- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Statistical Terminology
Содержание
- 2. Correlation
- 3. What is correlation?A statistical measurement that shows the relationship between two variables. Example: Height & Weight
- 4. Pearson’s Correlation CoefficientPearson’s r, which measures a
- 5. Correlation typesPositive correlationAn increase in one variable
- 6. Knowledge checkHeight and weightVehicle speed and travel
- 7. Case StudyIn WWII, the US formed the
- 8. Case Study (cont)When planes returned from missions,
- 9. Case Study (cont)Tip: Set a variable to
- 10. Case StudyIn WWII, bombing accuracy had a
- 11. Case StudyIn WWII, bombing accuracy had a
- 12. Case StudyStatisticians often report that in assessing
- 13. Case StudyStatisticians often report that in assessing
- 14. Case Study Economist recently announced that statistics prove
- 15. Case StudyEconomist recently announced that statistics prove
- 16. Statistical Terminology
- 17. Essential TermsSampleA portion of a populationStratified SampleThe
- 18. Essential TermsGeneralizationExtending conclusions from the sample to
- 19. Essential TermsMeanThe average after adding and dividing
- 20. Essential TermsDiscrete variableA variable with a finite
- 21. Variance“The average of the squared differences from
- 22. Standard DeviationThe square root of the variance
- 23. Standard Deviation ExampleDataset of height of cats
- 24. Standard Deviation ExampleIf the standard deviation is
- 25. Sample Standard DeviationHow is the sample SD
- 26. Essential termsRegression Analysis: estimates relationships between X
- 27. Descriptive & Inferential StatsDescriptive statisticsDescribes what’s happening in a datasetInferential statisticsGeneralizes sample findings to population
- 28. Descriptive & Inferential Stats50% of all Russian
- 29. Question Design
- 30. Open-ended vs. Closed-endedOpen-ended ? No response options providedClosed-ended ? A list of options provided
- 32. Open-ended vs. Closed-endedOpen-ended used in pilot studies
- 33. Closed-ended exampleForm a question asking about a
- 34. Question wordingBe aware of information and connotations
- 35. Question wordingBe aware of information and connotations
- 36. Question StructureAll reasonable responses included if closed.Responses
- 37. Question StructureLeading questionsDo you think that the
- 38. Social desirability biasSensitive issues lead to misreportingUnderstated
- 39. Question OrderContrast effectsWhen order results in greater
- 40. Question Order
- 41. Question Order
- 42. Question Order
- 43. The Good, The Bad, & The UglyHow
- 44. The Good, The Bad, & The UglyWhat
- 45. Скачать презентацию
- 46. Похожие презентации
Correlation












































Слайд 3
What is correlation?
A statistical measurement that shows the
relationship between two variables.
Слайд 4
Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient
Pearson’s r, which measures a ‘normalized’
covariance (how changes in one value are associated with
those of another), has a value between -1 and 11 – perfect positive linear correlation
0 – no linear correlation
-1 – perfect negative linear correlation
Слайд 5
Correlation types
Positive correlation
An increase in one variable will
lead to an increase in the other
Negative correlation
An increase
in one variable will lead to a decrease in the otherNote: In System Dynamics, these are called Positive and Negative Feedback loops
Слайд 6
Knowledge check
Height and weight
Vehicle speed and travel time
Gasoline
prices and global oil production
Caloric intake and weight
Hours spent
watching TV and school gradesCar value and car mileage
Слайд 7
Case Study
In WWII, the US formed the Statistical
Research Group to analyze situations like the following:
You don’t
want your planes shot down by enemy fighters, so you armor them. Armor makes the plane heavier, and heavier planes are slower and use more fuel. Too much armor and too little armor is bad. Where do you armor them?
Слайд 8
Case Study (cont)
When planes returned from missions, damage
was unevenly distributed. The fuselage and fuel system would
often have many bullet holes whereas the engines would have few. Should you put more armor on the fuselage?
Слайд 9
Case Study (cont)
Tip: Set a variable to zero
to test the probability.
Ex.: By imagining that a plane
is CERTAIN to be hit in the engine, the plane is CERTAIN to crash because planes can’t fly without working engines.Either German planes happen to hit every part of a plane but the engine, or the engine is a point of total vulnerability.
Слайд 10
Case Study
In WWII, bombing accuracy had a high
positive correlation with fighter opposition. The more fighters, the
better the bombing accuracy. Why?
Слайд 11
Case Study
In WWII, bombing accuracy had a high
positive correlation with fighter opposition. The more fighters, the
better the bombing accuracy. Why?Cloud cover. If there are too many clouds, fighters aren’t launched and bombers are inaccurate.
Слайд 12
Case Study
Statisticians often report that in assessing a
child’s likeliness to succeed at school, those children whose
parents played classical music recordings for the unborn children will result in better grades. Why true?
Слайд 13
Case Study
Statisticians often report that in assessing a
child’s likeliness to succeed at school, those children whose
parents played classical music recordings for the unborn children will result in better grades. Why true?Adopting such a parental strategy indicates the parents are interested in the child’s intelligence.
Слайд 14
Case Study
Economist recently announced that statistics prove the
taller you are, the more you are likely to
be paid. Why?
Слайд 15
Case Study
Economist recently announced that statistics prove the
taller you are, the more you are likely to
be paid. Why?The lurking variable is more likely gender, as typically men are on average taller than women.
Слайд 17
Essential Terms
Sample
A portion of a population
Stratified Sample
The sample
is chosen to reflect the population at large
Random Sample
The
sample is chosen by chance
Слайд 18
Essential Terms
Generalization
Extending conclusions from the sample to the
population. Only possible is sample is reflective.
Causation
When changes in
one variable affect the otherElasticity
How much a change in one variable affects the other
Bias or Skew
Margin of Error
Слайд 19
Essential Terms
Mean
The average after adding and dividing all
data
Median
The middle number of a dataset
Mode
Number(s) appearing most often
in a dataset
Слайд 20
Essential Terms
Discrete variable
A variable with a finite amount
of values
Continuous variable
A variable with many different values in
a range
Слайд 21
Variance
“The average of the squared differences from the
mean” ? how different the data is
Ex.: [12, 12,
12, 12, 12]Variance = 0
Ex.: [12, 12, 12, 12, 13]
Variance = 0.16
Ex.: [12, 12, 12, 12, 13013]
Variance = 27,044,160
Слайд 22
Standard Deviation
The square root of the variance (more
precise than variance) ? This is the main reason
for variance
Слайд 23
Standard Deviation Example
Dataset of height of cats in
cm:
[600, 470, 170, 430, 300]
Find the variance (Find
the mean, calculate the difference of each datum from the mean, square, then average).21,704
Find the standard deviation (square root of the mean).
~147
Слайд 24
Standard Deviation Example
If the standard deviation is 147,
then a datum is “1 standard deviation from the
mean”. A datum “2 standard deviations is 296” and so on…HOWEVER…
This is has been a ‘population’ standard deviation where each possible value was considered.
Слайд 25
Sample Standard Deviation
How is the sample SD different
from the population SD? How to correct the calculation?
Divide
by ‘n-1’ instead of ‘n’ when finding both the variance and SD. Now find the sample SD and sample variance of the previous dataset.Sample variance = 27,130
Sample SD = 164
Слайд 26
Essential terms
Regression Analysis: estimates relationships between X and
Y variables
Null hypothesis: Assumes no significant difference (states alternative
hypothesis false)P-value: indicates strong evidence against null hypothesis (x <= 0.05), or weak evidence (x > 0.05) ? “Statistical significance”
Слайд 27
Descriptive & Inferential Stats
Descriptive statistics
Describes what’s happening in
a dataset
Inferential statistics
Generalizes sample findings to population
Слайд 28
Descriptive & Inferential Stats
50% of all Russian men
are named Ivan.
20% of respondents are male
From 2000 to
2005, 70% of the land cleared in the Amazon and recorded in Brazilian government data was transformed into pasture.Receive your college degree increases your lifetime earning by 50%.
Teachers named Joshua demonstrate inferior intellect to teachers named Timmy.
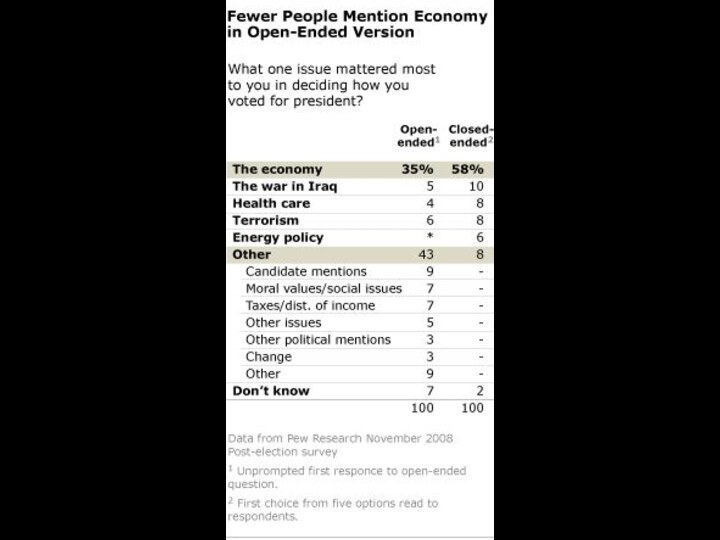
Слайд 30
Open-ended vs. Closed-ended
Open-ended ? No response options provided
Closed-ended
? A list of options provided
Слайд 32
Open-ended vs. Closed-ended
Open-ended used in pilot studies to
determine most common options
Subjective closed-ended ? Fewer options
Satisfaction with
economyFewer options avoids “recency effect”
Randomized order to ensure random bias
Objective closed-ended ? More options fine
Religious affliation
Слайд 33
Closed-ended example
Form a question asking about a student’s
satisfaction with their high school education (hint ? use
ordinal categories).How can you mitigate the recency effect?
Слайд 34
Question wording
Be aware of information and connotations in
questions.
“Do you favor or oppose taking military action against
Saddam Hussein?”Favor = 68%; Oppose = 25%
Слайд 35
Question wording
Be aware of information and connotations in
questions.
“Do you favor or oppose taking military action against
Saddam Hussein even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties?”Favor = 43%; Oppose = 48%
Слайд 36
Question Structure
All reasonable responses included if closed.
Responses shouldn’t
overlap.
One question at a time.
Bad: “How much confidence do
you have in Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?”
Слайд 37
Question Structure
Leading questions
Do you think that the new
cafeteria lunch menu offers a better variety of healthy
foods?Neutral questions
How do you feel about the new cafeteria lunch menu compared to the old one?
Слайд 38
Social desirability bias
Sensitive issues lead to misreporting
Understated alcohol/drug
use, tax evasion
Overstated donations, church attendance
SDB higher when
interviewer is presentInclude ‘Prefer Not to Answer’ option
Слайд 39
Question Order
Contrast effects
When order results in greater differences
in responses
Assimilation effects
When responses are similar because of order
Слайд 43
The Good, The Bad, & The Ugly
How likely
would you be to enroll in CookieDirect?
How organized and
interesting was the speaker?How helpful do you think our customer service representatives are?
Should the government force you to pay higher taxes?
How would you rate the career of legendary writer Dovlatov?
Слайд 44
The Good, The Bad, & The Ugly
What do
you like to do for fun?
How dumb is President
Trump at making America great again?Should teachers named Joshua offer pizza parties to obedient students?
In your opinion, how would you rate the quality of your work?
How do you feel about the following statement? We should reduce military spending.





























