British system of education
To find schools for Russian pupils
in order to master their English To compare these schools between itself
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть











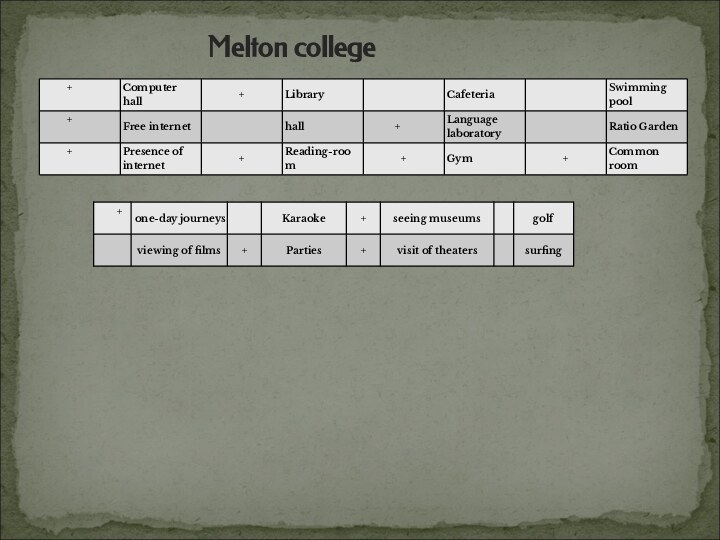






to estimate the possibilities in project activity
to get knowledge about schools of Great Britain
to do practical conclusions
to learn the analysis of text
to estimate the done work
Basic tasks
Research methods:
analysis
comparison
generalization
estimation
Research stages
raising of tasks
drafting of the plan of the work
search of the materials
analysis of the materials
discussion and consultations
preparation of the project
Theoretical Part:
Primary Schools
Secondary Schools
The majority of state secondary school pupils in England and Wales attend comprehensive schools. These largely take pupils without reference to ability or aptitude, providing a wide range of secondary education for all or most of the children in a district. Schools include those taking the 11 to 18 age-range, middle schools (8 to 14), and schools with an age-range of 11 or 12 to 16. Most other
state-educated children in England attend grammar or secondary modern schools, to which they are allocated after selection procedures at the age of 11.
Scottish secondary education is non-selective, consisting of comprehensive schools covering the age-range 12 to 18.
In Northern Ireland secondary education is organised largely along selective lines, with grammar schools admitting pupils on the basis of tests in English, maths and science. Most pupils attend non-grammar secondary schools.
Higher Education
Post-secondary or tertiary education, also referred to as third-stage, third level education, or higher education, is the non-compulsory educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education, such as a high school, secondary school, or gymnasium. Tertiary education is normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and training. Colleges and universities are the main institutions that provide tertiary education (sometimes known collectively as tertiary institutions). Examples of institutions that provide post-secondary education are vocational schools, community colleges and universities in the United States, the TAFEs in Australia, CEGEPs in Quebec,and the IEKs in Greece. They are sometimes known collectively as tertiary institutions. Tertiary education generally results in the receipt of certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Higher education includes teaching, research and social services activities of universities, and within the realm of teaching, it includes both the undergraduate level (sometimes referred to as tertiary education) and the graduate (or postgraduate) level (sometimes referred to as graduate school). In the United Kingdom post-secondary education below the level of higher education is referred to as further education. Higher education in that country generally involves work towards a degree-level or foundation degree qualification.
Independent Schools
The School Standards and Framework Act passed in July 1998 establishes a new framework for school organisation. The Government's aim is to maintain diversity in its promotion of higher standards (see p. 130) while ensuring fairness and coherence, and minimising disruption to individual schools:
Categories—Under the new legislation, there will be three mainstream categories: community, foundation and voluntary schools. The community category will initially accommodate county schools, while the foundation category is expected to include grant-maintained schools. All schools will be able to choose which category will best suit their circumstances and aspirations.
Funding and responsibilities—All state schools will work in partnership with, and receive their recurrent funding from, LEAs. Schools will continue to manage their own budgets and staffing.
Governing bodies—Schools will continue to be run by governing bodies. The governing bodies of church schools will also include church representatives.
Admissions—LEAs and school governing bodies responsible for admissions will be required to work with headteachers, the Churches and others in local forums to coordinate admissions arrangements, taking account of a statutory code of practice to be issued by the Government.
School Management
City Technology Colleges
There are 15 city technology colleges in England; these are non-fee-paying
School Curriculum
Some information
about Anglolang school :
Anglolang is an international English language school whose situation on the beautiful North East coast of Yorkshire provides an ideal, unspoilt environment in which to study whilst at the same time it offers convenient road and rail access to the busier main cities of England and Scotland Courses in an outstanding location.
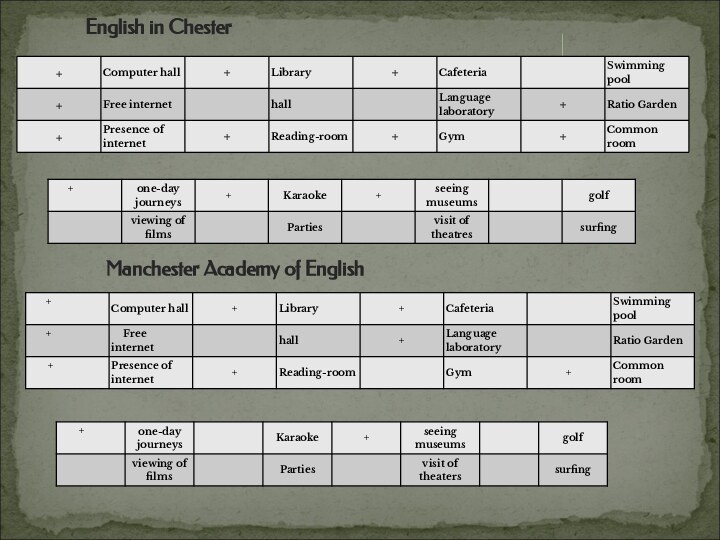
This is about English in Chester:
This school was established in 1976 and since then it has had 10,000 happy students. it is accredited by the British Council and is a member of English UK and English in the North/English UK North. It is also a member of IALC (The International Association of Language Centres).
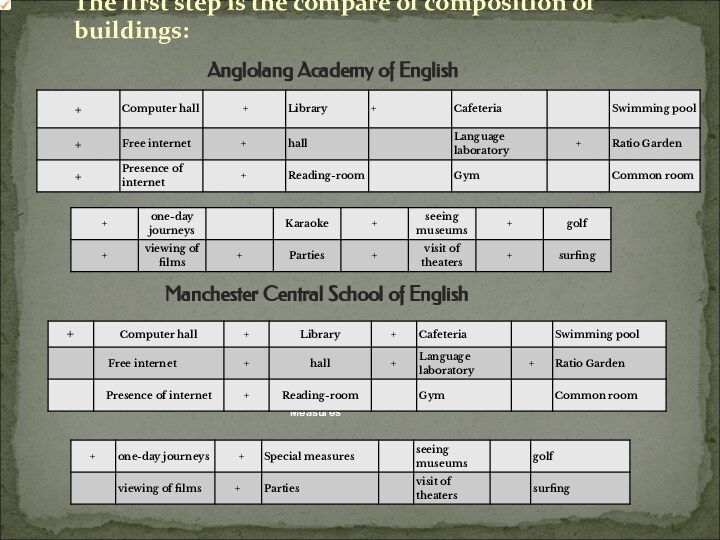
Anglolang Academy of English
Courses
Manchester Central School of English
This school has an interesting special part of teaching "optional" programme-teachers with students visit pubs, thus know traditions of English establishments and communicate in an informal situation.
Manchester Academy of English
The main feature of the school which differs it from a lot of other schools of the same type is taking out the pupils on optional excursions throughout the year with following the adaptation.