Слайд 2
contents
Introduction
History
Present education system
Higher education
Schools Today
Слайд 3
introduction
1. the three “ R’s ”
2. purpose of
the British Education
3. importance of education in Britain
4. feature
of British Education
5. the school tie
Слайд 4
History
1. the form of British education in
the past
2. the British education system is run by
the state today
3. Some changes to the British education system*
Слайд 5
▶Some changes to the British education system:
*before 1870, education was voluntary and many of the
existing schools had been set up by churches
*only 40% of children aged 10 went to school regularly
Слайд 6
(1) some caused by the Industrial Revolution
⇒government
decided to become involved in taking responsibility for
the education of children
*in 1870 the government passed a law which called for government-funded education
*by 1880, the attendance at school for children between 5 and 10 was compulsory rather than voluntary
Слайд 7
(2) Some caused by WWII
⇒the government
began planning to reconstruct the education system
①1944 Education
Act stipulates that all children were given the right to free secondary education
(failed)
②in the 1960s, comprehensive system was introduced into Britain
→ended the division between grammar schools and vocational schools
→entrance exams were abolished
Слайд 8
③the Education Reform Act 1988 provided for
the establishment of a National Curriculum for 5-16 year-olds
and regular examinations
→brought a big change
(reintroduced competition between schools)
Слайд 9
National Curriculum
The national curriculum occupies not less than
70% of the school timetable, the rest of the
time being used for subjects of the school’s choosing.
There are four key Stages. At each of the stages the core subjects of English, mathematics, science, technology, physical education and religious education are taught.
History, geography, music and art are also compulsory subjects up to 16 years old, but they become optional in Key Stage 4.
A modern foreign language is added to the
curriculum at Key Stages 3 and 4.
Слайд 10
The Present Education System
1. Education in the UK
is compulsory
(from the ages of 5 to
16)
2. State schools and private schools*
3. The schooling stages*
Слайд 11
The Present Education System
State schools and private schools
state schools: funded by local and central government (free)
*a system of “league tables”
private schools (public schools): receive
their funding through the private sector, tuition rates and government assistance
Слайд 12
The Present Education System
There are nine famous public
schools:
Winchester, Eton, St. Paul’s, Shrewsbury, Westminister,
Merchant Taylor’s, Rugby,
Harrow and Charterhouse.
Слайд 13
The Present Education System
Eton – (the public school)
the most famous school in the world, Britain’s biggest
boarding school and educator of its social elite since 1440. So far the school has educated 19 Prime Ministers and six Chancellors of Exchequer. Its literary figures include Henry Fielding, Percy Byshe Shelley, George Orwell. It was founded in 1440 by King Henry VI. In the past, almost all the students coming from upper class families. Now sons of accountants, doctors or businessmen also have access to it.
Слайд 14
Eton College is located in the town Eton
which is an urban district of southeast-central England on
the Thames River
Слайд 15
Eton is a public school for boys age
13-18. Almost all the pupils go on to study
A levels, 90% will go on to university, a quarter to Oxford and Cambridge. The pupil/teacher ration is 9.5 to one, while in state secondary school the ratio is 20 to one.
Слайд 17
The facilities include purpose-built theatres, libraries, swimming pools,
even a golf course.
Слайд 18
The Present Education System
The schooling stages
(1)up to age
5 → pre-primary schooling
(2)from the age of 5-11 →
primary schools
exam “the 11- plus” (co-educational/mixed)
Слайд 19
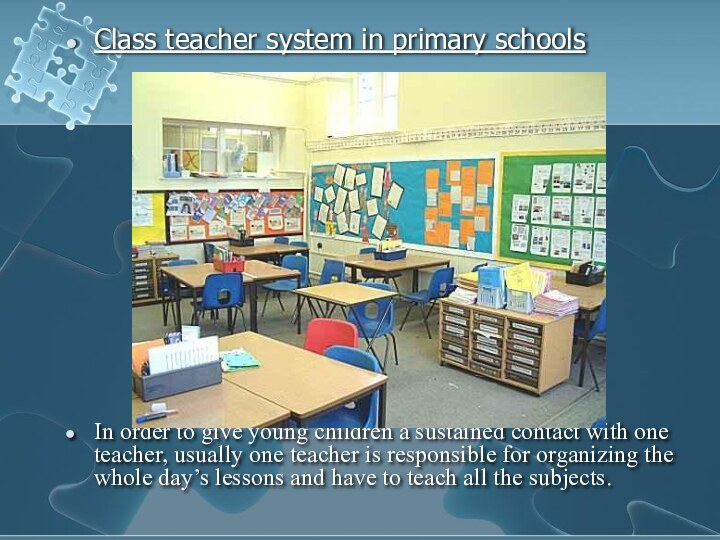
Class teacher system in primary schools
In
order to give young children a sustained contact with
one teacher, usually one teacher is responsible for organizing the whole day’s lessons and have to teach all the subjects.
Слайд 20
The Present Education System
(3)age of 11-19 → secondary
schools
(comprehensive/grammar)
①age of 16 → GCSE exams (some choices)
②age of 18 or 19 → A-levels exams
(after 2 years in the Sixth Form)
go to university / if not, take vacational training (GNVQs)
Слайд 21
The General Certificate of Secondary Education is taken
at the end of compulsory education at the age
of 16. All the students are required to take it.The results often help the students and their parents to made a choice whether they will go to college or not.
GCSE
Слайд 22
GCE A level
About 70% of 16 year old
pupils choose to continue in full-time education. Some students
continue in the same school for a further two years of study in the ‘sixth form’. After two-year study, three or four subjects are taken in the examination of the General Certificate of Education- Advanced level (GCE A level). The grades obtained in GCE A level are the main basis whether the students can go to college or not.
Слайд 23
Higher education and training in UK
1. Nearly all
universities are public bodies
2. Higher education has a long
history in the UK
3. The general condition of university students
4. Degrees*
5. Leading universities in UK*
6. Open university and further education*
Слайд 24
Degrees awarded
Bachelor of Arts (BA) or Bachelor of
Science (BSc) – after three years of full-time study.
Master
of Arts (MA) or Master of Science (MSc) after a further one year full-time or two year part-time study.
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) – after at least three years of original research.
Слайд 25
Leading universities in UK
The Guardian University Guide, 2003
Слайд 26
Cambridge University, Cambridge, east-central England
Слайд 27
The first college
Opened in some
1200s. the oldest
Building
dating
back to 1284.
Слайд 29
Oxford university, Oxford, northwest of London
Слайд 30
Oxford University, with its famed ‘dreaming spires’ was
founded in the 12th century and still dominates the
center of Oxford.
Слайд 31
Museum of Natural History, Oxford university
Слайд 32
Open university and further education
The open university is
a non-residential university offering degree and other courses for
adult students of all ages. They offer degrees which are the same as those of other universities.
Further education is often taken part-time or in the evening. Further education colleges have strong links with industry and commerce, employers often being involved in the design of the courses.
Слайд 35
Schools Today
Primary schools
Compulsory schooling starts at 5
Co-educational and
a class-teacher system
Three-term school year
Secondary schools
Compulsory schooling extends up
to 16
The selective system, comprehensive system and independent schools
Sixth form colleges/ tertiary colleges
Other schools
County schools
Voluntary schools
Слайд 36
The Selective System
A system for secondary schooling in
Britain, under which children take an examination, the “11
plus”, in their last year of primary education.
The results of the examination determine the kind of secondary schooling each child will receive.
Those with the highest marks go to grammar schools; others may go to technical schools, and the rest – by far majority – go to secondary modern schools.
Слайд 37
The Comprehensive System
A system for secondary schooling in
Britain, under which all children, regardless of ability, can
mix together.
In comprehensive schools, students study a wide variety of subjects at first until 2 or 3 years later, when they may study only those they like best.
Many new ideas in education are being tried out at present, and comprehensive schools vary widely throughout Britain.
Слайд 38
Independent Schools
Public schools: secondary private boarding schools that
prepare students chiefly for universities. They laid the foundations
of English education, but now are generally restricted to a comparatively small section of the population, mainly the rich and conservative in politics. Eton, Harrow and Rugby are the 3 most famous public schools.
Слайд 39
Independent Schools
Prep schools: small private boarding schools for
children up to 7 or 8 years old, which
help to prepare the children for the “common entrance” examination at the age of 13 for admission to a public school, and where Latin, French and mathematics are all started early.
Слайд 40
Other Schools
County schools: state-run secondary schools, most of
which are administered by the county or county borough.
About half of the money comes from the local authority and the other half from the central government.
Voluntary schools: also called mission schools in other countries, secondary schools in Britain that are mostly Church of England or Roman Catholic in origin, and partly maintained and controlled by the local authority. They give a certain amount of denominational religious instruction. Education is free in such schools.
Слайд 41
“Red Brick”
“Red brick”:The Redbrick Universities include all the
provincial universities of the period 1850-1930 as well as
London University. Because the favorite building material of the period between 1850-1930 is red brick, and all the universities of the time were built in red brick. Thus, they were called the Redbrick Universities.
Слайд 42
“Red brick”: a slightly contemptuous term used to
refer to the large group of 19th- and 20th-century
universities and university colleges in Britain. It describes their construction, which is contrasted with the more dignified and solid-looking ancient architecture of Oxford and Cambridge. The distinctive feature of these universities was that they were non-collegiate institutions which admitted men without reference to religion or background and that they concentrated on 'real-world' skills, often linked to engineering.