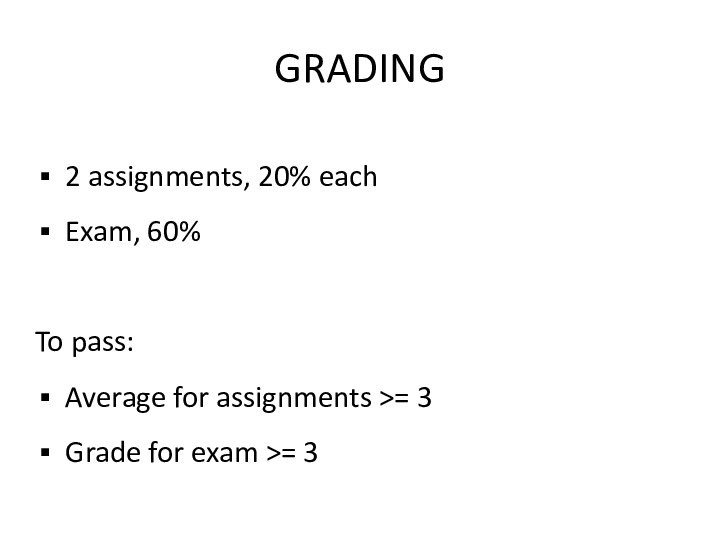
GRADING
2 assignments, 20% each
Exam, 60%
To pass:
Average for assignments
>= 3
Grade for exam >= 3
Слайд 42
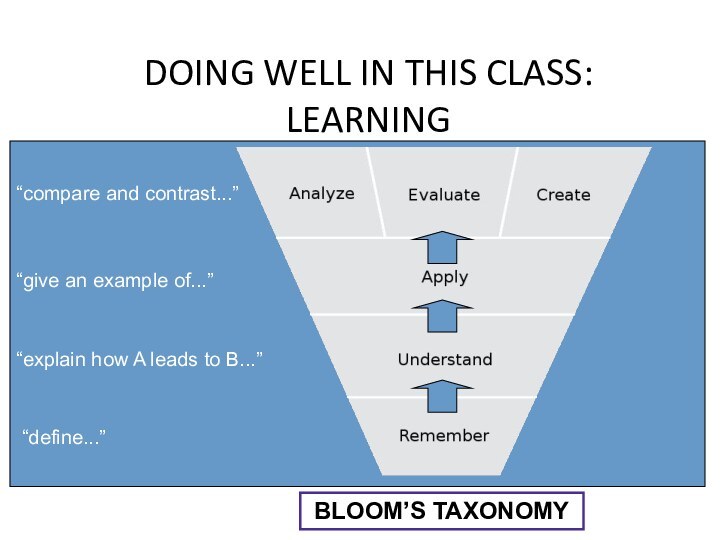
DOING WELL IN THIS CLASS: LEARNING
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY
“define...”
“explain how
A leads to B...”
“give an example of...”
“compare and contrast...”
Слайд 44
Formal institutions: Politics, laws, economics
Informal institutions: Cultures, ethics,
norms
Слайд 45
CONTACT INFO
Alexandra Dorina Mesteru (alexandra.mesteru@gmail.com)
+7 916 170
85 70
Office: Room 310