Слайд 2
Day 3 Learning Objectives
To understand the motivations for
the practice of information risk management within an enterprise
To
understand key concepts and the information risk management lifecycle
To develop an awareness of how to perform a risk assessment
To continue to develop an awareness of the main international standards and methodologies
Слайд 3
Session Overview
Why do we have to manage information
risk
What are the enterprise drivers
What is the relationship with
key enterprise business processes
Слайд 4
Why
Existing and growing dependency upon information infrastructure and
digital assets
Rapidly growing with pace of technology change
Both the
dependency and the assets have value which is exposed to risk and so may require protecting
Protection costs, is not 100% effective, and risk varies over time, so an understanding of the risks faced and a plan to manage them is required
Where manage may involve accepting and tolerating some risks whilst attempting to remove or reduce others or even avoiding them altogether
Слайд 5
YouTube incident coverage
Grocery Store 2008
Facebook 2012
Sony 2011
Stuxnet 2010
The Loop, Stuxnet 2010 Symantec
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Adg4chwKkM&feature=related
Слайд 6
Enterprise Drivers
Maximise output in the face of risk
Outputs
include services, products, revenue
Information Security can enable business objectives
which depend in some way upon information infrastructure and assets
E.g. customer retention, market growth and position, efficiency, agility…
Слайд 7
Relationship to process
Information infrastructure and services likely to
be used by majority of key business processes
Finance and
Administration
Supply Chain Management
Customer Relationship Management
Information and Technology Services
Sales
Logistics
Communications and PR
….
Слайд 8
Syndicate Exercise 1
Consider the exposure of a student
to information risk day-to-day in normal life, student life
and family life.
What are the key assets?
How might they be of interest to a threat?
What would be the impact to the student and their family should access be denied to assets, or assets loose integrity, or confidential assets become compromised?
Слайд 9
Definitions
Information Security Management entails the identification of an
organisations information assets and the development, documentation, and implementation
of policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines, which ensure their availability, integrity and confidentiality.
Risk management is the identification, measurement, control, and minimisation of loss associated with uncertain events or risks.
Official (ISC)2 Guide To The Certified Information Systems Security Professional Exam
Слайд 10
Definitions
Availability: ensuring that access is granted to authorised
users as required, within expected and declared parameters
Integrity: ensuring
that changes to assets can only be made by authorised users
Not the same as quality
Confidentiality: ensuring that only authorised users can access or view assets
Non-repudiation / accountability: ensuring that users can be held to account for their actions in respects of assets
Possible privacy issues not covered by confidentiality
Слайд 11
Definitions
Assets
Threats
Vulnerability
Exploits and Attack Vectors
Likelihood
Impact
Mitigation and control
Residual
risk
Слайд 12
Definitions
Risk Analysis: Process of analysing risk for a
particular environment (organisation, project, business unit…) resulting in the
risk assessment
Risk Management: Incorporates the risk assessment but includes the resulting activities associated with mitigating the risks overtime, including detecting new ones
Слайд 13
Definitions
Qualitative risk analysis
A relative scale: low, medium, high..,
1,2,3,4…
Appropriate where no accurate data exists or when new
to discipline of risk analysis
Highly subjective, hard to baseline, imprecise
Quantitative risk analysis
Uses numbers and calculations to determine exposure in a £ value
Often utilises probability theory and statistical models
E.g. Single Loss Expectancy X Average Annual Loss = Annualised Loss Expectancy
Very difficult to quantify value of loss when so much is intangible (e.g. loss to reputation)
Слайд 14
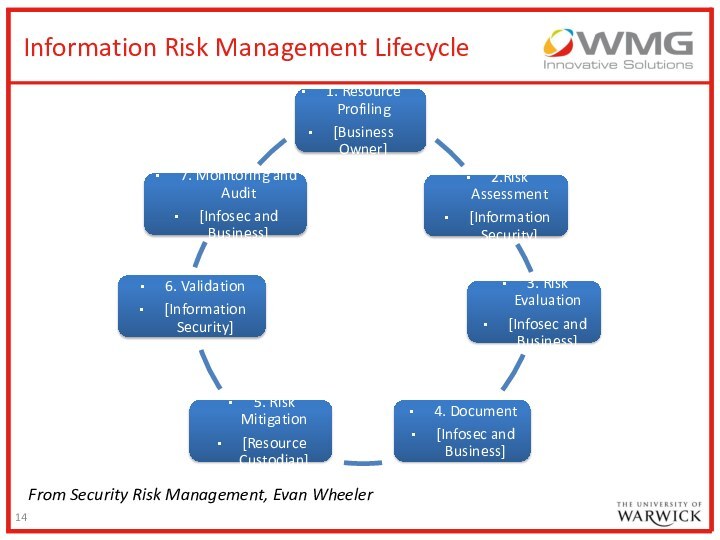
Information Risk Management Lifecycle
From Security Risk Management, Evan
Wheeler
Слайд 15
Resource Profiling
The act of identifying the assets and
resources requiring protection
Need to understand relative importance, to underpin
future prioritisation of effort
By importance to output or by impact if security breached
Might include a single system, an entire facility, business unit, 3rd party supplier service….
Security Risk Profile captures the data required to judge an assets sensitivity to security risk
Слайд 16
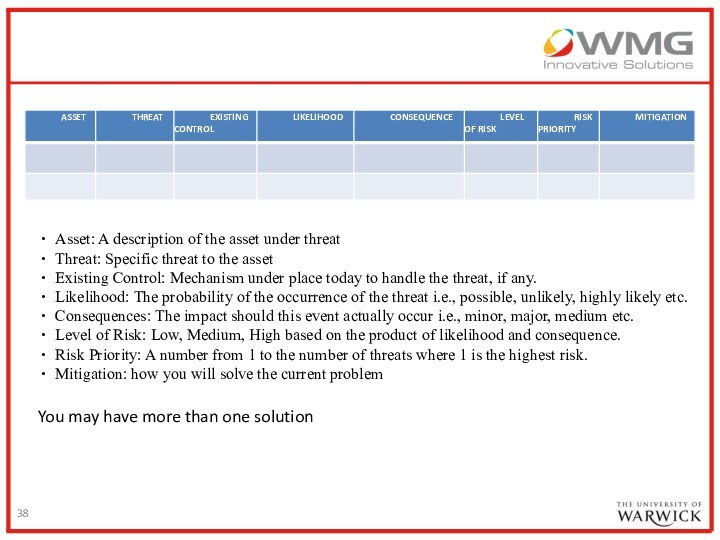
Risk Assessment
For the critical assets:
Identify the presence of
threat
Relate the threat to potential vulnerabilities
For each threat x
vulnerability pair, identify potential harm or impact (sometimes referred to as risk exposure) and likelihood of breach to calculate risk
Likelihood must consider the presence of existing security controls
Raw risk – controls and mitigations – residual risk
Слайд 17
Example Risk Exposure
“..communications could be intercepted in transit
and decrypted by a malicious party resulting in an
unauthorised disclosure of sensitive data for all customers in the UK, which would require a breach notification to regulators and affected clients, costing the organisation $2 million in lost revenue and financial sanctions.”
From Security Risk Management, Evan Wheeler
Слайд 18
Risk Evaluation
The process by which the risks output
from the assessment are balanced and prioritised, and the
response identified:
Avoid: no longer engaging in the activity
Mitigate: attempt to limit the impact
Transfer: moving the responsibility to a 3rd party (and possibly the liability)
Accept: live with it
As this is a cost / benefit decision some knowledge of potential mitigations is required
Слайд 19
Document
The results of the risk assessment and the
evaluation along with key points of rationale
The world changes
and should you experience a breach you need to understand where you went wrong in the analysis in order to do better
You may wish to demonstrate compliance to a standard, which will require evidence
Often you need/want to show process to a regulator, customer, or other stakeholder
You may need to obtain senior management approval for the actions resulting from the evaluation (including the ‘accept’ category), which will require exposure of the rationale and justification
Слайд 20
Risk Mitigation and Remediation
Implementing the plan.
Options (for any
particular risk) are:
Limit the severity of impact on system
Contain
through detection and response
Decrease the sensitivity of the resource
Move the data it holds to another part of the system
Reduce the likelihood of occurrence
Control the attack surface using firewalls etc
Risk remediation would involve removal of the vulnerability either through patching or removal of asset
Слайд 21
Validation
Verify adequacy of controls:
Design review
Configuration review
Policy review
Role and
responsibility awareness review
Penetration testing
Vulnerability scanning
Often before ‘go-live’ for any
particular system or major upgrade
Слайд 22
Monitoring and Audit
Through-life aspects:
Log and audit network activity
and security appliance alerts to maintain situational awareness
Monitor trends
in threat
Monitor attack surface and vulnerability posture
Re-assessing risk in face of significant business change
Слайд 23
Methods, Standards, Regulation
Risk Assessment and Management Methodologies:
HP Business
Risk Assessment
OCTAVE, DBSy, CRAMM, COBIT, RISK-IT
Standards:
ISO27001/2/5
NISTSP800-37
Regional laws and regulations
associated with data handling and privacy
Слайд 24
The OCTAVE Principals
Organisational and Cultural
Open communication, global perspective,
teamwork
Risk Management Principals
Forward-looking view, focus on the critical few,
integrated management
Information Security Risk Evaluation Principles
Self-direction, adaptable measures, defined process, foundation for a continuous process
Слайд 25
Basic Risk Assessment
Create resource profiles
Identify critical assets
Understand the
security requirements for critical assets
Security properties and organisational sensitivity
Identify
threats to critical assets
Identify current security practices and organisational vulnerabilities
Identify information infrastructure vulnerabilities
Assess impact and likelihood of risks and prioritise
Слайд 26
Types of Assets
Information and data (paper or electronic),
including intellectual property
Information systems and services (some combination of
assets)
Software
Hardware (in so far as it relates to information)
People
Other special circumstances
Assets may be independent or related
Слайд 27
Prioritising Assets
Rank in relation to business objectives or
business sensitivity (or some other measure such as regulatory
compliance)
Note that people will have differing views on this
Identify the subset which are most important
Document the rationale
Слайд 28
The Input Challenge
Understanding the critical assets will require
input from senior and middle management, since it necessarily
relates to business priorities
Both now and in future
Therefore, critical to the resource profiling will be the facilitation of workshops or interactions with the stakeholders
Can be difficult when they do not have a common view on priority
Board, senior management, security and technology operations, and more general staff are all likely to contribute differing view points
Слайд 29
Identify Threat
Consider threat sources in relation to the
high priority assets, and the range of negative impacts
a successful breach could result in
OCTAVE Threat Sources: deliberate actions by external or internal people; accidental actions by people; malware; system outage; natural disasters and interdependency on 3rd parties
Note some are malicious threats and some are not
OCTAVE Threat Outcomes: Disclosure, Modification, Loss / Destruction, Interruption
Слайд 30
Assess Consequence
For each asset and threat outcome determine
potential impact on organisation
There may be multiple potential impacts,
which will need to be enumerated
People may have differing views
Determine potential impact, likelihood
Low: Maybe deviation from best practice but no direct exposure of critical assets
Moderate: May indirectly contribute to unauthorised activity, or degrade service performance
High: May allow limited unauthorised access
Critical: May allow full access to system or prolonged outage of service
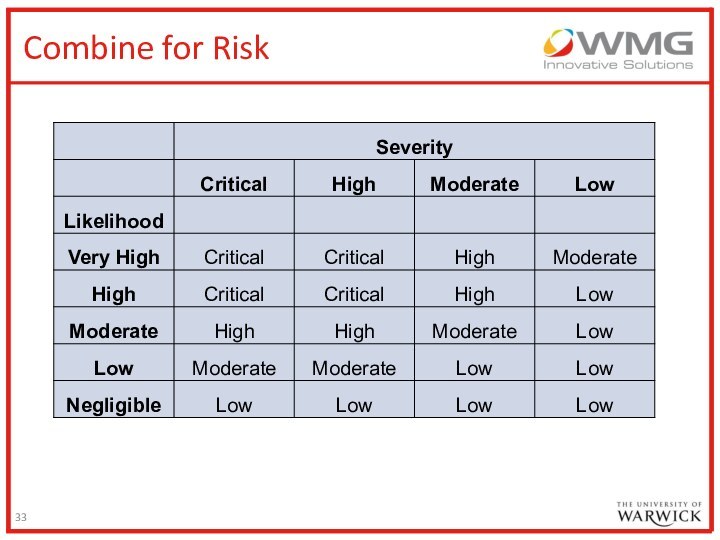
Слайд 32
Incorporate Probability
Assess how likely a particular threat will
attempt a breach:
Level of motivation (reward or incentive)
Capability (for
insider or outsider)
Opportunity (how vulnerable might the asset be)
Produce probability evaluation criteria
Negligible: Significant insider knowledge required, existing controls require direct physical access
Low: Threat source lacks motivation or capability
Moderate: Threat source motivated and capable but controls in place which limit ability to attack
High: Threat source is motivated and sufficiently capable and controls are considered highly effective
Very High: System vulnerability accessible publicly on the Internet, exploits exist in the open, threat is motivated
Слайд 34
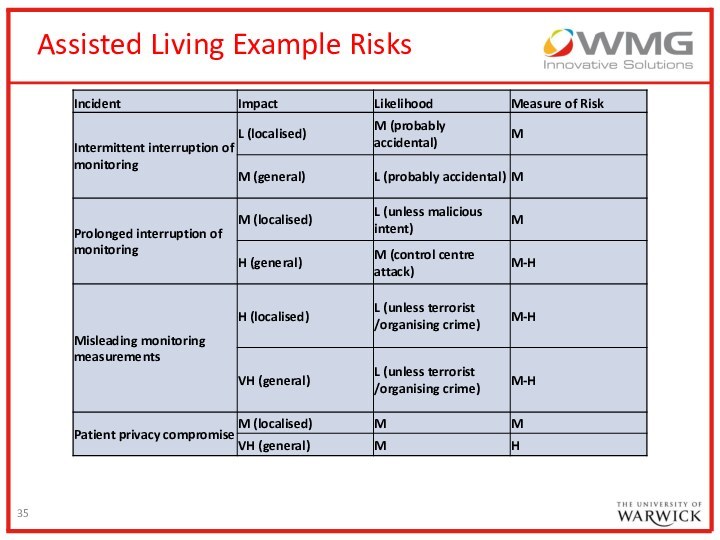
Scenario – Assisted Living
Local health authority has urgent
requirement to deliver more health services direct to patients
in their homes
Frail and elderly people find it more difficult to travel to health centres
Hospital represents a source of potential complications (infections) and cost, often when it is solely observation that is required
Continuous monitoring could allow earlier interventions and reduce total costs of healthcare
A variety of sensors will be deployed in homes of patients, linked to healthcare workers via the Internet monitoring
Mobility of patients
Drug usage
Nutrition levels
Vital life signs
Слайд 36
Identify Security Requirements
For risks determine security requirements, in
terms of
does it contain personally identifiable information, in which
case it will be subject to regulation and law
any other requirements to control access
requirements for availability, take into consideration commitments made to customers where appropriate
requirements for accuracy (integrity), and where they may be time-bounded
requirements for controls to meet standards
Слайд 37
Prioritize Security Requirements
Rank risks with critical at top
What is the relative ranking of the security requirements
(across the entire asset set)
Or, for a subset prioritised further by business priority
Often a difficult task
‘..they are all important…”
Develop mitigations which reflect the needs identified by the risk assessment