Слайд 2
The focus of part 3:
strategy in action
Criteria and techniques that can be used to evaluate
possible strategic options.
How strategies develop in organisations; the processes that may give rise to intended strategies or to emergent strategies.
The way in which organisational structures and systems of control are important in organising for strategic success.
The leadership and management of strategic change.
Who strategists are and what they do in practice.
Слайд 3
Strategy in Action
11: Evaluating Strategies
Слайд 4
Learning outcomes
Employ three success criteria for evaluating strategic
options:
– Suitability: whether a strategy addresses the key
issues relating to the opportunities and constraints an organisation faces.
– Acceptability: whether a strategy meets the expectations of stakeholders.
– Feasibility: whether a strategy could work in practice.
For each of these use a range of different techniques for evaluating strategic options, both financial and non-financial.
Слайд 5
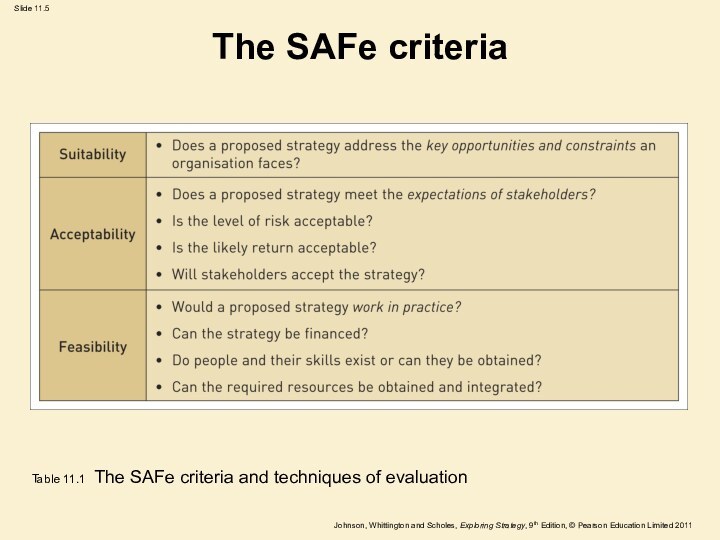
The SAFe criteria
Table 11.1 The SAFe criteria and
techniques of evaluation
Слайд 6
Suitability
Suitability is concerned with assessing which proposed
strategies address the key opportunities & constraints an organisation
faces, through an understanding of the strategic position of an organisation.
It is concerned with the overall rationale of the strategy:
Does it exploit the opportunities in the environment and avoid the threats?
Does it capitalise on the organisation’s strengths and strategic capabilities and avoid or remedy the weaknesses?
Слайд 7
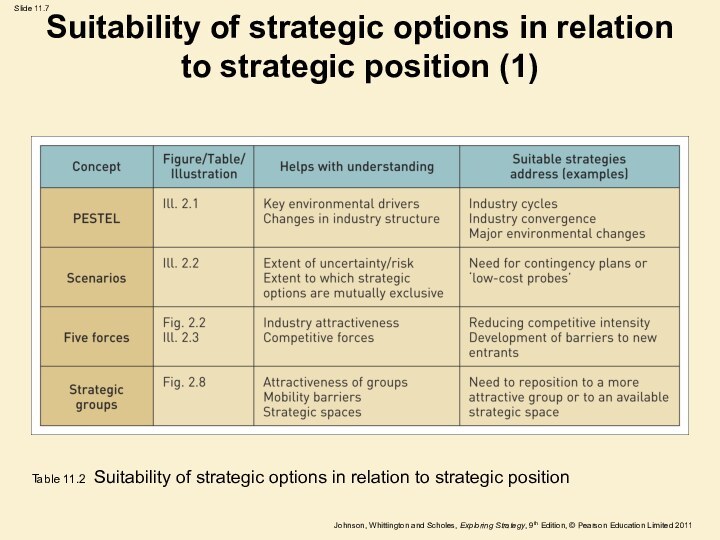
Suitability of strategic options in relation to strategic
position (1)
Table 11.2 Suitability of strategic options in relation
to strategic position
Слайд 8
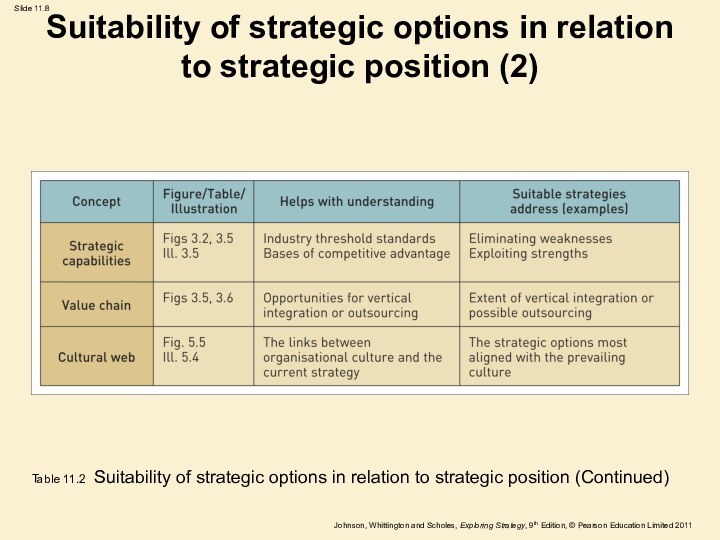
Suitability of strategic options in relation to strategic
position (2)
Table 11.2 Suitability of strategic options in relation
to strategic position (Continued)
Слайд 9
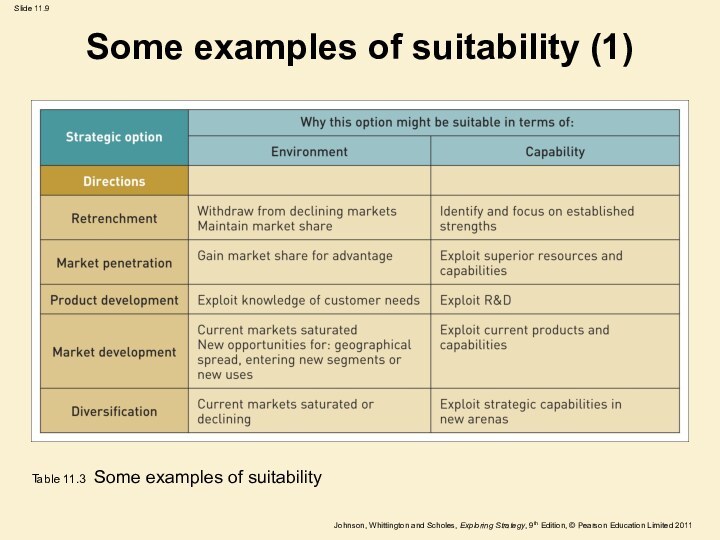
Some examples of suitability (1)
Table 11.3 Some examples
of suitability
Слайд 10
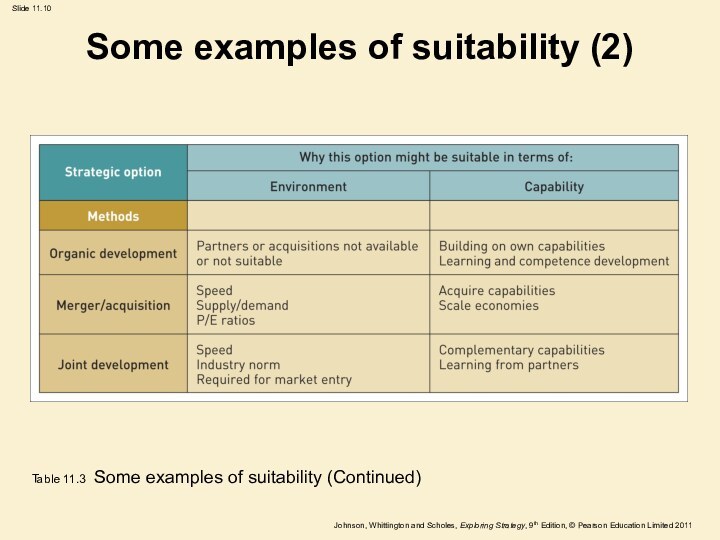
Some examples of suitability (2)
Table 11.3 Some examples
of suitability (Continued)
Слайд 11
Suitability – screening techniques
There are several useful techniques:
Ranking.
Using
scenarios.
Screening for competitive advantage.
Decision trees.
Life cycle analysis.
Слайд 12
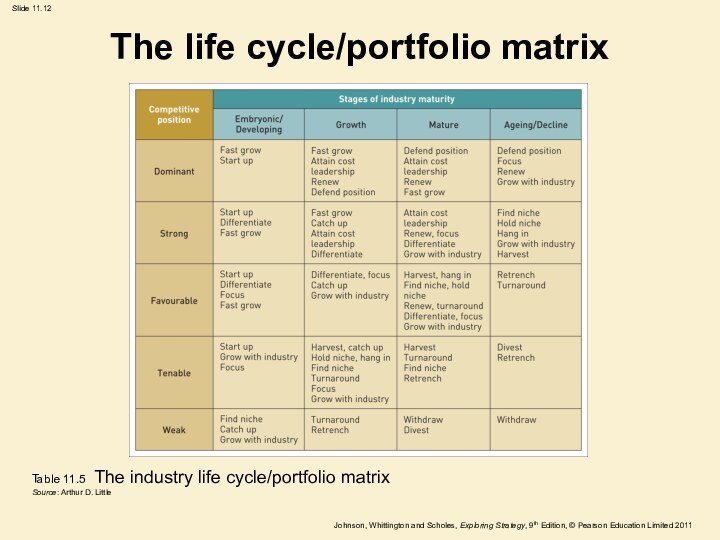
The life cycle/portfolio matrix
Table 11.5 The industry life
cycle/portfolio matrix
Source: Arthur D. Little
Слайд 13
Competitive position within an industry
Competitive position within an
industry can be:
A dominant position which is rare in
the private sector unless there is a quasi-monopoly position. In the public sector there can be a legalised monopoly status.
A strong position where organisations can follow strategies of their own choice without too much concern for competition.
A favourable position where no single competitor stands out, but leaders are better placed.
A tenable position can be maintained by specialisation or focus.
A weak position where competitors are too small to survive independently in the long run.
Слайд 14
Acceptability (1)
Acceptability is concerned with whether the
expected performance outcomes of a proposed strategy meet the
expectations of stakeholders.
Слайд 15
Acceptability (2)
There are three key aspects of acceptability
- the ‘3 R’s’:
Risk.
Return.
Reactions (of stakeholders).
Слайд 16
Risk
Risk concerns the extent to which the outcomes
of a strategy can be predicted.
Risk can be assessed
using:
Sensitivity analysis.
Financial ratios – e.g. gearing and liquidity.
Break-even analysis.
Слайд 17
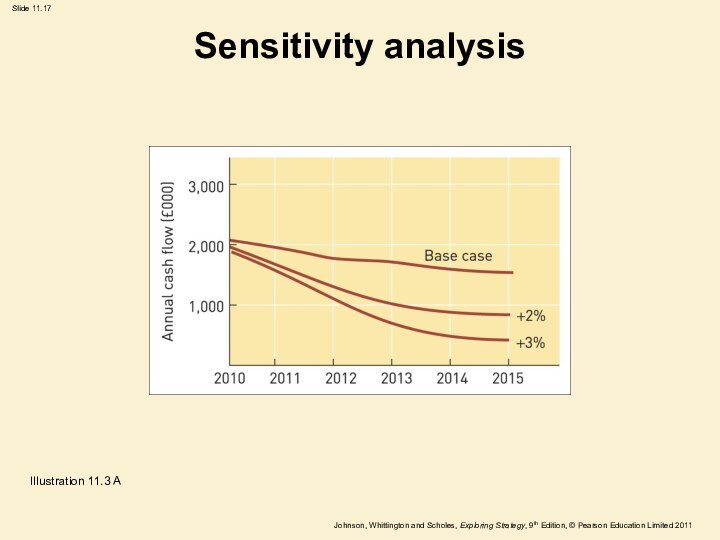
Sensitivity analysis
Illustration 11.3 A
Слайд 18
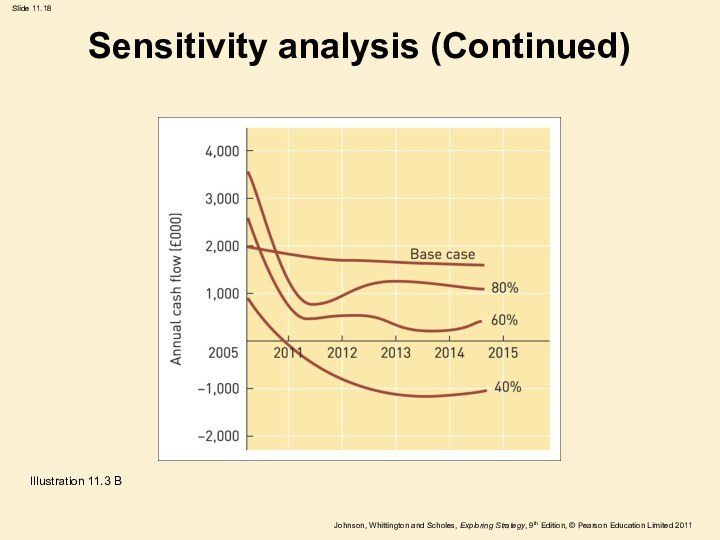
Sensitivity analysis (Continued)
Illustration 11.3 B
Слайд 19
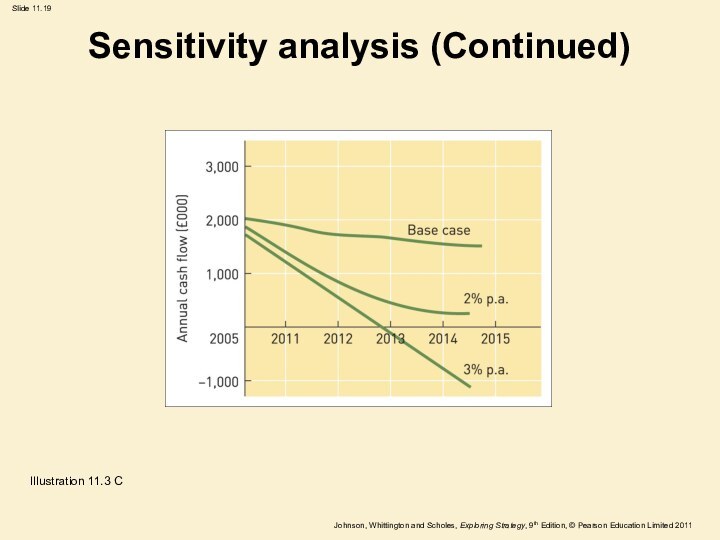
Sensitivity analysis (Continued)
Illustration 11.3 C
Слайд 20
Return
Returns are the financial benefits which stakeholders are
expected to receive from a strategy.
Different approaches to assessing
return:
Financial analysis.
Shareholder value analysis.
Cost–benefit analysis.
Real options.
Слайд 21
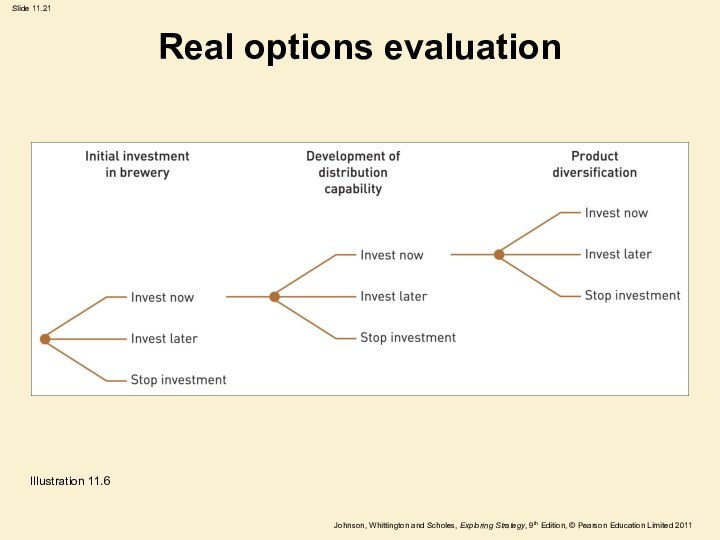
Real options evaluation
Illustration 11.6
Слайд 22
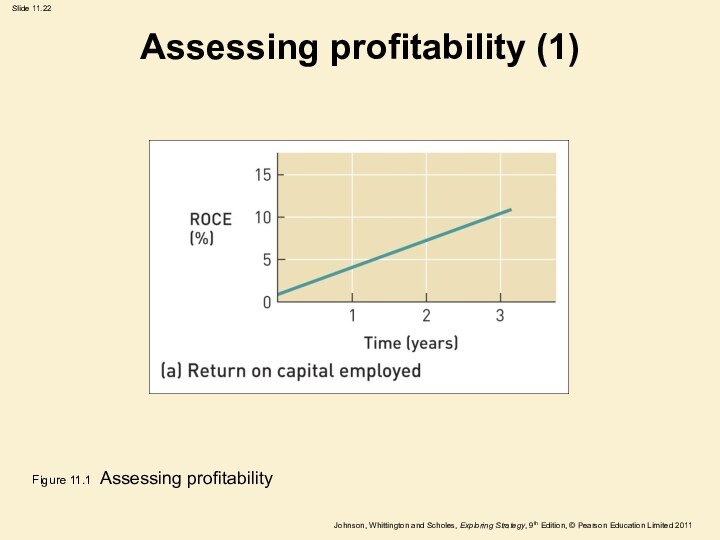
Assessing profitability (1)
Figure 11.1 Assessing profitability
Слайд 23
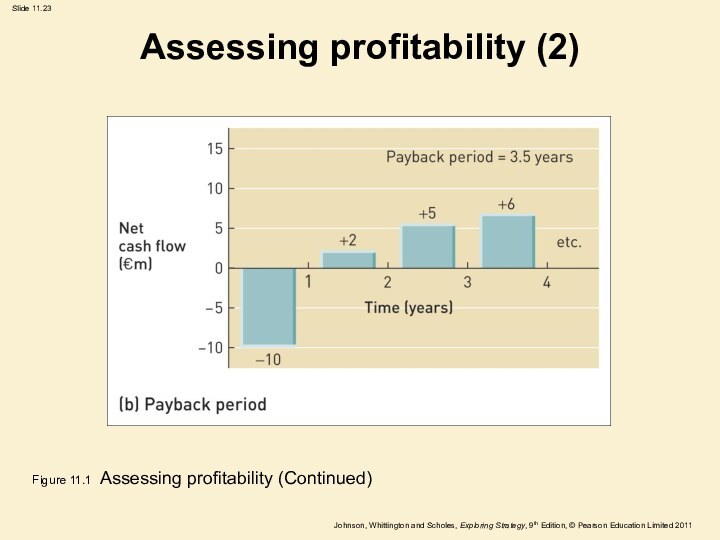
Assessing profitability (2)
Figure 11.1 Assessing profitability (Continued)
Слайд 24
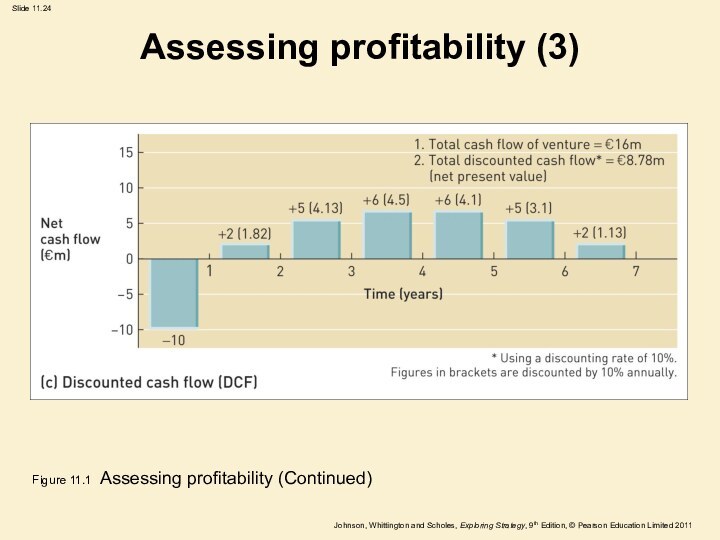
Assessing profitability (3)
Figure 11.1 Assessing profitability (Continued)
Слайд 25
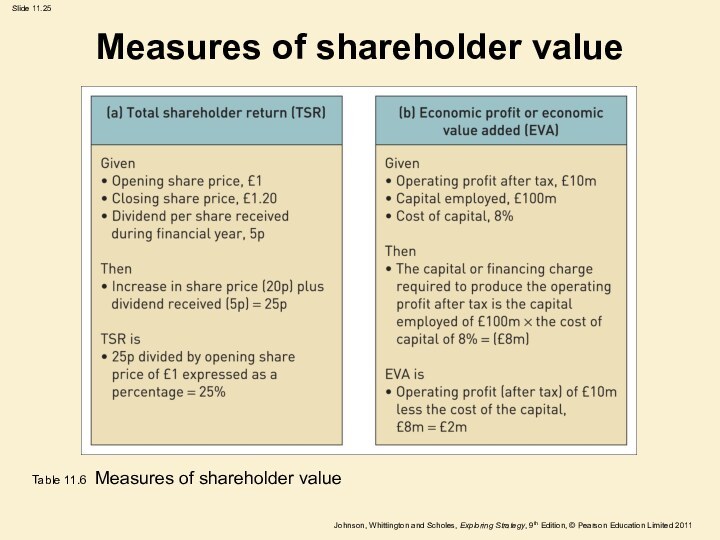
Measures of shareholder value
Table 11.6 Measures of shareholder
value
Слайд 26
Advantages of real options
There are four main benefits:
Bringing
strategic and financial evaluation closer together.
Valuing emerging options.
Coping
with uncertainty.
Offsetting conservatism.
Слайд 27
Reaction of stakeholders
Stakeholder mapping and the power/interest matrix
can be used to:
understand the political context of
strategies.
understand the political agenda.
gauge the likely reaction of stakeholders to specific strategies.
If key stakeholders find a strategy to be unacceptable then it is likely to fail
Слайд 28
Feasibility
Feasibility is concerned with whether a strategy
could work in practice i.e. whether an organisation has
the capabilities to deliver a strategy
Two key questions:
Do the resources and competences currently exist to implement the strategy effectively?
If not, can they be obtained?
Слайд 29
Financial feasibility
Need to consider:
The funding required.
Cash flow analysis
and forecasting.
Financial strategies needed for the different ‘phases’ of
the life cycle of a business.
Слайд 30
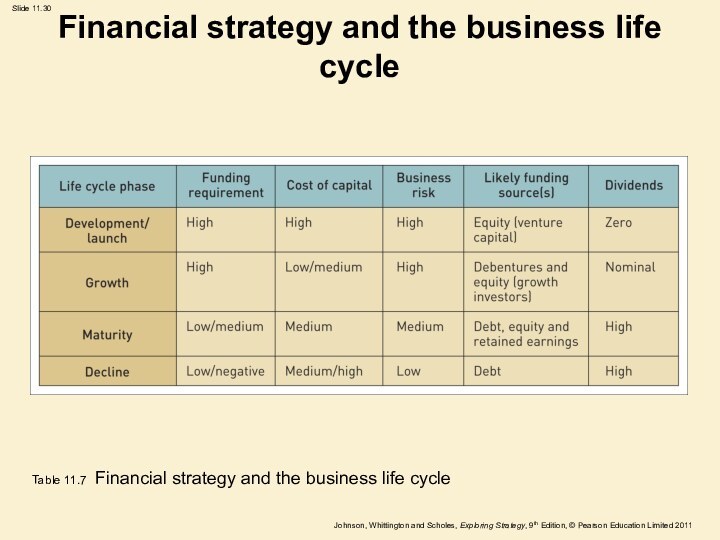
Financial strategy and the business life cycle
Table 11.7
Financial strategy and the business life cycle
Слайд 31
People and skills (1)
Three questions arise:
Do people
in the organisation currently have the competences to deliver
a proposed strategy?
Are the systems to support those people fit for the strategy?
If not, can the competences be obtained or developed?
Слайд 32
People and skills (2)
Critical issues that need to
be considered:
Work organisation – will this need to change?
Rewards
– are the incentives appropriate?
Relationships – will people interact differently?
Training and development – are current systems appropriate?
Staffing – are the levels and skills of the staff appropriate?
Слайд 33
Integrating resources
The success of a strategy depends on
the management of many resource areas, for example:
people,
finance,
physical
resources,
information,
technology and
resources provided by suppliers and partners.
It is essential to integrate resources – inside the organisation and in the wider value network.
Слайд 34
Evaluation criteria
Four qualifications:
Conflicting conclusions and the need for
management judgement.
Consistency between the different elements of a strategy
is essential.
The implementation and development of strategies might reveal unanticipated problems.
Strategy development in practice – it isn’t always a logical or even rational process.