- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Pipeline valve types and classification
Содержание
- 2. OverviewValve classificationValve typesValve usageBlock valves/ shut-down valves/ shut-off valves
- 3. Valve itselfVALVEcan stand for various Russian terms
- 4. Valve classificationValves can be classified in different
- 5. Valve classification1. by function or purpose: • To
- 6. Valve classification2. by closure member or mechanical
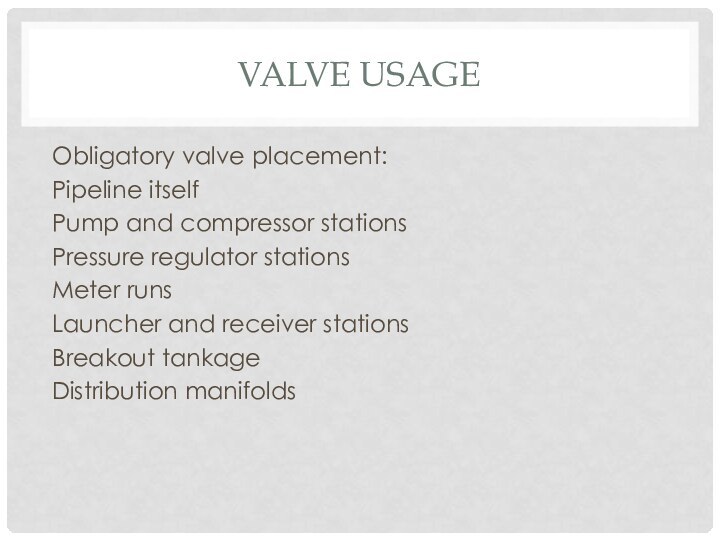
- 7. Valve usageObligatory valve placement:Pipeline itselfPump and compressor stationsPressure regulator stationsMeter runsLauncher and receiver stationsBreakout tankageDistribution manifolds
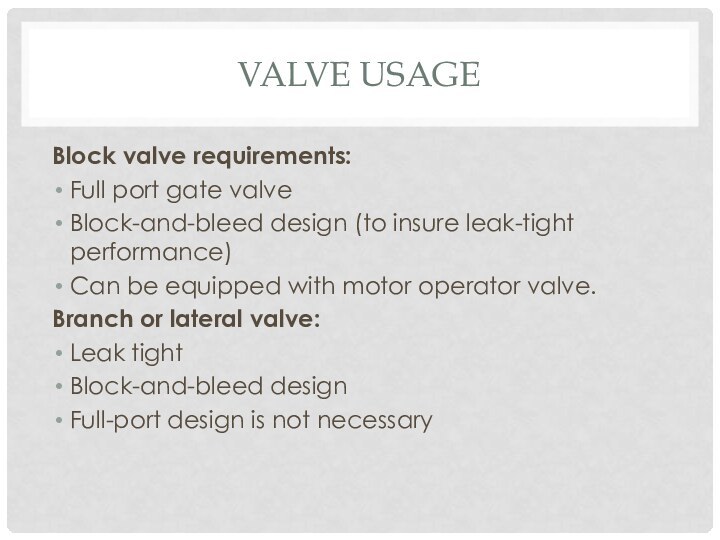
- 8. Valve usageBlock valve requirements:Full port gate valveBlock-and-bleed
- 9. Valve usageBreakout tank valves:Assurance of each tank
- 10. Block valves/ shut-down valves/ shut-off valvesRequirements:every 30-40
- 11. Скачать презентацию
- 12. Похожие презентации
OverviewValve classificationValve typesValve usageBlock valves/ shut-down valves/ shut-off valves







Слайд 2
Overview
Valve classification
Valve types
Valve usage
Block valves/ shut-down valves/ shut-off
valves
Слайд 3
Valve itself
VALVE
can stand for various
Russian terms
арматура,
задвижки, клапаны
Valve is an integral component used for controlling
& regulating flow of liquids or gases to maintain the process parameters such as flow, pressure etc.
Слайд 4
Valve classification
Valves can be classified in different ways:
the
function or purpose of application
2. the closure member or
mechanical motion
Слайд 5
Valve classification
1. by function or purpose:
• To start
and stop flow of fluids
• To regulate, throttle and control
fluid flow or pressure• To prevent back-flow
• To relieve excess pressure / vacuum
Thus, the following types are distinguished:
•Shut-off Valves (Block valves/ shut-down)
•Non-return Valves (back-pressure valve)
•Control Valves
•Safety Valves (pressure-relief valve, pressure safety valve, pressure/vacuum-relief valve, emergency relief valve)
Слайд 6
Valve classification
2. by closure member or mechanical motion
• Linear
Motion Valves. The Valves in which the closure member,
as in gate, globe, diaphragm, pinch,, moves in a straight line to allow, stop, or throttle the flow.• Rotary Motion Valves. When the Valve-closure member travels along an angular or circular path, as in butterfly, ball, plug, eccentric- and Swing Check Valves, the Valves are called rotary motion Valves.
• Quarter Turn Valves. Some rotary motion Valves require approximately a quarter turn, 0 through 90°, motion of the stem to go to fully open from a fully closed position or vice versa.
Слайд 7
Valve usage
Obligatory valve placement:
Pipeline itself
Pump and compressor stations
Pressure
regulator stations
Meter runs
Launcher and receiver stations
Breakout tankage
Distribution manifolds
Слайд 8
Valve usage
Block valve requirements:
Full port gate valve
Block-and-bleed design
(to insure leak-tight performance)
Can be equipped with motor operator
valve.Branch or lateral valve:
Leak tight
Block-and-bleed design
Full-port design is not necessary
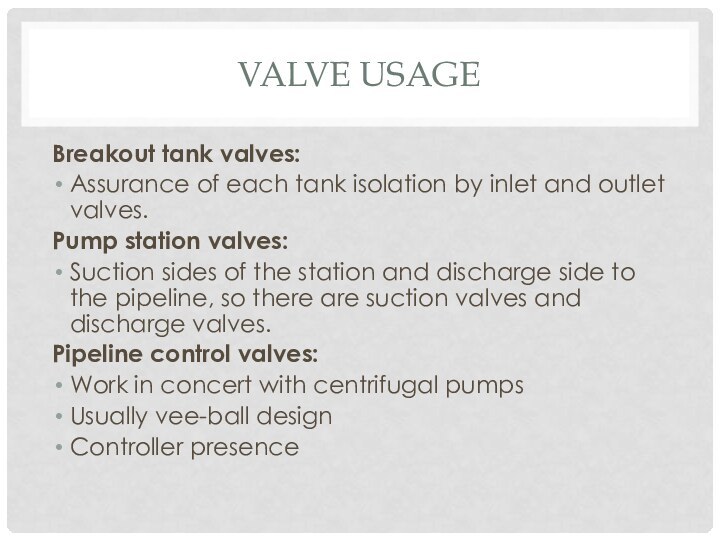
Слайд 9
Valve usage
Breakout tank valves:
Assurance of each tank isolation
by inlet and outlet valves.
Pump station valves:
Suction sides of
the station and discharge side to the pipeline, so there are suction valves and discharge valves.Pipeline control valves:
Work in concert with centrifugal pumps
Usually vee-ball design
Controller presence
Слайд 10
Block valves/ shut-down valves/ shut-off valves
Requirements:
every 30-40 km
installation.
Besides, block valves should be installed :
- on
both banks of the river crossing in a case of two or three lines;- in river crossing in a case of a line, however, in this very case the place of block valve installation is defined depending on the type of landscape close to the crossing;
- on both banks of the III type-bog which expends more than 500 m;
- at the beginning of every pipeline branch at a distance not less than 15 m;