- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему по английскому языку The oppositional method of studying language. Types of opposition. The marked and unmarked members of the binary opposition. Oppositional reduction (neutralization).
Содержание
- 2. Тема: «The oppositional method of studying
- 3. Использованная литератураМарк Яковлевич Блох «ТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКАЯ ГРАММАТИКА АНГЛИЙСКОГО
- 4. The grammatical category is a system of
- 5. The ordered set of grammatical forms expressing a categorical function constitutes a paradigm.
- 6. The paradigmatic correlations of grammatical forms in a category are exposed by the so-called "grammatical oppositions".
- 7. The notion of opposition in grammar (nouns, verbs, adjectives)
- 8. Ferdinand de Sausser suggested that the system
- 9. Later on Trubetskoy and Jacobson developed his idea.
- 10. The opposition is a pair of grammatical
- 11. Three main qualitative types of oppositions were established in phonology: "privative", "gradual", "equipollent"
- 12. By the number of members contrasted, oppositions
- 13. The gradual opposition is formed by a
- 14. An example of the gradual morphological opposition
- 15. The equipollent opposition is formed by a
- 16. An example of the equipollent opposition can
- 17. Both equipollent and gradual oppositions in morphology,
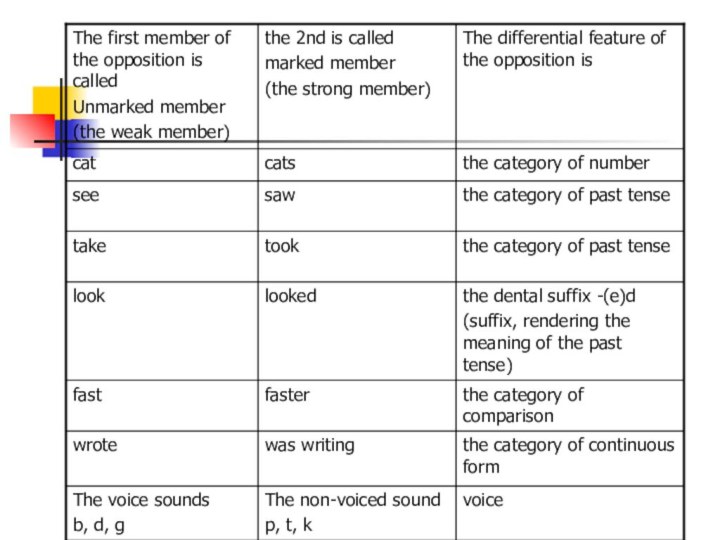
- 18. The most important type of opposition is
- 19. The binary privative opposition is formed by
- 20. The member in which the feature is
- 22. The meanings differentiated by the oppositions of
- 23. It should be noted the fact
- 24. Due to this difference in meaning, the
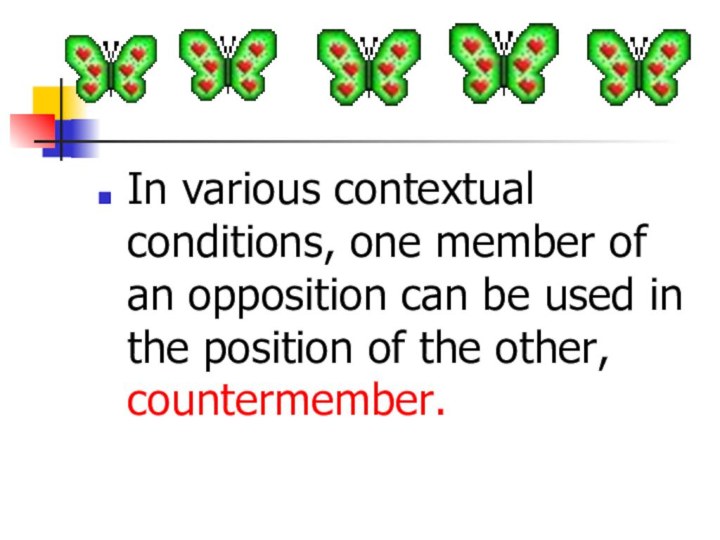
- 25. In various contextual conditions, one member of
- 26. This phenomenon should be treated under the heading of "oppositional reduction" or "oppositional substitution".
- 27. The first version of the term ("reduction")
- 28. The second version of the term ("substitution")
- 29. Man conquers nature. Человек покоряет природу.The noun
- 30. In other words, the noun is used
- 31. This kind of oppositional reduction should be
- 32. Скачать презентацию
- 33. Похожие презентации
Тема: «The oppositional method of studying language. Types of opposition. The marked and unmarked members of the binary opposition. Oppositional reduction (neutralization).»






























Слайд 3
Использованная литература
Марк Яковлевич Блох
«ТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКАЯ ГРАММАТИКА АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА»
Москва «Высшая школа» 1983
Борис Александрович Ильиш
«Строй современного английского языка»
ПРОСВЕЩЕНИЕ«ЛЕНИНГРАД
1971Материалы из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Слайд 4
The grammatical category is a system of expressing
a generalised grammatical meaning by means of paradigmatic correlation
of grammatical forms.
Слайд 5
The ordered set of grammatical forms expressing a
categorical function constitutes a paradigm.
Слайд 6
The paradigmatic correlations of grammatical forms in a
category are exposed by the so-called "grammatical oppositions".
Слайд 8
Ferdinand de Sausser suggested that the system of
a language should be studied on the opposition of
its concrete forms (units).
Слайд 10
The opposition is a pair of grammatical forms,
opposed to each other both in meaning and in
form.
Слайд 11
Three main qualitative types of oppositions were established
in phonology:
"privative",
"gradual",
"equipollent"
Слайд 12 By the number of members contrasted, oppositions were
divided into binary (two members) and more than binary
(ternary, quaternary, etc.).
Слайд 13
The gradual opposition is formed by a contrastive
group of members which are distinguished not by the
presence or аbsenсе of a feature, but by the degree of it.
Слайд 14
An example of the gradual morphological opposition can
be seen in the category of comparison:
strong —
stronger — the strongest
Слайд 15
The equipollent opposition is formed by a contrastive
pair or group in which the members are distinguished
by different positive features
Слайд 16
An example of the equipollent opposition can be
seen in the correlation of the person forms of
the verb be:am — are — is.